(Press-News.org) This summer, the planet is suffering from unprecedented heat waves and heavy rainfalls. Developing renewable energy and expanding associated infrastructure has become an essential survival strategy to ensure the sustainability of the planet in crisis, but it has obvious limitations due to the volatility of electricity production, which relies on uncertain variables like labile weather conditions. For this reason, the demand for energy storage systems (ESS) that can store and supply electricity as needed is ever-increasing, but lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) currently employed in ESS are not only highly expensive, but also prone to potential fire, so there is an urgent need to develop cheaper and safer alternatives.
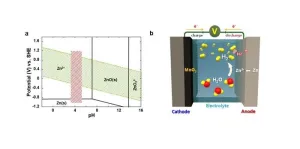
A research team led by Dr. Oh, Si Hyoung of the Energy Storage Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) has developed a highly safe aqueous rechargeable battery that can offer a timely substitute that meets the cost and safety needs. Despite of lower energy density achievable, aqueous rechargeable batteries have a significant economic advantage as the cost of raw materials is much lower than LIBs. However, inveterate hydrogen gas generated from parasitic water decomposition causes a gradual rise in internal pressure and eventual depletion of the electrolyte, which poses a sizeable threat on the battery safety, making commercialization difficult.
Until now, researchers have often tried to evade this issue by installing a surface protection layer that minimizes the contact area between the metal anode and the electrolyte. However, the corrosion of the metal anode and accompanying decomposition of water in the electrolyte is inevitable in most cases, and incessant accumulation of hydrogen gas can cause a potential detonation in long-term operation.
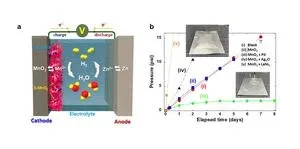
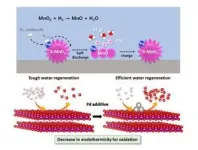
To cope with this critical issue, the research team has developed a composite catalyst consisting of manganese dioxide and palladium, which is capable of automatically converting hydrogen gas generated inside the cell into water, ensuring both the performance and safety of the cell. Manganese dioxide does not react with hydrogen gas under normal circumstances, but when a small amount of palladium is added, hydrogen is readily absorbed by the catalysts, being regenerated into water. In the prototype cell loaded with the newly developed catalysts, the internal pressure of the cell was maintained well below the safety limit, and no electrolyte depletion was observed.
The results of this research effectively solves one of the most concerning safety issues in the aqueous batteries, making a major stride towards commercial application to ESS in the future. Replacing LIBs by cheaper and safer aqueous batteries can even trigger a rapid growth of global market for ESS.
"This technology pertains to a customized safety strategy for aqueous rechargeable batteries, based on the built-in active safety mechanism, through which risk factors are automatically controlled." said Dr. Oh, Si Hyoung of KIST. "Moreover, it can be applied to various industrial facilities where hydrogen gas leakage is one of major safety concerns (for instance, hydrogen gas station, nuclear power plant etc) to protect public safety."
###
KIST was established in 1966 as the first government-funded research institute in Korea. KIST now strives to solve national and social challenges and secure growth engines through leading and innovative research. For more information, please visit KIST’s website at https://eng.kist.re.kr/
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Lee Jong-ho) through the Nano Future Material Source Technology Development Project and the Mid-Career Researcher Support Project, and the results were published on August 1 in the international journal Energy Storage Materials (IF 20.4).
END
A cheaper, safer alternative to lithium-ion batteries: Aqueous rechargeable batteries
Automatic conversion of hydrogen gas into water makes batteries safer. A breakthrough technology for the commercialization of cheaper, safer aqueous rechargeable batteries.
2023-10-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Most accurate test to date developed to measure biological aging
2023-10-13
A team of European researchers has developed a new test that can accurately measure biological aging in a clinical setting. The discovery was made while studying patients for the aging effects of chronic kidney disease.
The new test is an epigenetic clock – a type of biochemical assessment that looks at DNA to understand how well the body is aging in contrast to its chronological age – and is the first of these cutting-edge tests to be proven to perform accurately in a clinical setting, in ...
International experts push for innovation to improve stroke recovery
2023-10-13
Scientists from The Florey are among the world’s leading stroke experts who have mapped out how researchers and clinicians can improve outcomes for people who have survived a stroke.
The third Stroke Recovery and Rehabilitation Roundtable, an initiative of the International Stroke Recovery and Rehabilitation Alliance, has made a series of key recommendations about managing fatigue, measuring mobility, harnessing non-invasive brain stimulation technologies and improving how trials are designed. The highly influential gathering of world stroke experts published their findings in a special ...
Using closed-loop in type 1 pregnancy associated with type 1 diabetes
2023-10-13
A new study endorses closed-loop use in type 1 diabetes pregnancy and highlights how the technology can facilitate positive pregnancy experiences. The study is published in the peer-reviewed journal Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics (DTT). Click here to read the article now.
