(Press-News.org) SAN ANTONIO - October 17, 2023 — Southwest Research Institute has developed a unique technology (US20230242487A1) that enables the safe and efficient synthesis of organophosphorus nerve agent (OPNA) oxime antidotes. Using this technology, SwRI scientists can not only successfully synthesize currently known highly effective nerve agent countermeasures, but also effectively develop promising new drug candidates to treat nerve agent exposure.
Current treatments for OPNA exposure have not changed significantly since the 1950s. OPNAs are odorless and colorless chemicals that are used in both pesticides as well as in chemical weapons. OPNAs affect the central nervous system by interrupting the signals between nerve cells, which can cause nausea, vomiting, and abdominal cramps upon moderate exposure and finally arrhythmias, loss of consciousness and death upon severe exposure if not properly treated. An estimated 300,000 deaths per year are caused by OPNA exposure, making this issue a significant threat to both military and civilian populations worldwide.
“Overcoming the difficulties with synthesizing medical countermeasures is a longstanding challenge that SwRI has been actively addressing since the early 1990s. We recently had a breakthrough, developing an innovative manufacturing process that enabled us to develop two highly sought-after antidotes,” said SwRI’s Dr. Shawn Blumberg, a lead scientist in SwRI’s Pharmaceutical and Bioengineering Department. “Using this new methodology, we synthesized Hlö-7 and HI-6, which have strong potential to successfully treat OPNA exposure.”
The traditional development process for these complex compounds is challenging, requiring the use of an OSHA-regulated carcinogenic compound as well as limited ways to purify the resulting compounds. SwRI’s method circumvents the need for dangerous ingredients and integrates new methods for purification of the antidotes.
SwRI is one of more than 300 industry, government and nonprofit organizations supporting the medical countermeasures sector in the Medical CBRN Defense Consortium (MCDC). This sector was founded to support U.S. Department of Defense needs in areas of infectious diseases, chemical threats, and other medical countermeasures for military personnel.
SwRI’s Chemistry and Chemical Engineering Division is ISO 9001:2015 certified, meeting international quality standards for product development from initial design through production and service. SwRI scientists support drug development from discovery to clinical trials in FDA-inspected Current Good Manufacturing Practice facilities.
For more information, visit https://pharmdev.swri.org/.
END
SwRI develops novel solution to advance synthesis for nerve agent antidotes
Innovative chemical method addresses critical steps to safely synthesize, develop promising medical countermeasures
2023-10-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The Foundation for Angelman Syndrome Therapeutics to advance gene therapy candidate through IND-enabling studies conducted in partnership with the University of Pennsylvania
2023-10-17
October 17, 2023—The Foundation for Angelman Syndrome Therapeutics (FAST) announced today that the non-profit organization has entered into an exclusive global collaborative research and development agreement with the University of Pennsylvania to develop an investigational adeno-associated virus (AAV) gene therapy for Angelman syndrome (AS).
Angelman syndrome is a nondegenerative neurogenetic disorder that is estimated to impact approximately 1 in 15,000 births, or potentially 500,000 individuals world-wide, ...
Harnessing molecular power: electricity generation on the nanoscale
2023-10-17
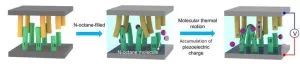
WASHINGTON, Oct. 17, 2023 – Wave energy technology is a proven source of power generation, but there is power inherent in every molecule of liquid on earth, even when the liquid is at rest. At the molecular scale, atoms and ions are always moving. If this nanoscale movement can be harvested, it could be a big source of energy.
“There are vast amounts of air and liquid on the earth, and their successful harvesting could produce a gigantic amount of energy for society,” author Yucheng Luan said.
In an article published this week in APL Materials, by AIP Publishing, Luan and his collaborators tested a molecular energy harvesting device that captures ...
Study reveals our European ancestors ate seaweed and freshwater plants
2023-10-17
For many people seaweed holds a reputation as a superfood, heralded for its health benefits and sustainability, but it appears our European ancestors were ahead of the game and were consuming the nutrient-rich plant for thousands of years.
Researchers say they have found “definitive” archaeological evidence that seaweeds and other local freshwater plants were eaten in the mesolithic, through the Neolithic transition to farming and into the Early Middle Ages, suggesting that these resources, now rarely eaten in Europe, only ...
