(Press-News.org) A door-to-balloon (D2B) time of 90-minutes or less is associated with improved outcomes for heart attack patients. However, during the COVID-19 pandemic certain obstacles—including the need for COVID-19 screening, associated isolation procedures and terminal cleaning in the cardiac cath lab—led to increased D2B times. According to a new study, presented at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) Quality Summit 2023, many health care facilities are still recovering from the pandemic and facing new challenges, causing D2B times to continue to lag.
A myocardial infarction, or heart attack, occurs when there has been a blockage of the flow of blood to the heart muscle. An ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) is often the most severe type of heart attack.
Delays in restoring blood flow to the heart muscle in heart attack patients (reperfusion) are associated with higher rates of mortality and morbidity. While some delays may be unavoidable—including uncertainty about diagnosis, evaluation and treatment of other life-threatening conditions, delays around informed consent and long transport times due to geographic distance or weather—D2B is the goal of getting heart attack patients from the emergency room (door) to the cath lab for a catheter to reopen a blockage in the heart (balloon) in 90 minutes or less. Recent research has determined that further decreasing D2B times is linked to improved outcomes and decreased mortality.
In April 2022, Ocean University Medical Center’s (OUMC) NCDR CathPCI data for the first quarter revealed a climbing D2B time of 73 minutes, which was well below their goal of 60 minutes. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, OUMC had averaged around 60 minutes for approximately two years.
“Some of the new national standards created in response to the COVID-19 pandemic created obstacles to heart attack care by adding minutes to D2B time. Although the incidence of COVID myocarditis increased during the pandemic and led to false activations, the total number of STEMI activations actually decreased,” said Sara Belajonas, MSN, MBA, CCRN, APN-C, Chest Pain Coordinator at Ocean University Medical Center in Brick Township, New Jersey, and author of the study. “I believe this created a scenario that our STEMI process was not utilized as often, therefore creating the need for re-education and the refocusing on the importance of time.”
According to the authors, heart attack hospitalizations decreased by 28% globally during the COVID-19 pandemic. It is suspected this is not due to a lower incidence of heart attack during this time but because patients did not seek medical treatment.
“We can learn a lot from these trends to help prepare ourselves for the future. Community education is imperative,” Belajonas said. “Utilizing past research and trends, we already know symptomatic patients are not getting the emergency care they need. All health care workers should do their part in educating the public on the importance of early heart attack care.”
During a review of the heart attack care processes, researchers examined the door-to-ECG (electrocardiogram), arrival to STEMI activation, arrival to case start and D2B. This review process determined that patients were spending too much time in the emergency room for an assortment of reasons that affected patient throughput and demonstrated the need for aggressive refocusing on time and process.
“I absolutely think other [health care] facilities face similar issues. One major issue arising from the COVID pandemic is national nursing and EMS shortages. These shortages hinder D2B and EMS to balloon times,” Belajonas said. “Many of these shortages unfortunately started during the COVID pandemic and have been linked to burnout. Simply, the demand for nurses and EMS workers outweighs what is available.”
It was also found that not all STEMIs brought in by advanced life support units were pre-activated, which is when the cardiac catherization lab at the hospital where the patient will be transported is notified in advance of the patient's arrival. This can allow patients to bypass the typical protocol of going to the emergency department first and instead go directly to the cardiac catherization lab, saving critical minutes.
According to the authors, the ongoing shortages of health care and EMS workers is concerning for future public health crises and STEMI care. Ongoing staff education will be key to ensuring stable processes and time management, as well as feedback and drills to identify gaps and opportunities. Research comparing pre- and post-COVID STEMI trends found a decrease in STEMI activation post-COVID, which was supported by OUMC’s own experience. There has also been an increase in STEMI over the last few months, according to Belajonas, who suspects we will see these trends repeat themselves as COVID numbers rise and fall.
Some of the processes that were implemented to reduce D2B times included:
Re-education of the multidisciplinary team
Involvement of additional staff to assist in the process
Review of all STEMI cases with time interval drill down
Re-education on ACC recommendation to pre-activate all field STEMIs regardless of transmitted ECG
Re-education on STEMI prep
Annual STEMI drills completed, including new heart and vascular to familiarize staff with cath lab 1 and 2
Collaboration with emergency medical services (EMS) to drill down transport delays
At the end of 2022, OUMC D2B time had reduced from 73 minutes to 72 minutes. However, recent months have shown continued improvement. In August 2023 they made their goal of 60 minutes.
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) is the global leader in transforming cardiovascular care and improving heart health for all. As the preeminent source of professional medical education for the entire cardiovascular care team since 1949, ACC credentials cardiovascular professionals in over 140 countries who meet stringent qualifications and leads in the formation of health policy, standards and guidelines. Through its world-renowned family of JACC Journals, NCDR registries, ACC Accreditation Services, global network of Member Sections, CardioSmart patient resources and more, the College is committed to ensuring a world where science, knowledge and innovation optimize patient care and outcomes. Learn more at www.ACC.org or follow @ACCinTouch.
