(Press-News.org) Cancer-related fatigue (CRF) is a debilitating yet all-too-common condition, which can severely affect quality of life for patients undergoing treatment. For those struggling with CRF, there have been no effective pharmaceutical treatments for the constellation of symptoms that together define the syndrome.
In a new study led by Yale Cancer Center researchers at Yale School of Medicine, the team found that a metabolism-targeting drug called dichloroacetate (DCA) helped alleviate CRF in mice, without interfering with cancer treatments. The findings are a pathway for future CRF research that may someday lead to a new therapy for patients.
The results were published in American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism on Oct. 2.
“This study identifies dichloroacetate, an activator of glucose oxidation, as the first intervention, and particularly the first metabolism-focused intervention, to prevent the whole syndrome of cancer-related fatigue in preclinical models,” said senior author Rachel Perry, who is a member of Yale Cancer Center.
Researchers used tumor-bearing mouse models to investigate the effectiveness of DCA in treating cancer-related fatigue for patients living with melanoma. The group found that DCA did not affect the rates of tumor growth or compromise the effectiveness of immunotherapy or chemotherapy in two mouse cancer models. DCA also significantly preserved physical function and motivation in mice with late-stage tumors.
The data suggests that DCA treatment may have several positive effects, including reducing oxidative stress in muscle tissue of tumor-bearing mice. The researchers said DCA could be a practice-changing approach in the future, when used as an adjuvant therapy to treat cancer-related fatigue.
“We hope that this research will provide the bedrock for future clinical trials using dichloroacetate — an FDA-approved drug for another indication (lactic acidosis) — to treat the debilitating syndrome of cancer-related fatigue,” said Perry, who is also an assistant professor of medicine (endocrinology) and of cellular and molecular physiology at Yale School of Medicine.
Perry was joined by Yale first author Xinyi Zhang. This study was funded by a Young Investigator Award from the Melanoma Research Alliance.
END
A promising treatment on the horizon for cancer-related fatigue
2023-10-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NRG Oncology-RTOG 1308 accrual completion: First phase III NCTN clinical trial comparing photon versus proton therapy to meet accrual target
2023-10-03
Effective September 26, 2023, NRG Oncology-RTOG 1308, a phase III randomized trial comparing overall survival after photon versus proton chemoradiotherapy for patients with inoperable stage II-IIIB non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has met its accrual target. The trial, one of several NRG Oncology ongoing clinical trials across various malignancies within the National Clinical Trials Network (NCTN) that compare photon versus proton radiation therapy techniques, is the first phase III head-to-head comparison of these ...
Carbon capture method plucks CO2 straight from the air
2023-10-03
Even as the world slowly begins to decarbonize industrial processes, achieving lower concentrations of atmospheric carbon requires technologies that remove existing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere — rather than just prevent the creation of it.
Typical carbon capture catches CO2 directly from the source of a carbon-intensive process. Ambient carbon capture, or “direct air capture” (DAC) on the other hand, can take carbon out of typical environmental conditions and serves as one weapon in the battle against climate change, particularly as reliance ...
Dr. Tanya Stoyanova receives Department of Defense award to find new lung cancer treatments
2023-10-03
Dr. Tanya Stoyanova, associate professor of molecular and medical pharmacology and urology at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, was awarded a $350,000 Idea Development Award from the Department of Defense.
The award will help Stoyanova, a member of the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center, to identify new cancer detection and treatment strategies for small cell lung cancer, a highly aggressive form of the disease that accounts for approximately 15% of lung cancers. Known for spreading quickly, most people diagnosed with the disease face low chances of survival beyond five years.
The award ...
Carol L. Silva elected fellow of the National Academy of Public Administration
2023-10-03
Carol L. Silva, the Edith Kinney Gaylord Presidential Professor of Political Science in the Dodge Family College of Arts and Sciences and Senior Associate Vice President for Research and Partnerships at the University of Oklahoma, has been elected a 2023 fellow of the National Academy of Public Administration.
“Carol is an experienced, dynamic leader with an extensive record of excellence in research and building successful multidisciplinary programs and convergent teams focused on grand challenge problems at the intersection of public policy and technology. We congratulate her on this election to the NAPA and look forward to the impact she will make among these national thought ...
Independent physician practices can keep up with larger consolidated practices in a pandemic
2023-10-03
Large health systems are acquiring smaller physician practices at what some consider an alarming rate, leaving fewer independent practices. When the COVID-19 pandemic occurred, it was unclear whether the independent practices would be able to “keep up” (maintain the same level of patient care) with larger practices, which have more resources, and if care for patients with chronic conditions might be disrupted by the pandemic.
A new study from Associate Dean of Research Alison Cuellar found that independent practices experienced a smaller drop in patient volume than ...
Join GSA in Tampa for the Nation’s Premier Aging Conference!
2023-10-03
The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) invites all journalists to attend its 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting — the country’s largest interdisciplinary conference in the field of aging — from November 8 to 12 in Tampa, Florida. Qualified media representatives intending to cover the meeting may register free of charge.
More than 3,000 professionals are expected to attend the five-day gathering at the Tampa Convention Center. The theme for 2023 is “Building Bridges > Catalyzing Research > Empowering All Ages,” and the program schedule contains ...
Female animals may learn mate preferences based on what sets other females’ choices apart from the crowd
2023-10-03
Females may infer what makes a male attractive by observing the choices of more experienced females, and the context of those choices matters, according to a mathematical model publishing October 3rd in the open access journal PLOS Biology. Rather than simply copying their peers, females might learn to prefer rare traits that set successful males apart from others, Emily DuVal at Florida State University, US, and colleagues report.
Sexual selection — where traits become more common because of their attractiveness to the opposite sex — can produce strange and elaborate characteristics, such as huge antlers, bright plumage, and ...
Despite increasing rates of tuberculosis in prisons across the globe, current WHO TB prevention guidelines fail to reach incarcerated populations
2023-10-03
Despite increasing rates of tuberculosis in prisons across the globe, current WHO TB prevention guidelines fail to reach incarcerated populations. Programs should instead prioritize them, argue a group of researchers from Stanford, Harvard, UCL and a range of other global institutions.
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Medicine: http://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1004288
Article Title: Prioritizing persons deprived of liberty in global guidelines for tuberculosis preventive treatment
Author Countries: United States
Funding: ...
Computer model predicts who needs lung cancer screening
2023-10-03
A machine learning model equipped with only data on people’s age, smoking duration and the number of cigarettes smoked per day can predict lung cancer risk and identify who needs lung cancer screening, according to a new study publishing October 3rd in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by Thomas Callender of University College London, UK, and colleagues.
Lung cancer is the most common cause of cancer death worldwide, with poor survival in the absence of early detection. Screening for lung cancer among those at highest risk could reduce ...
Rural counties showing steeper decline in health measures compared to urban counties in 2015 versus 2019—though all areas showed declines in health measures over time
2023-10-03
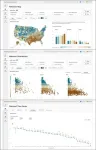
Residents of rural counties have overall worse health outcomes than their urban counterparts. A study published in PLOS Global Public Health by William Weeks at Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, Washington, United States and colleagues introduces a Health Equity Dashboard for policy makers to visualize health disparities in specific locations, and to examine the relationship between health-related measures and socio-demographic characteristics.
Despite overall decreasing mortality rates prior to 2020, health disparities between rural and urban areas in the United States have increased. To better understand inequities in health-related measures between rural and non-rural populations, ...