(Press-News.org) East Hanover, NJ – October 6, 2023 –The labor force participation and employment-to-population ratio have held relatively steady throughout the summer and into the fall for people with disabilities, while percentages for people without disabilities may have maxed out at their pre-pandemic baseline, according to today’s National Trends in Disability Employment – semi-monthly update (nTIDE), issued by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability (UNH-IOD). In comparison, the employment-to-population ratio for people without disabilities remained flat with no change, while their labor force participation decreased slightly.
“The stability of percentages for both people with and without disabilities over the past four months might signal the desired soft landing from the recession hoped for by the Federal Reserve," explained John O’Neill, PhD, director of the Center for Employment and Disability Research at Kessler Foundation.
Month-to-Month nTIDE Numbers (comparing August 2023 to September 2023)
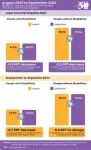
Based on data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) Jobs Report released today, the employment-to-population ratio for people with disabilities (ages 16-64) decreased from 37.9 percent in August 2023 to 37.2 percent in September 2023 (down 1.8 percent or 0.7 percentage points). For people without disabilities (ages 16-64), the employment-to-population ratio remained the same at 75.2 percent. The employment-to-population ratio, a key indicator, reflects the percentage of people who are working relative to the total population (the number of people working divided by the number of people in the total population multiplied by 100).
Why has the labor force participation of people without disabilities remained the same? “In a sense, they may have returned to their pre-pandemic level and ‘topped out’ at this point,” added Dr. O’Neill.
The labor force participation rate for people with disabilities (ages 16-64) decreased from 41.2 percent in August 2023 to 40.3 percent in September 2023 (down 2.2 percent or 0.9 percentage points). For people without disabilities (ages 16-64), the labor force participation rate decreased from 78.2 percent in August 2023 to 77.9 percent in September 2023 (down 0.4 percent or 0.3 percentage points). The labor force participation rate reflects the percentage of people who are in the labor force (working, on temporary layoff (on furlough), or actively looking for work in the last four weeks) relative to the total population (the number of people in the labor force divided by the number of people in the total population multiplied by 100).
“The labor force participation of people with disabilities has remained relatively stable at all-time highs over the summer and into September,” said Andrew Houtenville, PhD, professor of economics and research director of the UNH-IOD.
Year-to-Year nTIDE Numbers (comparing September 2022 to September 2023)
Compared to this time last year, the employment-to-population ratio for people with disabilities (ages 16-64) increased from 34.9 percent in September 2022 to 37.2 percent in September 2023 (up 6.6 percent or 2.3 percentage points). For people without disabilities (ages 16-64), the employment-to-population ratio also increased from 74.6 percent in September 2022 to 75.2 percent in September 2023 (up 0.8 percent or 0.6 percentage points).
Similarly, the labor force participation rate for people with disabilities (ages 16-64) increased from 38 percent in September 2022 to 40.3 percent in September 2023 (up 6.1 percent or 2.3 percentage points). For people without disabilities (ages 16-64), the labor force participation rate also increased from 77.1 percent in September 2022 to 77.9 percent in September 2023 (up 1 percent or 0.8 percentage points).
In September, among workers ages 16-64, the 6,323,000 workers with disabilities represented 4.2 percent of the total 150,541,000 workers in the U.S. workforce.
Ask Questions about Disability and Employment
Each nTIDE release is followed by an nTIDE Lunch & Learn online webinar. This live broadcast, hosted via Zoom Webinar, offers attendees Q&A on the latest nTIDE findings, provides news, updates from the field, and features invited panelists who discuss current disability-related findings and events.
On October 6, 2023, at 12:00 pm – 1:00 pm Eastern, guest presenters Leslie Jones, Executive Director and Dalia Sakas, Director of Music Studies at The Filomen M. D’Agostino Greenberg Music School joins Drs. O’Neill and Houtenville. Join our free Lunch & Learn live or visit the nTIDE archives at: ResearchonDisability.org/nTIDE. Also, register now for our mid-month Deeper Dive into employment trends at nTIDE Deeper Dive – 10/20/2023.
NOTE: The statistics in the nTIDE are based on BLS numbers but are not identical. They are customized by UNH to combine the statistics for men and women of working age (16- 64). nTIDE is funded by Kessler Foundation and was initially funded by grants from the National Institute on Disability, Independent Living and Rehabilitation Research (NIDILRR) (90RT5037).
