(Press-News.org) On October 2, 2023, BGI Genomics signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Colombian National Cancer Institute (INC or Instituto Nacional de Cancerologia). This collaboration, which aims to foster research and further develop cutting-edge solutions based on genetic sequencing for early diagnosis of cervical and colorectal cancer, reflects a shared dedication to enhancing health outcomes in the region.
The MoU was formally inked at INC facilities by Dr. Carolina Wiesner, INC Director, and Mr. Rainer Perez, alternate legal representative of BGI Genomics in Colombia. Mr. Marco Antonio Rincón, Latin America Business Director, BGI Genomics, notes: "BGI Genomics is 100 percent committed to providing cost-effective tools for the prevention and management of Human papillomavirus (HPV) and colorectal cancer to make a meaningful impact on the healthcare of Colombian people." As part of this MoU, BGI Genomics will also train INC personnel.
The Colombian National Cancer Institute was created in 1934, and for over seven decades the INC has been committed to the provision of a comprehensive approach to prevention, treatment, rehabilitation and research of cancer in the Colombian population. Earlier, on September 26, 2023, Mr. Rincón took part as a panelist on behalf of BGI Genomics at the Health and Innovation Event during the 8th China-Colombia Dialogue Conference, held in Bogota, Colombia.
This event, organized by the Colombian Chinese Chamber of Investment & Commerce and the Embassy of the People's Republic of China in Colombia, provided a platform for thought leaders to discuss critical healthcare issues. Dr. Carolina Gómez, Manager of Bogotá Bio and Colombian Health Ministry Advisor, moderated a panel where Mr. Rincón emphasized BGI Genomics' commitment to strengthening local human skills and talent with every local project. He also emphasized that the company seeks to promote access to innovative, precision and cost-effective technologies for the country's health system.
About BGI Genomics:
BGI Genomics, headquartered in Shenzhen, China, is the world's leading integrated solutions provider of precision medicine. Our services cover more than 100 countries and regions, involving more than 2,300 medical institutions. In July of 2017, as a subsidiary of BGI Group, BGI Genomics (300676.SZ) was officially listed on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange.
END
Colombian National Cancer Institute signs MOU with BGI Genomics to combat cancer
2023-10-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ginger pigment molecules found in fossil frogs
2023-10-06
UCC palaeontologists discover molecular evidence of phaeomelanin, the pigment that produces ginger colouration.
“This will paint a more accurate picture of ancient animal colour.”
Phaeomelanin is now toxic to animals – discovery may be first step in understand its evolution.
Palaeontologists at University College Cork (UCC) have found the first molecular evidence of phaeomelanin, the pigment that produces ginger colouration, in the fossil record.
The new study reports ...
Scientists discover ‘long colds’ may exist, as well as long Covid
2023-10-06
A new study from Queen Mary University of London, published in The Lancet’s EClinicalMedicine, has found that people may experience long-term symptoms —or ‘long colds’—after acute respiratory infections that test negative for COVID-19.
Some of the most common symptoms of the ‘long cold’ included coughing, stomach pain, and diarrhea more than 4 weeks after the initial infection. While the severity of an illness appears to be a key driver of risk of long-term symptoms, ...
Our sense of smell changes the colors we see, show scientists
2023-10-06
Our five senses bombard us with environmental input 24/7. One way our brain makes sense of this abundance of information is by combining information from two or more senses, such as between smells and the smoothness of textures, pitch, color, and musical dimensions. This sensory integration also causes us to associate higher temperatures with warmer colors, lower sound pitches with less elevated positions, and colors with the flavor of particular foods – for example, the taste of oranges with the color of the same name.
Now, a study in Frontiers in Psychology has shown experimentally that such unconscious 'crossmodal' ...