###
END
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 14:00 BST / 09:00hrs ET Wednesday 4 October 2023
Peer reviewed
Observational and experimental studies
People and cells
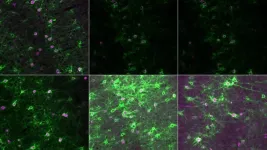
A research team at the Francis Crick Institute and Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH)/UCL Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health have identified new potential treatments for children with rare genetic conditions of blood vessels, which cause severe, lifelong, and disabling symptoms like seizures and impaired development.
Through two papers published today in the Journal of Investigative ...
Developing brains become shaped by the sights, sounds, and experiences of early life. The brain’s circuits grow more stable as we age. However, some experiences later in life open up opportunities for these circuits to be rapidly rewired. New research from Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Associate Professor Stephen Shea helps explain how the brain adapts during a critical period of adulthood: the time when new mothers learn to care for their young.
Shea’s work in mice shows how this learning process ...
After a yearlong and extensive nationwide search, the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS), the nation’s largest professional organization of bariatric and metabolic surgeons and integrated health professionals, has named healthcare association veteran Diane M. Enos MPH, RDN, CAE, FAND, to serve as its new executive director.
Before joining ASMBS, Enos, a registered dietitian and certified association executive with a master’s degree in public health from the University of Texas Health Science Center in Houston, was Chief Learning Officer of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, ...
A team led by researchers from Mass General Brigham reports promising results for a monoclonal antibody that takes aim at a new target for Alzheimer’s disease. Inspired by their previous identification of a genetic variant in the APOE gene that provides extreme resistance against Alzheimer’s disease, the team, which includes investigators from Mass Eye and Ear and Massachusetts General Hospital, developed a therapy that mimics the behavior of this genetic variant in a preclinical model, reducing ...
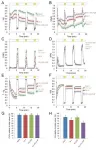
The potential for exposure to fluctuating light has necessitated that plants evolve protective mechanisms for when the light intensity exceeds photosynthetic capacity. Under these conditions, reactive oxygen species cause photoinhibition, which hinders photosynthetic efficiency. To counter this loss in photosynthetic efficiency, chloroplasts evolved thioredoxin (Trx) proteins that regulate redox balance within the photosynthetic apparatus and provide a photoprotective function. These proteins allow plants to modulate photosynthesis in response to variations in light intensity. ...
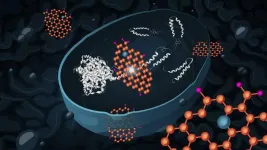
A probable early driver of Alzheimer's disease is the accumulation of molecules called amyloid peptides. These cause cell death, and are commonly found in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients. Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, have now shown that yeast cells that accumulate these misfolded amyloid peptides can recover after being treated with graphene oxide nanoflakes.
Alzheimer’s disease is an incurable brain disease, leading to dementia and death, that causes suffering for both the patients and their ...
Scientists have created a new zebrafish xenograft platform to screen for novel treatments for an aggressive brain tumor called glioblastoma, according to a new study by the Gerhardt and De Smet labs published in EMBO Molecular Medicine.
Joint press release – Max Delbrück Center, VIB, and KU Leuven
Glioblastoma is an aggressive and difficult-to-treat brain tumor in adults. On average, patients survive for only 1.5 years. The standard of care treatment for this disease, which includes surgery followed by radiation and chemotherapy, has not changed in 18 years. That’s partly because the cancer is ...
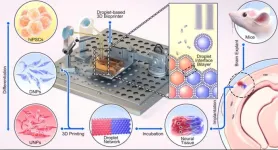
Researchers have produced an engineered tissue representing a simplified cerebral cortex by 3D printing human stem cells.
When implanted into mouse brain slices, the structures became integrated with the host tissue.
The technique may ultimately be developed into tailored repairs to treat brain injuries.
A breakthrough technique developed by University of Oxford researchers could one day provide tailored repairs for those who suffer brain injuries. The researchers demonstrated for the first time that neural cells can be 3D printed to mimic the architecture of the cerebral cortex. The results have been published today in the ...
Premature babies in neonatal care units are extremely vulnerable, and susceptible to life-threatening infections. To help keep these babies safe the risk of infection needs to be kept as low as possible.
A particular problem is late onset sepsis that starts from three days after birth, when bacteria get into the blood and grow. This can be very dangerous and babies with late onset sepsis end up staying in hospital longer, need more treatment with antibiotics and can be left with life-long effects on their health.
Bacteria from the Staphylococcus family are the most common causes ...
An educational and social support intervention for caregivers reduced elder mistreatment of older adults with chronic illness, including dementia. That’s the result of a recent double-blind, randomized controlled trial published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
Elder mistreatment is defined as “an intentional act or failure to act by a caregiver or another person in a relationship involving an expectation of trust that causes or creates a risk of harm to an older adult.” Through the Comprehensive Older Adult and Caregiver Help (COACH) intervention tested in this trial, coaches met with caregivers weekly for up to 12 sessions to listen to their ...