About the Institute on Disability at the University of New Hampshire
The Institute on Disability (IOD) at the University of New Hampshire (UNH) was established in 1987 to provide a university-based focus for the improvement of knowledge, policies, and practices related to the lives of persons with disabilities and their families. For information on the NIDILRR-funded Research and Training Center on Disability Statistics, visit ResearchOnDisability.org.
About Kessler Foundation
Kessler Foundation, a major nonprofit organization in the field of disability, is a global leader in rehabilitation research. Our scientists seek to improve cognition, mobility, and long-term outcomes, including employment, for adults and children with neurological and developmental disabilities of the brain and spinal cord including traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injury, stroke, multiple sclerosis, and autism. Kessler Foundation also leads the nation in funding innovative programs that expand opportunities for employment for people with disabilities. For more information, visit KesslerFoundation.org.
Press Contacts at Kessler Foundation:
Deborah Hauss, DHauss@kesslerfoundation.org
Carolann Murphy, CMurphy@KesslerFoundation.org
Stay Connected with Kessler Foundation
Twitter | Facebook | YouTube | Instagram | iTunes & SoundCloud
END
nTIDE September 2023 Jobs Report: Employment trend holds steady at historic highs through early autumn for people with disabilities
National Trends in Disability Employment (nTIDE) – Issued semi-monthly by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire
2023-10-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Kidney disease gene also has a protective mutation
2023-10-06
African Americans have long been known to be at increased risk of kidney disease due to a dangerous genetic mutation that creates a hole in the kidney cells, but Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) researchers have now discovered a protective genetic mutation that covers the hole to eliminate the risk.
The findings on the apolipoprotein L1 (APOL1) gene, published today in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, could have immediate and broad implications for kidney health because people with both the disease-causing and protective mutation are not at increased risk.
“Our team discovered ...
Aston University offers talented Indian graduates opportunity to study for Masters degrees
2023-10-06
Aston University, UK, is offering a group of highly talented graduates of Symbiosis Institute of Technology (SIT), India the opportunity to study for a Masters degree.
The two institutions have signed a progression agreement which is designed to make it easier for top SIT graduates to apply for courses at Aston University.
The Aston-SIT partnership has been developed from the support of the British Council via its going global partnerships exploratory grant scheme. The areas of study cover a wide range of MSc programmes in engineering, physical sciences and business studies.
Aston University is in Birmingham, ...
New research led by Mays Cancer Center reveals how mutations in BRCA1 affect cancer susceptibility in women
2023-10-06
SAN ANTONIO, Oct. 6, 2023 – Three decades after discoveries linking mutations in the BRCA1 gene to breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility, research led by Mays Cancer Center at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) has pinpointed the molecular mechanism by which a large portion of these mutations cause cancers in women.
The discovery, unveiled in an Oct. 4 research article in the journal Molecular Cell, is poised to assist researchers in developing drugs to battle breast and ovarian cancers and to help identify women who are at an elevated risk of developing these cancers, according to the ...
How the war in Ukraine is challenging two academic disciplines
2023-10-06
Since the beginning of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, two academic disciplines have come to fore: peace and conflict studies and East European studies. Experts from both fields represent important voices in the public discourse. A symposium entitled ‘War and Peace in Ukraine: Reflecting, Studying and Engaging Across Disciplines” will be held from 12 until 13 October 2023 at Bielefeld University. It brings together experts from both fields in order to discuss the relationship between them and challenges of participating in a highly ...
How do our brains tell us what went wrong?
2023-10-06
Whether improperly closing a door or shanking a kick in soccer, our brains tell us when we’ve made a mistake because these sounds differ from what we expect to hear. While it’s long been established that our neurons spot these errors, it has been unclear whether there are brain cells that have only one job—to signal when a sound is unexpected or “off.”
A team of New York University neuroscientists has now identified a class of neurons—what it calls “prediction-error neurons”—that are not responsive to sounds in general, ...
New pathways of Alzheimer's disease identified
2023-10-06
Dementia, which includes Alzheimer's disease, currently affects around 1.8 million people in Germany. The exact cause has not yet been clarified, but genetic factors play a significant role in the development of the disease. Most previous analyses aimed at the identification of novel Alzheimer's genes used, a "case-control design". "With this conventional and highly simplistic analysis strategy, a vast amount of clinical information is lost that can be valuable for elucidating new disease mechanisms," says Prof. Dr. Lars Bertram, head of the Lübeck Interdisciplinary Platform for Genome Analysis at the University ...
