(Press-News.org) OAK BROOK, Ill. – Locally run large language models (LLMs) may be a feasible option for extracting data from text-based radiology reports while preserving patient privacy, according to a new study from the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (NIH CC) published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). LLMs are deep-learning models trained to understand and generate text in a human-like way.
Recently released LLM models such as ChatGPT and GPT-4 have garnered attention. However, they are not compatible with healthcare data due to privacy constraints.
“ChatGPT and GPT-4 are proprietary models that require the user to send data to OpenAI sources for processing, which would require de-identifying patient data,” said senior author Ronald M. Summers, M.D., Ph.D., senior investigator in the Radiology and Imaging Sciences Department at the NIH. “Removing all patient health information is labor-intensive and infeasible for large sets of reports.”
In this study, led by Pritam Mukherjee, Ph.D., staff scientist at the NIH CC, researchers tested the feasibility of using a locally run LLM, Vicuna-13B, to label key findings from chest X-ray reports from the NIH and the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care (MIMIC) Database, a publicly available dataset of de-identified electronic health records.
“Preliminary evaluation has shown that Vicuna, a free publicly available LLM, approaches the performance of ChatGPT in tasks such as multi-lingual question answering,” Dr. Summers said.
The study dataset included 3,269 chest X-ray reports obtained from MIMIC and 25,596 reports from the NIH.
Using two prompts for two tasks, the researchers asked the LLM to identify and label the presence or absence of 13 specific findings on the chest X-ray reports. Researchers compared the LLM’s performance with two widely used non-LLM labeling tools.
A statistical analysis of the LLM output showed moderate to substantial agreement with the non-LLM computer programs.
“Our study demonstrated that the LLM’s performance was comparable to the current reference standard,” Dr. Summers said. “With the right prompt and the right task, we were able to achieve agreement with currently used labeling tools.”
Dr. Summers said LLMs that can be run locally will be useful in creating large data sets for AI research without compromising patient privacy.
“LLMs have turned the whole paradigm of natural language processing on its head,” he said. “They have the potential to do things that we've had difficulty doing with traditional pre-large language models.”
Dr. Summers said LLM tools could be used to extract important information from other text-based radiology reports and medical records, and as a tool for identifying disease biomarkers.
“My lab has been focusing on extracting features from diagnostic images,” he said. “With tools like Vicuna, we can extract features from the text and combine them with features from images for input into sophisticated AI models that may be able to answer clinical questions.
“LLMs that are free, privacy-preserving, and available for local use are game changers,” he said. “They're really allowing us to do things that we weren't able to do before.”
###
“Feasibility of Using the Privacy-preserving Large Language Model Vicuna for Labeling Radiology Reports.” Collaborating with Drs. Summers and Mukherjee were Benjamin Hou, Ph.D., and Ricardo B. Lanfredi, Ph.D.
In 2023, Radiology is celebrating its 100th anniversary with 12 centennial issues, highlighting Radiology’s legacy of publishing exceptional and practical science to improve patient care.
Radiology is edited by Linda Moy, M.D., New York University, New York, N.Y., and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (https://pubs.rsna.org/journal/radiology)
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on chest X-rays, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
END
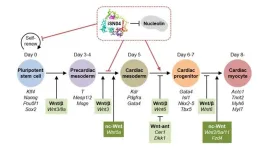
Generating specific cell lineages from induced pluripotent stem cells and embryonic stem cells is the holy grail of regenerative medicine. Guiding iPSCs toward a target cell line has garnered much attention, but the process remains challenging. Now, researchers from Japan have discovered that an anti-nucleolin DNA aptamer, iSN04, can determine a cell’s lineage during differentiation. By demonstrating the generation of cardiomyocytes from murine pluripotent stem cells, their concept shows promise as a regenerative therapy.
Self-renewal ...
Emissions associated with mining operations in Africa’s Copperbelt can be quantified from space, according to new research led by the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR).
