(Press-News.org) BOSTON – Although several medications are approved to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), some individuals experience limited benefits from the drugs or develop side effects from their use. A recent clinical trial published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of Mass General Brigham (MGB), has demonstrated that the drug solriamfetol may be an effective alternative for managing ADHD in adults.
Solriamfetol is currently approved in the United States for treating excessive daytime sleepiness in patients with narcolepsy or obstructive sleep apnea. The drug increases the amounts of certain natural substances in the brain—specifically, dopamine and norepinephrine—that control sleep and wakefulness, thus sharing some of the properties of current ADHD medications.
To test the potential of solriamfetol for treating ADHD, researchers randomized 60 adults with the condition to solriamfetol (75 or 150 mg) or placebo for 6 weeks. Participants were interviewed serially using the primary outcome measure for the trial, the Adult ADHD Investigator Symptom Rating Scale (AISRS). ADHD symptoms were further evaluated by a patient-reported measure. ADHD related impairment was assessed using the Clinical Global Impressions scale (CGI), and executive function challenges were measured using the participant rated Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function-Adult Form (BRIEF-A).
By the end of the study, a greater proportion of individuals taking solriamfetol had improved measures on all of these scales, when compared with patients taking placebo.
Solriamfetol had no significant effect on sleep quality as evaluate by the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index, or on average heart rate or blood pressure. Adverse experiences that occurred at a higher numerical rate than placebo fell under the categories of decreased appetite, headache, gastrointestinal symptoms, insomnia, increased energy, cardiovascular and neurologic effects.
“Our results suggest that solriamfetol may be a safe and effective treatment for ADHD in adults. Larger studies replicating these findings could confirm the strong evidence of benefit and the tolerability of this agent as a treatment,” says lead author Craig B.H. Surman, MD, the Director of the Clinical and Research Program in Adult ADHD at MGH and Associate Professor of Psychiatry at Harvard Medical School. “Although there are currently safe and effective treatments for ADHD, they are not effective for all individuals with ADHD or tolerated well by all patients. Our findings offer hope of a new method of supporting the daily challenges that individuals with ADHD face.”
Additional authors include Daniel M. Walsh, BA; Nora Horick, MS; Maura DiSalvo, MPH; Chloe Hutt Vater, BA; and Daniel Kaufman, BS.
This research was an investigator-initiated trial supported by Jazz Pharmaceuticals and Axsome Therapeutics. Materials for this study were provided by Jazz Pharmaceuticals and Axsome Therapeutics.
About the Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital, founded in 1811, is the original and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School. The Mass General Research Institute conducts the largest hospital-based research program in the nation, with annual research operations of more than $1 billion and comprises more than 9,500 researchers working across more than 30 institutes, centers and departments. In July 2022, Mass General was named #8 in the U.S. News & World Report list of "America’s Best Hospitals." MGH is a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system.
END
Clinical trial demonstrates benefits of solriamfetol for adults with ADHD
The drug may help patients who don’t benefit from current ADHD medications
2023-10-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tropical ecosystems more reliant on emerging aquatic insects, study finds, potentially putting them at greater risk
2023-10-09
A team of researchers from Queen Mary University of London and the University of Campinas in Brazil has found that tropical forest ecosystems are more reliant on aquatic insects than temperate forest ecosystems and are therefore more vulnerable to disruptions to the links between land and water.
The study, published in the journal Ecology Letters, is the first to directly compare the interconnections between land and water in tropical and temperate environments via the emergence of aquatic insects. The researchers used a technique called stable isotope analysis to trace ...
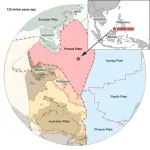
Plate tectonic surprise: Utrecht geologist unexpectedly finds remnants of a lost mega-plate
2023-10-09
Utrecht University geologist Suzanna van de Lagemaat has reconstructed a massive and previously unknown tectonic plate that was once one-quarter the size of the Pacific Ocean. Her colleagues in Utrecht had predicted its existence over 10 years ago based on fragments of old tectonic plates found deep in the Earth’s mantle. Van de Lagemaat reconstructed lost plates through field research and detailed investigations of the mountain belts of Japan, Borneo, the Philippines, New Guinea, and New Zealand. To her surprise, she found that oceanic remnants on northern Borneo must have belonged to the long-suspected plate, which scientists have named Pontus. She has now reconstructed ...