Consistent metabolism may prove costly for insects in saltier water
2023-10-06
Increased salinity usually spells trouble for freshwater insects like mayflies. A new study from North Carolina State University finds that the lack of metabolic responses to salinity may explain why some freshwater insects often struggle in higher salinity, while other freshwater invertebrates (like mollusks and crustaceans) thrive. Salinity in this case refers to the concentrations of all the salts in an aquatic environment, not just sodium.
“Freshwater habitats in general are getting saltier for a number of reasons, including road salt and ...
Clinical trials: two arms are better than one
2023-10-06
The German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) has responded critically to a reflection paper by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) on the approval of new drugs based on single-arm studies. The EMA correctly points out that studies without a control arm are subject to bias and that, in general, it is hardly possible to estimate causal effects from them. However, it does not provide clear criteria for limiting drug approval based on such studies to extremely rare exceptional cases.
The FDA shows how to do it
There is also no recommendation on external controls - in contrast to guidance published ...
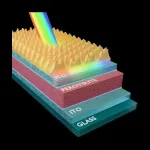
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale
2023-10-06
Perovskite-based solar cells, widely considered as successors to the currently dominant silicon cells, due to their simple and cost-effective production process combined with their excellent performance, are now the subject of in-depth research. A team of scientists from the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy ISE and the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw presented perovskite photovoltaic cells with significantly improved optoelectronic properties in the journal Advanced Materials and Interfaces. Reducing optical losses in the ...
BU researcher awarded $3.7 million to study how endothelial cell health impacts disease
2023-10-06
(Boston)—Naomi Hamburg, MD, the Joseph A. Vita Professor of Medicine at Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, has been awarded a five-year, $3.7 million grant from the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute for her research study, “Endothelial Cell Health Across the Spectrum of Cardiometabolic Disease.”
Cardiometabolic diseases are a group of common but often preventable conditions including heart attack, stroke, diabetes, insulin resistance and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. The escalating prevalence of cardiometabolic risk factors including obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New tool reveals the secrets of HIV-infected cells
HMH scientists calculate breathing-brain wave rhythms in deepest sleep
Electron microscopy shows ‘mouse bite’ defects in semiconductors
Ochsner Children's CEO joins Make-A-Wish Board
Research spotlight: Exploring the neural basis of visual imagination
Wildlife imaging shows that AI models aren’t as smart as we think
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
Self-cleaning fuel cells? Researchers reveal steam-powered fix for ‘sulfur poisoning’
Bacteria found in mouth and gut may help protect against severe peanut allergic reactions
Ultra-processed foods in preschool years associated with behavioural difficulties in childhood
A fanged frog long thought to be one species is revealing itself to be several
Weill Cornell Medicine selected for Prostate Cancer Foundation Challenge Award
Largest high-precision 3D facial database built in China, enabling more lifelike digital humans
SwRI upgrades facilities to expand subsurface safety valve testing to new application
Iron deficiency blocks the growth of young pancreatic cells
Selective forest thinning in the eastern Cascades supports both snowpack and wildfire resilience
A sea of light: HETDEX astronomers reveal hidden structures in the young universe
Some young gamers may be at higher risk of mental health problems, but family and school support can help
Reduce rust by dumping your wok twice, and other kitchen tips
High-fat diet accelerates breast cancer tumor growth and invasion
Leveraging AI models, neuroscientists parse canary songs to better understand human speech
Ultraprocessed food consumption and behavioral outcomes in Canadian children
The ISSCR honors Dr. Kyle M. Loh with the 2026 Early Career Impact Award for Transformative Advances in Stem Cell Biology
The ISSCR honors Alexander Meissner with the 2026 ISSCR Momentum Award for exceptional work in developmental and stem cell epigenetics
The ISSCR honors stem cell COREdinates and CorEUstem with the 2026 ISSCR Public Service Award
Minimally invasive procedure effectively treats small kidney cancers
SwRI earns CMMC Level 2 cybersecurity certification
Doctors and nurses believe their own substance use affects patients
Life forms can planet hop on asteroid debris – and survive
Sylvia Hurtado voted AERA President-Elect; key members elected to AERA Council
[Press-News.org] nTIDE September 2023 Jobs Report: Employment trend holds steady at historic highs through early autumn for people with disabilitiesNational Trends in Disability Employment (nTIDE) – Issued semi-monthly by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire