(Press-News.org) Premature babies in neonatal care units are extremely vulnerable, and susceptible to life-threatening infections. To help keep these babies safe the risk of infection needs to be kept as low as possible.
A particular problem is late onset sepsis that starts from three days after birth, when bacteria get into the blood and grow. This can be very dangerous and babies with late onset sepsis end up staying in hospital longer, need more treatment with antibiotics and can be left with life-long effects on their health.
Bacteria from the Staphylococcus family are the most common causes of late onset sepsis. Most members of this large group of bacteria are harmless; they are normal colonisers of our skin, which can even protect us from harmful microbes. However, some strains, when they end up in the wrong place and get inside the body, can cause major problems, particularly for immunocompromised individuals like neonatal babies.
Staphylococcus capitis is an example of this. This is a species which is usually content living on our scalp, face and neck; capitis means “of the head’ in Latin. Some strains of S. capitis are however associated with late onset sepsis. One particular strain, known as NRCS-A, has been identified as causing serious infections in neonates around the world.
Scientists think this strain first emerged in the 1960s and spread globally throughout the 1980s as it evolved resistance to the commonly used antibiotic vancomycin. Strains circulating now show resistance to multiple antibiotics and a reduced susceptibility to antiseptics that we use to sterilise the skin of babies. This makes the bacteria harder to treat and control, but exactly why this NRCS-A strain has become so globally successful has remained a mystery.
To try and understand what makes this strain able to spread around the world and to develop better ways to keep it under control, Professor Mark Webber and his team from the Quadram Institute and University of East Anglia analysed the genomes of hundreds of S. capitis isolates. They worked with two Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICUs), one in the UK and one in Germany, obtaining samples of S. capitis from the skin and gut of neonatal babies, with and without late onset sepsis.
Their results, published in the journal Microbial Genomics, found that the NRCS-A strain was commonly carried on the skin and in the gut of uninfected neonatal babies, that transmission between babies within NICUs was likely.
By reading the complete genome of each sample, the team were able to identify tiny genetic differences between the S. capitis strains that caused disease and those that don’t.
Professor Webber and his team found that the NRCS-A strains that can cause disease carried a set of unique genes, which they think allows them to survive in the gut as well as on the skin. This would make cleaning the skin to eradicate the bacteria ineffective as the babies will carry a reservoir in their gut microbiomes that cannot be easily removed, but can act as a source of infection.
The genes found in the NRCS-A strains allow them to be resistant to nisin, an antimicrobial compound naturally produced by bacteria in the gut. They also carried genes to survive exposure to the toxic metals that our immune system uses to kill bacteria, as well as genes to scavenge essential metals that are known to be hard for bacteria to access in the gut environment.
Further experiments also showed that the bacteria grow better in acidic conditions as found in the gut. Together, the evidence supports the idea these bacteria are adapted to exploit growth in the gut.
If metal scavenging is critical to infection, this may also be the bacteria’s Achilles heel, presenting a new way to counter its threat. There is early evidence that feeding babies a probiotic supplement of benign bacteria reduces the rate of late onset sepsis and that these ‘good bacteria’ can extract metals before the S. capitis, preventing their growth.
“Studying how strains like NRCS-A have become globally successful is crucial to understanding how bacteria evolve to colonise different environments, and to give us new ideas about how to reduce the risks of infection in vulnerable populations” said Professor Webber.
“We hope this work can be the starting point for more research to develop better ways to protect newborn babies from the terrible consequences of infection.”
Dr Heather Felgate from the Quadram Institute and lead author on the study said “There are still many questions to answer as to why NRCS-A has become so globally spread amongst NICU. But, working out how NRCS-A can evade the host immune system, spread and survive can also give us a head start with many other Staphylococcal species that cause sepsis in immunocompromised people in NICU and Intensive care units.”
END
Tracking the bacteria behind life-threatening sepsis in premature babies
2023-10-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Intervention for caregivers helps prevent elder mistreatment
2023-10-04
An educational and social support intervention for caregivers reduced elder mistreatment of older adults with chronic illness, including dementia. That’s the result of a recent double-blind, randomized controlled trial published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
Elder mistreatment is defined as “an intentional act or failure to act by a caregiver or another person in a relationship involving an expectation of trust that causes or creates a risk of harm to an older adult.” Through the Comprehensive Older Adult and Caregiver Help (COACH) intervention tested in this trial, coaches met with caregivers weekly for up to 12 sessions to listen to their ...
Does COVID-19 or COVID-19 vaccination worsen migraines?
2023-10-04
Research published in the European Journal of Neurology indicates that COVID-19 and COVID-19 vaccination have negligible effects on migraine severity.
Among 550 adults who had received migraine-related care at a Spanish headache clinic, 44.9% (247) reported COVID-19 at least once and 83.3% (458) had been vaccinated; 61 patients (24.7%) reported migraine worsening since COVID-19 and 52 (11.4%) since vaccination.