Julia Lawton, from the University of Edinburgh, and coauthors, on behalf of the AiDAPT Collaborative Group, interviewed closed-loop participants in the Automated insulin Delivery Amongst Pregnant women with T1D (AiDAPT) trial. “Women described how closed-loop lessened the physical and mental demands ...
A step towards understanding early interventions for Huntington’s Disease
2023-10-13
Huntington’s Disease is the most common neurodegenerative disorder controlled by a single gene and is characterized by motor and cognitive deficits and psychiatric symptoms. Currently, no treatments can stop or reverse the disease, but new research from Boston Children’s Hospital suggests that there might be a way to protect the brain and prevent or slow cognitive decline.
Research from the lab of Beth Stevens, PhD suggests that parts of the immune system – complement proteins and microglia – mediate the loss of specific synapses connecting the brain’s cortex and striatum. The findings, recently published in Nature Medicine, could ...
Landmark publication calls for increased attention to workplace mental health
2023-10-13
A landmark scientific article on the workplace as a major determinant of health is published today (Thursday, 12 October) in The Lancet, and reveals a global picture of the work-related causes of mental health conditions.
Carried by University College Cork (UCC) researchers for the Lancet Series on work and health, the paper illustrates that major progress in population health can be made by an increased focus on improving people’s work environments.
The paper, ‘Work-related causes of mental health conditions and interventions for their improvement in workplaces’, ...
DNA methylation: The hidden mechanism enabling plants to adapt in a warmer world
2023-10-13
As global warming continues to redefine ecosystems, plants are increasingly tasked with swift adaptation to ensure their survival. One primary mechanism facilitating such rapid adaptation is epigenetic memory, specifically DNA methylation. DNA methylation, a form of epigenetic modification, involves the addition of a methyl group to the cytosine bases of the DNA, altering its accessibility in chromatin and modulating gene expression. In the context of a warming climate, changes in DNA methylation can be triggered by environmental factors like increased temperature. Such epigenetic adaptations ...
Unlocking the secrets of cold tolerance: a deep dive into tomato plants' molecular responses to chilling stress
2023-10-13
Cold sensitivity poses a significant challenge for certain essential crops. While there's an indication that these plants may possess cold acclimation capabilities, the molecular dynamics, particularly involving the CRT binding factor (CBF) family, are not fully explored. One primary concern has been the disparity in cold tolerance between temperate plants and tropical species such as the tomato. Additionally, the accumulation of small metabolites, termed cryoprotectants, plays a crucial role in enabling plants to resist damage from low temperatures. Adding ...
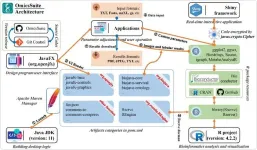
OmicsSuite: A customized and pipelined suite for analysis and visualization of multi-omics big data
2023-10-13
Abstract:
With the advancements in high-throughput sequencing technologies such as Illumina, PacBio, and 10X Genomics platforms, and gas/liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, large volumes of biological data in multiple formats can now be obtained through multi-omics analysis. Bioinformatics is constantly evolving and seeking breakthroughs to solve multi-omics problems, however it is challenging for most experimental biologists to analyze data using command-line interfaces, coding, and scripting. Based on experience with multi-omics, we have developed OmicsSuite, a desktop suite that comprehensively integrates statistics and multi-omics analysis and visualization. The suite ...
Stress wrecks male big brown bat fertility during breeding season
2023-10-13
Even on a good day the environment can be wildly unpredictable, from unexpected gusts of wind to food scarcity, and as humans continue to edge out the natural world, the stress on wild populations is increasing. ‘Bats are critical for the maintenance and stability of many terrestrial ecosystems’, say Mattina Alonge [University of California, Berkeley (UCB), USA] and Lucas Greville (McMaster University, Canada) and the animals are known to be particularly sensitive when under strain. But little was known about the impact that stress might have on their ability to reproduce. Concerned about the effect of stress on already vulnerable bat populations, Alonge and her colleagues ...
Almost half of patients with skin disease suffer from sleep disturbances, global study finds
2023-10-13
(Friday, 13 October 2023, Berlin, Germany) Almost half (42%) of patients with skin disease experience sleep disturbances, a major study presented today at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) Congress 2023 has revealed.1
The ALL PROJECT, a comprehensive international research initiative, analysed over 50,000 adults across 20 countries to assess the impact of skin diseases.2
Notably, these sleep disturbances were found to have broader implications on patients' quality of life. Nearly half (49%) of patients with skin disease reported reduced productivity at work, in contrast with just one in five (19%) participants without a skin disease.1
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
[Press-News.org] A cheaper, safer alternative to lithium-ion batteries: Aqueous rechargeable batteriesAutomatic conversion of hydrogen gas into water makes batteries safer. A breakthrough technology for the commercialization of cheaper, safer aqueous rechargeable batteries.