(Press-News.org) Clinicians who show more empathy promote better psychological health among breast cancer patients, according to a Rutgers study examining how oncology doctors facilitate psychological well-being.
“Our findings suggest that provider communication is a key component to reducing uncertainty, and thus providers play a key role in helping to facilitate psychological well-being,” said Liesl Broadbridge, a doctoral degree candidate at the Rutgers School of Communication and Information (SC&I) and the lead author of the study published in Patient Education and Counseling.
Researcher findings suggest that discussing uncertainties with patients and being empathetic to their concerns is critical to their healing and recovery.
“Our findings are directly applicable as targets for communication training modules for health care providers, because by continuing to advance skills in empathic communication, clinicians can enhance the health care experiences of their patients,” Broadbridge said.
In addition to Broadbridge, the authors of the study include SC&I Professor of Communication Kathryn Greene; SC&I Associate Professor of Communication Maria Venetis; SC&I doctoral degree student Lauren Lee; SC&I alumna Smita C. Banerjee, an associate attending behavioral scientist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center; Biren Saraiya, an associate professor of medicine at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School (RWJMS) and medical oncologist at Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey; and Katie A. Devine, an associate professor of pediatrics at RWJMS and chief of pediatric population science, outcomes, and disparities research at Rutgers Cancer Institute.
According to research, patients with breast cancer are at significant risk for developing symptoms of anxiety and depression related to their cancer diagnosis.
“As health communication researchers, we are interested in how health care providers can communicate in ways that help their patients cope with/manage their illness and support their psychological health,” said Broadbridge.
The research team also investigated how the process of managing psychological well-being differs depending on whether the patients they surveyed were currently undergoing cancer treatment or had already completed their treatments.
She said current and former patients experience different appointment types (i.e., treatment decision-making for current patients, watchful waiting for former patients). Therefore, they have had different lengths of time to adjust to diagnoses and, potentially, have different relationships with their providers (i.e., more or less time to develop a relationship with the health care team).
“Although our findings were true for both current and former patients, the strength of the relationship between uncertainty and psychological adjustment was stronger for former patients than for current patients,” Broadbridge said. “This means that cancer care teams must continue to focus on uncertainty and issues regarding psychological health in cancer monitoring appointments and beyond the initial diagnosis/treatment phases of breast cancer survivorship.”
The researchers used online surveys to assess current and former breast cancer patients’ perceptions of their oncologists’ communication, the uncertainty they have about their diagnosis/treatment and how they are coping with the illness.
They recruited 121 current and 187 former breast cancer patients to participate in the study through the Love Research Army, a research registry hosted by the Dr. Susan Love Foundation for Breast Cancer Research, a national advocacy organization for breast cancer patients, survivors, and at-risk family members.
The authors partnered with this community organization to broaden the sample of participants beyond the local New Brunswick area and to contribute to the larger conversations about cancer communication. The team also partnered with Rutgers Cancer Institute, with three of the study members (Broadbridge, Greene and Devine) receiving $4,800 to complete the project through a Cancer Survivorship and Outcomes Center Award.
“The findings of this study highlight the importance of both eliciting and addressing breast cancer patients’ uncertainty throughout the cancer trajectory to facilitate psychological adjustment,” Broadbridge said. “This is important because it underscores the role that clinicians play in helping patients manage both their physical and emotional/psychological health after breast cancer diagnosis.”
END
Empathetic cancer clinicians promote psychological well-being in breast cancer patients
Supportive communication is key to reducing uncertainty cancer patients feel about diagnosis and treatment, Rutgers researchers find
2023-10-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MSU leads $2M NSF project to create carbon-negative construction materials
2023-10-16
Images
Highlights:
Researchers at Michigan State University and Purdue University were awarded $2 million by the National Science Foundation to develop new “living materials” for construction that can repair themselves and sequester carbon dioxide.
The materials will be sourced from sustainable biomass, including agricultural waste, and imbued with microbes that absorb carbon dioxide and synthesize polymers and minerals to bolster the materials’ strength.
Unlike ...
U of I researchers develop organic nanozymes suitable for agricultural use
2023-10-16
URBANA, Ill. – Nanozymes are synthetic materials that mimic the properties of natural enzymes for applications in biomedicine and chemical engineering. They are generally considered too toxic and expensive for use in agriculture and food science. Now, researchers from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed a nanozyme that is organic, non-toxic, environmentally friendly, and cost effective. In a newly published paper, they describe its features and its capacity to detect the presence of glyphosate, a common agricultural herbicide. Their goal is to eventually create a user-friendly ...
Women at much higher risk of depression after traumatic brain injury, analysis finds
2023-10-16
SAN FRANCISCO — Women are nearly 50% more likely than men to develop depression after suffering a concussion or other traumatic brain injury (TBI), according to an analysis of nine studies and nearly 700,000 people presented at the ANESTHESIOLOGY® 2023 annual meeting.
“Most studies showing the link between TBI and depression have focused on men,” said Isaac G. Freedman, M.D., MPH, lead author of the study and an anesthesiology resident at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston. ...
Argonne to receive new funding to develop quantum networks
2023-10-16
Quantum networks hold enormous potential for groundbreaking advances in many areas of science and technology. Once this technology matures, it is expected to be an essential component of quantum computing. It could have the equivalent impact as the internet has had on digital communication.
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has announced that three collaborative projects in quantum networking will receive $24 million for up to three years. The DOE’s Argonne National Laboratory will ...
Hillman grant for Penn Nursing professor to study virtual reality & loneliness
2023-10-16
PHILADELPHIA (October 16, 2023) – Penn Nursing, with partners from the Annenberg Virtual Reality ColLABorative and New York University’s Rory Meyers College of Nursing, have been awarded 2023 grant from the Hillman Emergent Innovation: Serious Illness and End of Life program to study the use of social virtual reality (VR) in enhancing the treatment experience and reducing loneliness in people undergoing hemodialysis. This grant is awarded by The Rita and Alex Hillman Foundation.
Hemodialysis is a life-saving treatment for people experiencing ...
High-performance ICUs reduce mortality rates during pandemics and other health crises
2023-10-16
A new study published by CHEST Science Journal shows that high-performance intensive care units (ICUs) might also have better patient outcomes during health crises. The study used as a benchmark the mortality rate observed in Brazilian ICUs before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, and analyzed data from over 380,000 patients of private hospital ICUs across 10 Brazilian states. The research was coordinated by the D'Or Institute for Research and Education (IDOR) and concluded that the mortality rate during the pandemic was significantly reduced in ICUs that exhibited high efficiency before the pandemic.
The COVID-19 ...
Information about abortion care largely omitted or buried on 80% of health systems’ patient-facing websites
2023-10-16
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 16 October 2023
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. Information ...
Andrea Califano receives Alfred G. Knudson award from NCI
2023-10-16
Andrea Califano, Dr, has been honored with the 26th Alfred G. Knudson Award in Cancer Genetics by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) for his exceptional contributions to the field of cancer research. Califano, a pioneer in the field of cancer genetics, is the Clyde and Helen Wu Professor of Chemical and Systems Biology at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons and a member of the Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center.
The award is named in honor of geneticist and cancer researcher Alfred G. Knudson, MD, a 1947 graduate of the Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, who helped uncover several major genetic mysteries behind ...
Learning more about how cancer affects stroke risk
2023-10-16
Patients with a previous or current cancer diagnosis are more likely to have a stroke than the general population, but how are specific cancers and treatments associated with stroke risk?
A collaborative team led by University of Cincinnati, University of North Carolina (UNC) and Duke University researchers is seeking to answer that question.
Soma Sengupta, MD, PhD, now division chief of neuro-oncology at UNC, had the idea to study the prevalence of stroke in patients with different cancer types while a faculty member at UC. She recruited a team that included stroke experts Stacie Demel, DO, PhD, of UC and Wuwei Feng of Duke to put together a retrospective pilot study.
“This ...
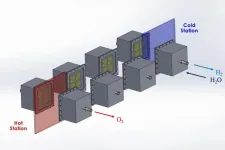
MIT design would harness 40% of the sun’s heat to produce clean hydrogen fuel
2023-10-16
MIT engineers aim to produce totally green, carbon-free hydrogen fuel with a new, train-like system of reactors that is driven solely by the sun.
In a study appearing today in Solar Energy Journal, the engineers lay out the conceptual design for a system that can efficiently produce “solar thermochemical hydrogen.” The system harnesses the sun’s heat to directly split water and generate hydrogen — a clean fuel that can power long-distance trucks, ships, and planes, while in the process emitting no greenhouse gas emissions.
Today, hydrogen is largely produced through processes that involve natural gas and other fossil fuels, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Urine tests confirm alcohol consumption in wild African chimpanzees
Barshop Institute to receive up to $38 million from ARPA-H, anchoring UT San Antonio as a national leader in aging and healthy longevity science
Anion-cation synergistic additives solve the "performance triangle" problem in zinc-iodine batteries
Ancient diets reveal surprising survival strategies in prehistoric Poland
Pre-pregnancy parental overweight/obesity linked to next generation’s heightened fatty liver disease risk
Obstructive sleep apnoea may cost UK + US economies billions in lost productivity
Guidelines set new playbook for pediatric clinical trial reporting
Adolescent cannabis use may follow the same pattern as alcohol use
Lifespan-extending treatments increase variation in age at time of death
From ancient myths to ‘Indo-manga’: Artists in the Global South are reframing the comic
Putting some ‘muscle’ into material design
House fires release harmful compounds into the air
Novel structural insights into Phytophthora effectors challenge long-held assumptions in plant pathology
Q&A: Researchers discuss potential solutions for the feedback loop affecting scientific publishing
A new ecological model highlights how fluctuating environments push microbes to work together
Chapman University researcher warns of structural risks at Grand Renaissance Dam putting property and lives in danger
Courtship is complicated, even in fruit flies
Columbia announces ARPA-H contract to advance science of healthy aging
New NYUAD study reveals hidden stress facing coral reef fish in the Arabian Gulf
36 months later: Distance learning in the wake of COVID-19
Blaming beavers for flood damage is bad policy and bad science, Concordia research shows
The new ‘forever’ contaminant? SFU study raises alarm on marine fiberglass pollution
Shorter early-life telomere length as a predictor of survival
Why do female caribou have antlers?
How studying yeast in the gut could lead to new, better drugs
Chemists thought phosphorus had shown all its cards. It surprised them with a new move
A feedback loop of rising submissions and overburdened peer reviewers threatens the peer review system of the scientific literature
Rediscovered music may never sound the same twice, according to new Surrey study
Ochsner Baton Rouge expands specialty physicians and providers at area clinics and O’Neal hospital
New strategies aim at HIV’s last strongholds
[Press-News.org] Empathetic cancer clinicians promote psychological well-being in breast cancer patientsSupportive communication is key to reducing uncertainty cancer patients feel about diagnosis and treatment, Rutgers researchers find