In participants who perceived that their migraines worsened, those who had been infected were 2.5-times more ...
Are opioid prescription rates changing for US adolescents?
2023-10-04
A new analysis reveals that rates of opioid prescribing to US adolescents have decreased in recent years, primarily limited to non-surgery indications. Opioid prescription rates for surgery have remained stable.
The analysis, which is published in Pediatric Anesthesia, assessed data from the 2015–2020 Medical Expenditure Panel Surveys, which are nationally representative, large-scale surveys conducted annually by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
Among 26,909 children aged 10–19 years, 4.7% underwent a surgical procedure in 2015–2020. ...
Can public financing for political campaigns affect voter participation?
2023-10-04
Policies that provide public financing for political campaigns have gained popularity in the United States. One example is the Democracy Vouchers program that was implemented in Seattle, Washington in 2017 to potentially reduce candidates' reliance on large donations. Research published in Contemporary Economic Policy studied the effects of this program on voter registration and turnout.
In Seattle’s Democracy Vouchers program, every registered voter in the city receives $100 worth of publicly funded vouchers to donate to candidates for municipal office, and candidates ...
Study reveals novel therapeutic target to eliminate unwanted and misfolded proteins
2023-10-04
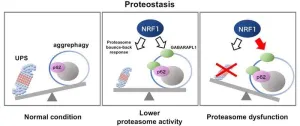
Biological cells contain in-built "housekeeping" mechanisms for taking care of damaged cellular structures. This includes the ubiquitin‒proteasome system (UPS), which selectively tags unwanted proteins with the ubiquitin molecule, and then clears them. When the UPS mechanism fails, cells activate a compensatory protein clearance process called "aggrephagy," in which protein aggregates are degraded by the cell in a controlled manner. However, thus far, the mechanism behind aggrephagy has been unknown.
Now, a landmark paper published on 1 September ...
Women living in more walkable neighborhoods have lower rates of obesity-related cancers
2023-10-04
Residing in a more walkable neighborhood protects against the risk of overall obesity-related cancers in women, specifically postmenopausal breast cancer, but also ovarian cancer, endometrial cancer, and multiple myeloma, according to a new study by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and NYU Grossman School of Medicine. Obesity has been linked to increased risk for 13 types of cancer in women, and physical activity, independent of body size, lowers risk for some of these cancers. Neighborhood walkability ...
Extreme fires and heavy rainfall driving platypuses from their homes
2023-10-04
Australia’s emerging pattern of severe mega bushfires and heavy rainfall may be driving platypuses from their homes, a new study by University of Melbourne researchers has shown.
Analysis of platypus DNA in rivers and creek water samples collected before and after the Black Summer 2019-2020 megafires suggest Australia’s beloved semi-aquatic monotremes might be abandoning severely bushfire-affected areas for up to 18 months after a fire, especially if heavy rainfall has followed the fire.
The study uses the recent technique of environmental DNA sampling, where animal DNA is collected from water, soil, air, or snow ...
Antigen testing can reduce, but not eliminate, the risk of COVID-19 clusters according to mathematical model
2023-10-04
A research group has created a new model to calculate the probability of the occurrence of localized clusters caused by novel coronavirus infections. Led by Shingo Iwami at Nagoya University with collaborators in the United Kingdom and South Korea model, they revealed that screening of infected persons by antigen testing is effective in significantly reducing the probability of cluster occurrence. However, their findings also suggest that it is not sufficient to prevent clusters caused by highly infectious mutant strains, such as Omicron.
With the availability of COVID-19 vaccines and population immunity, countries around the world are seeking to ...
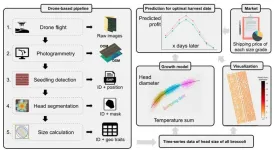
AI drones to help farmers optimize vegetable yields
2023-10-04
For reasons of food security and economic incentive, farmers continuously seek to maximize their marketable crop yields. As plants grow inconsistently, at the time of harvesting, there will inevitably be variations in quality and size of individual crops. Finding the optimal time to harvest is therefore a priority for farmers. A new approach making heavy use of drones and artificial intelligence demonstrably improves this estimation by carefully and accurately analyzing individual crops to assess their likely growth characteristics.
Some optimistic science fiction stories talk about a post-scarcity future, where human needs are catered for and hard labor ...
Wastewater detects signs of antimicrobial resistance in aged care
2023-10-04
A new study published today, analysing wastewater samples from several aged care and retirement homes in Adelaide, has uncovered worrying signs of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in at least one facility.
High levels of bacterial resistance against three common antibiotics – ceftazidime, cefepime and ciprofloxacin – were identified in one aged care residential home. A second facility recorded above average levels of antimicrobial resistance to gentamicin, putting residents’ health at risk.
The listed antibiotics are used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including pneumonia, ...