Effects of the million hearts model on heart attacks, strokes, and Medicare spending
2023-10-17
About The Study: The Million Hearts Model, which encouraged and paid health care organizations to assess and reduce cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk, reduced first-time heart attacks and strokes. The results support guidelines to use risk scores for CVD primary prevention.
Authors: Laura Blue, Ph.D., of Mathematica in Washington, D.C., is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.19597)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional ...
Climate network analysis helps pinpoint regions at higher risk of extreme weather
2023-10-17
WASHINGTON, Oct. 17, 2023 – Climate change and the rapid increase in frequency of extreme weather events around the globe – such as wildfires and floods – reinforces the reality that these events are not only not random but, rather, interconnected. Interlinked climate behavior, or teleconnections, isn’t a well understood field but will be necessary to fully comprehend how our climate system works.
In Chaos, from AIP Publishing, a team of researchers affiliated with Beijing Normal University and Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications in China and the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research in Germany describes a climate network analysis method to explore ...
Race and ethnicity and prehospital use of opioid or ketamine analgesia in acute traumatic injury
2023-10-17
About The Study: The results of this study of over 4.7 million patient encounters across the U.S. during a 3-year period suggest that patients from racial and ethnic minority groups with acute traumatic injuries do not have their pain treated equitably in the prehospital setting.
Authors: Eli Carrillo, M.D., of the Stanford University School of Medicine in Stanford, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.38070)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional ...
Adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and the risk of dementia
2023-10-17
About The Study: In this study of 109,000 individuals born between 1933 and 1952 and followed up in old age, adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) was associated with an increased risk of dementia. Policy makers, caregivers, patients, and clinicians may wish to monitor reliably for ADHD in old age.
Authors: Stephen Z. Levine, Ph.D., of the University of Haifa in Haifa, Israel, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.38088)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
AI models identify biodiversity from animal sounds in tropical rainforests
2023-10-17
Tropical forests are among the most important habitats on our planet. They are characterised by extremely high species diversity and play an eminent role in the global carbon cycle and the world climate. However, many tropical forest areas have been deforested and overexploitation continues day by day.
Reforested areas in the tropics are therefore becoming increasingly important for the climate and biodiversity. How well biodiversity develops on such areas can be monitored very well with an automated analysis of animal sounds. This was reported by researchers in the journal Nature Communications.
Recordings on Former Cocoa Plantations and Pastures
As part of the DFG research group ...
Recognizing clinical signs of hyperthyroidism leads to appropriate treatments, reduces adverse impact on health
2023-10-17
(Boston)—Untreated hyperthyroidism, conditions where there is excess thyroid hormone present, can adversely affect health, leading to increased risks for abnormal heart rhythms, heart failure, osteoporosis, adverse pregnancy outcomes, metabolic abnormalities and increased mortality risk. Hyperthyroidism can occur due to several different etiologies, including Graves’ disease, toxic (overactive) thyroid nodules, and thyroiditis. It is important to recognize, correctly diagnose, and appropriately treat the underlying cause of hyperthyroidism to minimize its impacts on health.
In a new review article in the Journal ...
Adults with ADHD are at increased risk for developing dementia
2023-10-17
Adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are nearly three times more likely to develop dementia than adults without ADHD, according to a Rutgers study.
The study, coauthored by Michal Schnaider Beeri, director of the Herbert and Jacqueline Krieger Klein Alzheimer’s Research Center at Rutgers Brain Health Institute (BHI) was published in JAMA Network Open. It followed more than 100,000 older adults in Israel over 17 years to examine if adults with ADHD are at increased risk for dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease.
Although more than 3 percent of the adult population in the United States has ADHD, there is limited research ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
Jumping ‘DNA parasites’ linked to early stages of tumour formation
Ultra-sensitive CAR T cells provide potential strategy to treat solid tumors
Early Neanderthal-Human interbreeding was strongly sex biased
North American bird declines are widespread and accelerating in agricultural hotspots
Researchers recommend strategies for improved genetic privacy legislation
How birds achieve sweet success
More sensitive cell therapy may be a HIT against solid cancers
Scientists map how aging reshapes cells across the entire mammalian body
[Press-News.org] SwRI develops novel solution to advance synthesis for nerve agent antidotesInnovative chemical method addresses critical steps to safely synthesize, develop promising medical countermeasures