Super-efficient laser light-induced detection of cancer cell-derived nanoparticles
2023-10-06
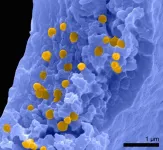
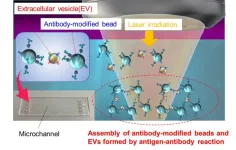
Osaka, Japan - Can particles as minuscule as viruses be detected accurately within a mere 5 minutes? Osaka Metropolitan University scientists say yes, with their innovative method for ultrafast and ultrasensitive quantitative measurement of biological nanoparticles, opening doors for early diagnosis of a broad range of diseases.
Nanoscale extracellular vesicles (EVs) including exosomes, with diameters of 50–150 nm, play essential roles in intercellular communication and have garnered attention as biomarkers for various diseases and drug delivery capsules. Consequently, the rapid and sensitive detection of nanoscale EVs from trace samples is ...
Fathers’ parental leave might protect men against alcohol-related morbidity
2023-10-06
Men who have been on parental leave have a significantly reduced risk of being hospitalized due to alcohol consumption. This is shown by a study published in Addiction from researchers at the Department of Public Health Sciences, Stockholm University.
The aim of the study was to assess whether fathers’ parental leave influences alcohol-related morbidity and mortality. In order to try to find out if that is the case, the researchers have investigated the effects of parental leave policy that was implemented in Sweden in 1995. The policy encouraged fathers to use parental leave by reserving 30 days of leave for their use alone and resulted in the proportion ...
A 130g soft robot gripper lifts 100kg?
2023-10-06
Utilizing soft, flexible materials such as cloth, paper, and silicone, soft robotic grippers is an essential device that acts like a robot's hand to perform functions such as safely grasping and releasing objects. Unlike conventional rigid material grippers, they are more flexible and safe, and are being researched for household robots that handle fragile objects such as eggs, or for logistics robots that need to carry various types of objects. However, its low load capacity makes it difficult to lift heavy objects, and its poor grasping stability makes it easy to lose the object even under mild external impact.
Dr. ...
USTC researchers revolutionize understanding of supermassive black hole accretion radiation in quasars
2023-10-06
Associate Professor CAI Zhenyi and Professor WANG Junxian from the Department of Astronomy at the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), through the study of the optical to extreme ultraviolet radiation generated by the accretion of supermassive black holes at the centers of quasars, have discovered that their spectral energy distribution is independent to the intrinsic brightness of quasars, overturning the traditional ...
Climate change brings earlier arrival of intense hurricanes
2023-10-06
Intense tropical cyclones are one of the most devastating natural disasters in the world due to torrential rains, flooding, destructive winds, and coastal storm surges. New research co-authored by a University of Hawai‘i at Mānoa atmospheric scientist revealed that since the 1980s, Category 4 and 5 hurricanes (maximum wind speed greater than 131 miles per hour) have been arriving three to four days earlier with each passing decade of climate change. Their findings were published recently in Nature.
“When intense tropical cyclones occur earlier than usual, they cause unexpected problems for communities,” said Pao-Shin Chu, atmospheric ...
Ex-football players with medical and mental health conditions at higher odds of receiving premature CTE diagnosis
2023-10-06
PITTSBURGH, Oct. 4, 2023 – Former professional American football players who have medical and mental health conditions including depression, anxiety or sleep apnea are more likely to receive an unverified diagnosis of chronic traumatic encephalopathy, or CTE, compared to those without those conditions, report researchers from the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Harvard University and Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Sports Medicine today.
Receiving a CTE diagnosis that cannot be verified until after death could further exacerbate mental health conditions in former players due to the current lack of ...
Natural GM crops: grasses take evolutionary shortcut by borrowing genes from their neighbours
2023-10-06
New study shows grasses are taking an evolutionary shortcut by continually borrowing genes from their neighbours to grow bigger, stronger and taller
The research, led by the University of Sheffield, is the first to show how frequently grasses exchange genes in the wild
The naturally occurring process observed in grasses, including in some of the crops we eat, may mirror methods used to make genetically modified crops
Understanding the rate is important to know the potential impact it can have on a plant’s ...