(Press-News.org) Our five senses bombard us with environmental input 24/7. One way our brain makes sense of this abundance of information is by combining information from two or more senses, such as between smells and the smoothness of textures, pitch, color, and musical dimensions. This sensory integration also causes us to associate higher temperatures with warmer colors, lower sound pitches with less elevated positions, and colors with the flavor of particular foods – for example, the taste of oranges with the color of the same name.
Now, a study in Frontiers in Psychology has shown experimentally that such unconscious 'crossmodal' associations with our sense of smell can affect our perception of colors.
“Here we show that the presence of different odors influences how humans perceive color,” said lead author Dr Ryan Ward, a senior lecturer at Liverpool John Moores University in Liverpool, UK.
Sensory-deprived room
Ward and colleagues tested for the existence and strength of odor-color associations in 24 adult women and men between 20 and 57 years of age. The participants were seated in front of a screen in a room devoid of unwanted sensory stimuli for the duration of the experiments. They wore no deodorants or perfumes, and none reported being color-blind or having an impaired sense of smell.
All ambient odors in the isolation room were purged with an air purifier for four minutes. Then one of six odors (chosen at random from caramel, cherry, coffee, lemon, and peppermint, plus odorless water as a control) was broadcast into the room with an ultrasonic diffuser for five minutes.
“In a previous study, we had shown that the odor of caramel commonly constitutes a crossmodal association with dark brown and yellow, just like coffee with dark brown and red, cherry with pink, red, and purple, peppermint with green and blue, and lemon with yellow, green, and pink,” explained Ward.
Participants were presented with a screen that showed them a square filled with a random color (from an infinite range) and were invited to manually adjust two sliders – one for yellow to blue, and another for green to red – to change its color to neutral grey. After the final choice had been recorded, the procedure was repeated, until all odors had been presented five times.
Overcompensating for unconscious associations
The results showed that participants had a weak but significant tendency to adjust one or both of the sliders too far away from neutral grey. For example, when presented with the odor of coffee, they wrongly perceived ‘grey’ to be more of a red-brown color than true neutral grey. Likewise, when presented with the odor of caramel, they wrongly perceived a color enriched in blue as grey. The presence of the smell thus distorted the participants’ color perception in a predictable manner.
An exception was when the odor of peppermint was presented: here, the participants’ choice of hue was different from the typical crossmodal association demonstrated for the other odors. As expected, the participants’ selection likewise corresponded to true grey when presented with the neutral scent of water.
“These results show that the perception of grey tended towards their anticipated crossmodal correspondences for four out of five scents, namely lemon, caramel, cherry, and coffee,” said Ward.
“This 'overcompensation' suggests that the role of crossmodal associations in processing sensory input is strong enough to influence how we perceive information from different senses, here between odors and colors.”
Questions remain
The researchers emphasize the need to investigate how far-reaching such crossmodal associations between odors and colors are.
“We need to know the degree to which odors influence color perception. For example, is the effect shown here still present for less commonly encountered odors, or even for odors encountered for the first time?” said Ward.
END
Our sense of smell changes the colors we see, show scientists
Unconscious associations with odor can distort perception of colors
2023-10-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Super-efficient laser light-induced detection of cancer cell-derived nanoparticles
2023-10-06
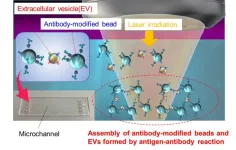
Osaka, Japan - Can particles as minuscule as viruses be detected accurately within a mere 5 minutes? Osaka Metropolitan University scientists say yes, with their innovative method for ultrafast and ultrasensitive quantitative measurement of biological nanoparticles, opening doors for early diagnosis of a broad range of diseases.
Nanoscale extracellular vesicles (EVs) including exosomes, with diameters of 50–150 nm, play essential roles in intercellular communication and have garnered attention as biomarkers for various diseases and drug delivery capsules. Consequently, the rapid and sensitive detection of nanoscale EVs from trace samples is ...
Fathers’ parental leave might protect men against alcohol-related morbidity
2023-10-06
Men who have been on parental leave have a significantly reduced risk of being hospitalized due to alcohol consumption. This is shown by a study published in Addiction from researchers at the Department of Public Health Sciences, Stockholm University.
The aim of the study was to assess whether fathers’ parental leave influences alcohol-related morbidity and mortality. In order to try to find out if that is the case, the researchers have investigated the effects of parental leave policy that was implemented in Sweden in 1995. The policy encouraged fathers to use parental leave by reserving 30 days of leave for their use alone and resulted in the proportion ...
A 130g soft robot gripper lifts 100kg?
2023-10-06
Utilizing soft, flexible materials such as cloth, paper, and silicone, soft robotic grippers is an essential device that acts like a robot's hand to perform functions such as safely grasping and releasing objects. Unlike conventional rigid material grippers, they are more flexible and safe, and are being researched for household robots that handle fragile objects such as eggs, or for logistics robots that need to carry various types of objects. However, its low load capacity makes it difficult to lift heavy objects, and its poor grasping stability makes it easy to lose the object even under mild external impact.
