(Press-News.org) Researchers at Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center have discovered a druggable target on natural killer cells that could potentially trigger a therapeutic response in patients with immunotherapy-resistant, triple-negative breast cancer.
Currently, only about 15% of early-stage, triple-negative breast cancer patients benefit from combining immunotherapy, drugs that target immune cells to attack the tumor, with chemotherapy. Identifying why most patients don’t respond is critical for personalizing treatment plans and minimizing therapy side effects in patients.
The research, published in Cancer Discovery, highlighted NKG2A receptors as potential targets for overcoming immunotherapy resistance in breast cancer. These receptors exist on immune cells (‘natural killers’) capable of destroying cancer cells.
In this study, the researchers led by Justin Balko, PharmD, PhD, Ingram Associate Professor of Cancer Research, studied tumor-specific Major Histocompatibility Complex I (tsMHC-I), a molecule that is essential to the immune system’s ability to recognize tumor cells. Analyzing the variability of tsMHC-I in human breast cancers and in mouse models, they found high heterogeneity in the expression of this molecule. This variability was linked with a lack of benefit from the addition of immunotherapy. They then set about exploring how to overcome this therapeutic resistance in patients. Their findings suggest that combining anti-NKG2A with anti-PD-L1 therapy may represent a promising, yet underexplored approach for treating triple-negative breast cancer. This study deepens the understanding of why immunotherapies are ineffective for many triple-negative breast cancer patients and how to overcome this drug resistance.
“These findings shed some light on at least one reason why only a small fraction of breast cancer patients benefit from immunotherapy — their tumors have already found a way to remove a critical component for immunotherapy response. However, understanding this gives us a potential biomarker for identifying those patients and, perhaps more importantly, exposes a new way to target the tumor cells that have escaped the immune system,” said Balko, the study’s corresponding author.
The lead authors of the study are Brandie C. Taylor, MS, and Xiaopeng Sun, who are graduate students in the Balko Lab.
“This study was the result of a collaborative effort between researchers and clinicians. We hope our findings will help determine which triple-negative breast cancer patients should receive immunotherapy and which patients may benefit from the addition of anti-NKG2A in clinical trials,” the two lead authors stated.
Other Vanderbilt researchers who contributed to the study are Paula Gonzalez-Ericsson, MD, Melinda Sanders, MD, Elizabeth Wescott, Susan Opalenik, PhD, Ann Hanna, PhD, Brian Lehmann, PhD, Vandana Abramson, MD, and Jennifer Pietenpol, PhD.
The research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (SPORE 2P50CA098131-17) (T32CA009592), the Department of Defense (BC170037) and Susan G. Komen (ASP231038783).
END
Vulnerability found in immunotherapy-resistant triple-negative breast cancer
2023-10-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
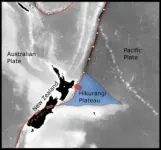
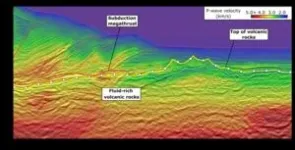
Discovery of massive undersea water reservoir could explain New Zealand’s mysterious slow earthquakes
2023-10-04
Researchers have discovered a sea’s worth of water locked within the sediment and rock of a lost volcanic plateau that’s now deep in the Earth’s crust. Revealed by a 3D seismic image, the water lies two miles under the ocean floor off the coast of New Zealand, where it may be dampening a major earthquake fault that faces the country’s North Island.
The fault is known for producing slow-motion earthquakes, called slow slip events. These can release pent-up tectonic pressure harmlessly over days and weeks. Scientists want to know why they happen more often at some ...
Should fathers be screened for postpartum depression?
2023-10-04
Dads can suffer from postpartum depression, and a new pilot study at the University of Illinois Chicago suggests they can and should be screened for the condition. Given the intertwined effects of mothers’ and fathers’ physical and mental health, addressing the health of fathers may be a powerful untapped tool in improving the nation’s ongoing maternal health crisis.
The researchers got mothers’ permission to interview and screen 24 dads, 30% of whom screened positive for postpartum depression on the same tool ...
