(Press-News.org) More than 150 species of wild animals across every continent are contaminated with flame retardant chemicals, according to a new map tracking peer-reviewed research worldwide. Polluted wildlife include killer whales, red pandas, chimpanzees and other endangered species. Added to furniture, electronics, vehicles, and other everyday products to meet flammability standards, the chemicals often do not work as intended. They also migrate out of products and into wildlife—and people.
“Flame retardants don’t actually make TV enclosures and car interiors more fire-safe, but they can harm people and animals,” said project lead Lydia Jahl, a scientist at the Green Science Policy Institute. “Though these product flammability standards may seem protective at first glance, many cause widespread and lasting harm for no real benefit.”
Flame retardants found in wildlife include both older phased-out chemicals like polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) as well as newer replacements chemicals like chlorinated paraffins and organophosphate flame retardants. Though known to cause liver, thyroid, and kidney cancers in laboratory animals, chlorinated paraffins are still commonly used in consumer products, with more than one million tons produced annually. Similarly, use of organophosphate flame retardants is proliferating, though even low levels may harm IQ, attention, and memory in children.
Flame retardants accumulate up the marine and terrestrial food chains with the highest levels in marine mammals and birds of prey. For example, PCB levels in killer whales have been linked to lower calf survival rates and weaker immune systems. Orca pods in Greenland, the Strait of Gibraltar, and Hawaii have been ravaged by accumulating flame retardants. Indeed, scientists calculate that PCB contamination could wipe out half the world’s killer whale populations over the next century. That’s despite the fact that PCBs have been banned since the 1970s.
“Killer whales shouldn’t have to swim in a sea of flame retardants. The science is clear that these chemicals harm their development—as well as that of our children,” said Arlene Blum, executive director of the Green Science Policy Institute. “We need to update ineffective flammability standards to stop these toxics from entering the environment, wild animals, and us.”
Sentinels for the harms of increasing use of chlorinated paraffins in products include black-spotted frogs living near electronic-waste facilities in China. These chemicals are linked to shrinking livers in the frogs and they can also be transferred to their eggs.
Flame retardants are also found in species living in areas far from their production, use, and disposal, showing their potential for long-range transport. For example, high levels of flame retardants have been detected in chimpanzees in a protected Ugandan National Park.
“This map illustrates the global consequences of repeatedly replacing harmful flame retardants with others that turn out to be similarly harmful,” Jahl said. “Instead of this endless cycle of regrettable substitutions, we need to evaluate whether many of the flammability standards that drive the use of flame retardants are even helpful. Some standards—such as California’s old furniture standard—have already been proven ineffective and revised. Many more wouldn’t stand up to scrutiny either, and they are wreaking havoc on wildlife and people alike.”
END
Map: Wildlife polluted by flame retardants on massive scale
Belugas to butterflies plagued by harmful (and often ineffective) chemicals
2023-10-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New insights into the genetics of the common octopus: genome at the chromosome level decoded
2023-10-18
Octopuses are fascinating animals – and serve as important model organisms in neuroscience, cognition research and developmental biology. To gain a deeper understanding of their biology and evolutionary history, validated data on the composition of their genome is needed, which has been lacking until now. Scientists from the University of Vienna together with an international research team have now been able to close this gap and, in a study, determined impressive figures: 2.8 billion base pairs - organized in ...
Researchers unveil fire-inhibiting nonflammable gel polymer electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries
2023-10-18
A collaborative research team, led by Professor Hyun-Kon Song in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST, Dr. Seo-Hyun Jung from Research Center for Advanced Specialty Chemicals at Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT), and Dr. Tae-Hee Kim from the Ulsan Advanced Energy Technology R&D Center at Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER), has achieved a groundbreaking milestone in battery technology. Their remarkable achievement in developing a non-flammable gel polymer electrolyte (GPE) is set to revolutionize the safety of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) by ...
Test of police implicit bias training shows modest improvements
2023-10-18
SPOKANE, Wash. – A two-part training designed to help police officers recognize their implicit bias, revealed some behavior improvement and lowered citizen discrimination complaints in a controlled study. While a small study involving one police department, it is the first-known research to provide evidence that this type of training can produce positive behavioral effects.