Dr. ...
USTC researchers revolutionize understanding of supermassive black hole accretion radiation in quasars
2023-10-06
Associate Professor CAI Zhenyi and Professor WANG Junxian from the Department of Astronomy at the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), through the study of the optical to extreme ultraviolet radiation generated by the accretion of supermassive black holes at the centers of quasars, have discovered that their spectral energy distribution is independent to the intrinsic brightness of quasars, overturning the traditional ...
Climate change brings earlier arrival of intense hurricanes
2023-10-06
Intense tropical cyclones are one of the most devastating natural disasters in the world due to torrential rains, flooding, destructive winds, and coastal storm surges. New research co-authored by a University of Hawai‘i at Mānoa atmospheric scientist revealed that since the 1980s, Category 4 and 5 hurricanes (maximum wind speed greater than 131 miles per hour) have been arriving three to four days earlier with each passing decade of climate change. Their findings were published recently in Nature.
“When intense tropical cyclones occur earlier than usual, they cause unexpected problems for communities,” said Pao-Shin Chu, atmospheric ...
Ex-football players with medical and mental health conditions at higher odds of receiving premature CTE diagnosis
2023-10-06
PITTSBURGH, Oct. 4, 2023 – Former professional American football players who have medical and mental health conditions including depression, anxiety or sleep apnea are more likely to receive an unverified diagnosis of chronic traumatic encephalopathy, or CTE, compared to those without those conditions, report researchers from the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Harvard University and Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Sports Medicine today.
Receiving a CTE diagnosis that cannot be verified until after death could further exacerbate mental health conditions in former players due to the current lack of ...
Natural GM crops: grasses take evolutionary shortcut by borrowing genes from their neighbours
2023-10-06
New study shows grasses are taking an evolutionary shortcut by continually borrowing genes from their neighbours to grow bigger, stronger and taller
The research, led by the University of Sheffield, is the first to show how frequently grasses exchange genes in the wild
The naturally occurring process observed in grasses, including in some of the crops we eat, may mirror methods used to make genetically modified crops
Understanding the rate is important to know the potential impact it can have on a plant’s ...
Cambridge University receives $72 million gift for habitat restoration projects across Europe’s land and seas
2023-10-06
Arcadia has made a major new philanthropic donation to the University of Cambridge, taking its total support for the Endangered Landscapes & Seascapes Programme to over $138 million.
The Endangered Landscapes & Seascapes Programme supports the large-scale restoration of Europe’s most treasured but endangered ecosystems, enriching biodiversity while revitalising local economies.
The work recognises humanity’s dependence on healthy, functioning ecosystems - for example in preventing urban flooding, and reducing the impacts ...
New UC Davis study looks at attitudes towards political violence
2023-10-06
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — A small segment of the U.S. population considers violence, including lethal violence, to be usually or always justified to advance political objectives. This is according to newly published research from the UC Davis Violence Prevention Research Program (VPRP).
The study provides a complex portrait of the attitudes and concerns about the state of democracy in the U.S. It also highlights the underlying beliefs that may inform the potential for violence.
The study was published Sept. 29, 2023, in Injury Epidemiology. A preprint, or version that had not yet been peer reviewed, was shared online ...
Mays Cancer Center: Targeting certain molecular interactions could yield new strategies for treating prostate cancer
2023-10-06
SAN ANTONIO, Oct. 6, 2023 – Research led by Mays Cancer Center at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) has discovered that altering certain molecular interactions could yield new strategies for treating prostate cancer and related diseases.
The study focuses on androgen receptors (AR), which are protein molecules that help direct the development of male sexual characteristics, essentially by turning genes on or off as necessary.
The researchers determined that an optimum level of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
The research that got sick veterans treatment
Study finds that on-demand wage access boosts savings and financial engagement for low-wage workers
Antarctica has lost 10 times the size of Greater Los Angeles in ice over 30 years
Scared of spiders? The real horror story is a world without them
New study moves nanomedicine one step closer to better and safer drug delivery
Illinois team tests the costs, benefits of agrivoltaics across the Midwest
Highly stable self-rectifying memristor arrays: Enabling reliable neuromorphic computing via multi-state regulation
Composite superionic electrolytes for pressure-less solid-state batteries achieved by continuously perpendicularly aligned 2D pathways
Exploring why some people may prefer alcohol over other rewards
How expectations about artificial sweeteners may affect their taste
Ultrasound AI receives FDA De Novo clearance for delivery date AI technology
Amino acid residue-driven nanoparticle targeting of protein cavities beyond size complementarity
New AI algorithm enables scientific monitoring of "blue tears"
Insufficient sleep among US adolescents across behavioral risk groups
Long COVID and recovery among US adults
Trends in poverty and birth outcomes in the US
[Press-News.org] Our sense of smell changes the colors we see, show scientistsUnconscious associations with odor can distort perception of colors