BGI Genomics breaks new ground in Saudi Arabian precision medicine
2023-10-04
The Saudi Society of Medical Genetics Annual Conference 2023 was held in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, on September 29-30, 2023. As the most authoritative academic conference on precision medicine in the Kingdom, this conference attracted global experts worldwide.
One of the highlights of the conference was the presentation entitled "Spatial-temporal sequencing and some large-scale application of precision medicine technologies," delivered by Dr. Louis (Renyuan) Luo, VP of BGI Genomics West Asia, at the invitation of the Saudi Society of Medical Genetics.
Dr. Luo's presentation discussed the importance of spatiotemporal sequencing technology ...
Portable laboratory devices can detect SARS-CoV-2
2023-10-04
Washington, D.C. — A new study has demonstrated rapid and sensitive on-site detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA from environmental surfaces using a portable laboratory device. The study was published in Microbiology Spectrum, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
“Our findings hold promising implications for scenarios where access to testing laboratories is challenging, such as in cruise ships, international travel, remote islands and tourist destinations,” said lead study author Kouichi Kitamura, Ph.D., National Institute of Infectious ...
Challenges in acute heart attack care continue post COVID-19
2023-10-04
A door-to-balloon (D2B) time of 90-minutes or less is associated with improved outcomes for heart attack patients. However, during the COVID-19 pandemic certain obstacles—including the need for COVID-19 screening, associated isolation procedures and terminal cleaning in the cardiac cath lab—led to increased D2B times. According to a new study, presented at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) Quality Summit 2023, many health care facilities are still recovering from the pandemic and facing new challenges, causing D2B times to continue to lag.
A myocardial infarction, or heart attack, occurs when there has been a blockage ...
Researchers design potential therapy to prevent brain deterioration in children with rare genetic conditions
2023-10-04
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 14:00 BST / 09:00hrs ET Wednesday 4 October 2023
Peer reviewed
Observational and experimental studies
People and cells
A research team at the Francis Crick Institute and Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH)/UCL Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health have identified new potential treatments for children with rare genetic conditions of blood vessels, which cause severe, lifelong, and disabling symptoms like seizures and impaired development.
Through two papers published today in the Journal of Investigative ...
Reactivate, repurpose, and rewire the brain
2023-10-04
Developing brains become shaped by the sights, sounds, and experiences of early life. The brain’s circuits grow more stable as we age. However, some experiences later in life open up opportunities for these circuits to be rapidly rewired. New research from Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Associate Professor Stephen Shea helps explain how the brain adapts during a critical period of adulthood: the time when new mothers learn to care for their young.
Shea’s work in mice shows how this learning process ...
American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery names new executive director after yearlong search
2023-10-04
After a yearlong and extensive nationwide search, the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS), the nation’s largest professional organization of bariatric and metabolic surgeons and integrated health professionals, has named healthcare association veteran Diane M. Enos MPH, RDN, CAE, FAND, to serve as its new executive director.
Before joining ASMBS, Enos, a registered dietitian and certified association executive with a master’s degree in public health from the University of Texas Health Science Center in Houston, was Chief Learning Officer of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, ...
Antibody therapy inspired by patient case reduced tau tangles in a preclinical model of Alzheimer’s disease
2023-10-04
A team led by researchers from Mass General Brigham reports promising results for a monoclonal antibody that takes aim at a new target for Alzheimer’s disease. Inspired by their previous identification of a genetic variant in the APOE gene that provides extreme resistance against Alzheimer’s disease, the team, which includes investigators from Mass Eye and Ear and Massachusetts General Hospital, developed a therapy that mimics the behavior of this genetic variant in a preclinical model, reducing ...
Demystifying the role of plant x- and y-type thioredoxins
2023-10-04
The potential for exposure to fluctuating light has necessitated that plants evolve protective mechanisms for when the light intensity exceeds photosynthetic capacity. Under these conditions, reactive oxygen species cause photoinhibition, which hinders photosynthetic efficiency. To counter this loss in photosynthetic efficiency, chloroplasts evolved thioredoxin (Trx) proteins that regulate redox balance within the photosynthetic apparatus and provide a photoprotective function. These proteins allow plants to modulate photosynthesis in response to variations in light intensity. ...