Led by Washington State University researcher Lois James, the study found some improvement in the anti-bias trained officers’ behavior toward homeless people in particular, ...
Wearable device makes memories and powers up with the flex of a finger
2023-10-18
Researchers have invented an experimental wearable device that generates power from a user’s bending finger and can create and store memories, in a promising step towards health monitoring and other technologies.
The innovation features a single nanomaterial incorporated into a stretchable casing fitted to a person’s finger. The nanomaterial enabled the device to generate power with the user bending their finger.
The super-thin material also allows the device to perform memory tasks, as outlined below.
Multifunctional devices normally require several materials in layers, which involves the time-consuming challenge of stacking nanomaterials with high precision.
The team, led ...
AI and 10 seconds of voice can screen for diabetes, new study reveals
2023-10-18
Determining whether a person is diabetic could be as easy as having them speak a few sentences into their smartphone, according to a groundbreaking study from Klick Labs that combines voice technology with artificial intelligence in a major step forward in diabetes detection.
The new study, published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Digital Health, outlines how scientists used six to 10 seconds of people’s voice, along with basic health data, including age, sex, height, and weight, to create an AI model ...
AI identifies antimalarial drug as possible osteoporosis treatment
2023-10-18
Correction (Oct. 17, 2023): The paper’s title has been corrected to “Deep Learning-Predicted Dihydroartemisinin Rescues Osteoporosis by Maintaining Mesenchymal Stem Cell Stemness through Activating Histone 3 Lys 9 Acetylation
Artificial intelligence has exploded in popularity and is being harnessed by some scientists to predict which molecules could treat illnesses, or to quickly screen existing medicines for new applications. Researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have used one such deep learning algorithm, and found that dihydroartemisinin ...
Simplifying the generation of three-dimensional holographic displays
2023-10-18
Holograms that offer a three-dimensional (3D) view of objects provide a level of detail that is unattainable by regular two-dimensional (2D) images. Due to their ability to offer a realistic and immersive experience of 3D objects, holograms hold enormous potential for use in various fields, including medical imaging, manufacturing, and virtual reality. Holograms are traditionally constructed by recording the three-dimensional data of an object and the interactions of light with the object. However, this technique is computationally highly intensive as it requires ...
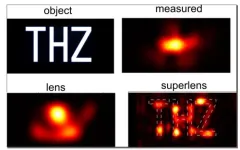
Superlensing without a super lens: physicists boost microscopes beyond limits
2023-10-18
Ever since Antonie van Leeuwenhoek discovered the world of bacteria through a microscope in the late seventeenth century, humans have tried to look deeper into the world of the infinitesimally small.
There are, however, physical limits to how closely we can examine an object using traditional optical methods. This is known as the ‘diffraction limit’ and is determined by the fact that light manifests as a wave. It means a focused image can never be smaller than half the wavelength of light used to observe an object.
Attempts to break this limit with “super lenses” have all hit the hurdle of extreme visual losses, making the lenses opaque. ...
Collaborative study focuses on using computer algorithms to find molecular adaptations to improve COVID-19 drugs
2023-10-18
As the COVID-19 pandemic scattered and isolated people, researchers across Virginia Tech connected for a data-driven collaboration seeking improved drugs to fight the disease and potentially many other illnesses.
A multidisciplinary collaboration spanning several colleges at Virginia Tech resulted in a newly published study, “Data Driven Computational Design and Experimental Validation of Drugs for Accelerated Mitigation of Pandemic-like Scenarios,” in the Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters.
The study focuses on using computer algorithms to generate adaptations to ...
Study predicts potential for 110% electricity increases in U.S. urban buildings
2023-10-18
A research study led by University of Oklahoma assistant professor Chenghao Wang and recently published in the journal Nature Communications tackled the critical issue of how city-scale building energy consumption in urban environments will evolve under the influence of climate change.
Fossil fuels account for approximately 40% of all building energy use in urban city centers in the United States, and the U.S. Energy Information Administration reports that residential and commercial buildings in U.S. cities are one of the major energy ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
[Press-News.org] Map: Wildlife polluted by flame retardants on massive scaleBelugas to butterflies plagued by harmful (and often ineffective) chemicals