Researchers identify largest ever solar storm in ancient 14,300-year-old tree rings
2023-10-09
An international team of scientists have discovered a huge spike in radiocarbon levels 14,300 years ago by analysing ancient tree-rings found in the French Alps.
The radiocarbon spike was caused by a massive solar storm, the biggest ever identified.
A similar solar storm today would be catastrophic for modern technological society – potentially wiping out telecommunications and satellite systems, causing massive electricity grid blackouts, and costing us billions of pounds.
The academics are warning of the importance ...
Should a more individualized model replace the current method for determining which people should be screened for lung cancer?
2023-10-09
A new study found that an alternative model to identify patients with lung cancer eligible for screening was more accurate than the currently used method based on the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) criteria. The results are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths, and using low-dose computed tomography scans to screen people who are at elevated risk for lung cancer reduces lung cancer deaths. The USPSTF criteria use age and smoking history to determine ...
Is this how antidepressants work, and why they take weeks to kick-in?
2023-10-09
Type of work: peer-reviewed/randomised controlled trial/people
SSRI antidepressants normally take a few weeks before any showing mental health benefits, but how come it takes so long? Now a study from a group of clinicians and scientists provides the first human evidence that this is due to physical changes in the brain leading to greater brain plasticity developing over the first few weeks of SSRI intake. This may also begin to explain one of the mechanisms of how antidepressants work.
This work is presented at the ECNP conference in Barcelona on 9th October. This ...
Teaching expectant mothers to bond with their babies
2023-10-09
Type of work: Peer-reviewed / experimental study / people
Up to a third of mothers don’t bond well with their babies after birth, causing intense emotional distress to both mother and baby1. Now researchers have found that they can train at-risk expectant mothers to recognise and regulate emotions better, potentially reducing their risk of postpartum depression.
Presenting the work at the ECNP Congress in Barcelona, researcher Dr Anne Bjertrup said:
People generally have an automatic tendency to see the positive or negative in any situation. In previous studies we saw that certain ...
Young children who are close to their parents are more likely to grow up kind, helpful and ‘prosocial’
2023-10-09
A loving bond between parents and their children early in life significantly increases the child’s tendency to be ‘prosocial’, and act with kindness and empathy towards others, research indicates.
The University of Cambridge study used data from more than 10,000 people born between 2000 and 2002 to understand the long-term interplay between our early relationships with our parents, prosociality and mental health. It is one of the first studies to look at how these characteristics interact over a long period spanning childhood and adolescence.
The researchers ...
The hidden scars: Stigmatization a major impact of skin diseases across Europe
2023-10-09
(Lugano, Monday, 9 October 2023) A major pan-European study has revealed that almost all patients affected by skin diseases face embarrassment, with the psychological burden compounding the physical impact of living with the disease.1,2
The Burden of Skin Disease in Europe, published today in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (JEADV), analysed 19,015 individuals with a range of skin diseases and revealed the huge psychological toll of living with a disease. The diseases examined included, amongst others, fungal skin infections, acne, atopic dermatitis (eczema), alopecia, psoriasis and sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
With high levels of stigmatisation, ...
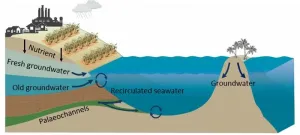
Discovery of invisible nutrient discharge on Great Barrier Reef raises concerns
2023-10-08
Scientists using natural tracers off Queensland’s coast have discovered the source of previously unquantified nitrogen and phosphorous having a profound environmental impact on the Great Barrier Reef.
The findings, published today in Environmental Science and Technology, indicate current efforts to preserve and restore the health of the Reef may require a new perspective.
Southern Cross University’s Dr Douglas Tait leads the ground-breaking study, ‘Submarine groundwater discharge exceeds river inputs as a source of nutrients to the Great Barrier Reef’.
Submarine ...
Scientists upcycle polyesters through new waste-free, scalable process
2023-10-07
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a new chemical process which upcycles polyesters, including PET in plastic bottles, to morpholine amide, a versatile and valuable building block for synthesizing a vast range of compounds. The reaction is high yield, waste-free, does not require harmful chemicals, and is easily scalable. The team successfully break the often costly closed-loop recycling loop of plastic waste, allowing upcycling to more valuable products.
Recycling plays an indispensable part of our fight against plastic waste. But at what ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Clinical trial demonstrates benefits of solriamfetol for adults with ADHDThe drug may help patients who don’t benefit from current ADHD medications