Mining for copper and cobalt in Africa has rapidly increased, the latter in response to growing global demand for electric vehicles, laptops, smartphones, and other devices that rely on lithium-ion batteries, the vast majority of which contain cobalt.
The new study is published in Geophysical Research Letters, ...
INDIANAPOLIS – Knowing which populations are following cancer screening guidelines is important to public health officials and policy makers as well as researchers developing strategies to improve adherence. A recent study is one of the first to compare using health information exchange (HIE) data with patient self-reported data as a means of gathering this intelligence.
The researchers found that completeness of information differed by data source and screening test. HIE data provided more information than patient self-reports about ...
Every day we store memories, some of which we are able to recall later. But while we do so, do we keep on storing? Yes! We cannot afford to stop memory formation while we are retrieving prior ones. Imagine, for instance, that you are navigating the city while recalling last night’s events to a friend tagging along. Your brain must memorize aspects of the route even while you are in the story, so that you can find your way back later or reach your next destination.
We seem to perform this task without much conscious effort. Big deal, one could say, as we know that the brain has trillions of synaptic connections, so parallel processing ...
The design concept of a disaster alert balloon, capable of changing its color like a chameleon, has been honored for its design excellence at the internationally renowned International Design Excellence Award (IDEA) 2023.
The awarded concept, named SAFEUP, serves as a hazard indicator, providing visual information about the condition of accident sites from a safe distance. Developed by Professor Chajoong Kim and his team in the Department of Design at UNIST, SAFEUP has received the ‘IDEA 2023’ Bronze Award in the category of Concepts & Speculative Design. The ...
A group of ribosomal protein genes connect animal models of depression to human patients with major depressive disorder. In order to research depression treatments, scientists use a mouse model, inducing a state with similarities to depression though exposure to variable, unpredictable, and uncontrolled stressors over days or weeks. But is this state molecularly akin to what humans with major depressive disorder experience? To find out, Xiaolu Zhang, Mahmoud Ali Eladawi, and colleagues examine transcriptomics data from postmortem human brain tissue and from several mouse models of stress, seeking to pinpoint conserved ...
Positron, the antiparticle of electron, has the same mass and charge as that of an electron but with the sign flipped for the charge. It is an attractive particle for scientists because the use of positrons has led to important insights and developments in the fields of elementary particle physics, atomic physics, materials science, astrophysics, and medicine. For instance, positrons are known to be components of antimatter. They are also powerful in detecting lattice defects in solids and semiconductors and in structural analysis of the topmost surface of crystals. Positronic compounds, namely ...
First study to determine the role pre-pregnancy obesity plays in future poor heart health
Those with overweight or obese BMI in early pregnancy had a higher risk of developing hypertensive disorders of pregnancy
‘If pre-pregnancy obesity is the culprit or cause of risk, we should be targeting this with interventions’
Pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia and gestational diabetes have recently been associated with a higher risk of developing heart disease later in life. But a new Northwestern Medicine study has found obesity before or during ...
Having obesity before and during early pregnancy appears to be a strong indicator of risk for developing future cardiovascular disease and was significantly linked with adverse outcomes during pregnancy such as high blood pressure, preeclampsia, and gestational diabetes, according to a study published in Circulation Research that was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Researchers have known obesity is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease and pregnancy complications related to blood pressure. However, they did not know which factors – obesity or the pregnancy complications – played larger roles in influencing a person’s ...
Increased demand for water due to global population growth, coupled with the increasing frequency of extreme weather events, endangers our water security. Nonetheless, little is known about the relationship of water use by sectors and the occurrence of drought-heatwave events, particularly at the large scale. To unveil this issue, a group of researchers from the Department of Physical Geography from Utrecht University evaluated the responses of sectoral water use during droughts, heatwaves and compound (combined) events at a global scale. The study published in Environmental Research Letters shows that stronger sectoral water use responses are found for heatwaves compared to ...