(Press-News.org) DURHAM, N.C. – A vaccine designed to protect against three different deadly coronaviruses shows success in mouse studies, demonstrating the viability of a pan-coronavirus vaccine developed by researchers at the Duke Human Vaccine Institute.
Publishing in the journal Cell Reports, the single nanoparticle vaccine included components of a previous vaccine that was shown to protect mice and primates against multiple variants of SARS-CoV-2, which is the virus that causes COVID-19. In this study, the vaccine protected mice from SARS-CoV-1, another form of SARS coronavirus that can infect humans, and a MERS coronavirus that has led to periodic, deadly outbreaks around the world.
“We are making important progress toward a broadly protective coronavirus vaccine,” said senior author Kevin O. Saunders, Ph.D., associate director of the Duke Human Vaccine Institute. “These are pathogens that cause or have the potential to cause significant human infections and loss of life, and a single vaccine that provides protection could slow down or even prevent another pandemic.”
Saunders and colleagues built the tri-valent vaccine using a nanoparticle loaded with a key fragment called a receptor binding domain from each of the coronaviruses. The fragment – a docking site on the virus that enables it to infiltrate the body’s cells – provides enough information for immune cells to build an effective response against actual coronaviruses that enter the body.
In earlier studies in mice and primates, the researchers demonstrated that an earlier iteration of the nanoparticle vaccine was effective against multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants. Human tests are planned next year for a version that carries immunogens to different SARS-CoV-2 strains, including those that have dominated since the original outbreak in late 2019.
The current work expands the components of the vaccine to include an additional SARS-related virus and MERS virus. In lab studies, as well as in mice, the researchers found that the vaccine candidate generated inhibitory immune molecules called antibodies against all three pathogenic human coronavirus types.
Importantly, vaccinated mice did not grow sick when challenged with either SARS-like or MERS-like viruses.
“This study demonstrates proof-of-concept that a single vaccine that protects against both MERS and SARS viruses is an achievable goal,” Saunders said. “Given that one MERS and two SARS viruses have infected humans in the last two decades, the development of universal coronavirus vaccines is a global health priority.”
In addition to Saunders, study authors include lead author David R. Martinez, who is now at Yale School of Medicine, and Alexandra Schäfer, Tyler D. Gavitt, Michael L. Mallory, Esther Lee, Nicholas J. Catanzaro, Haiyan Chen, Kendra Gully, Trevor Scobey, Pooja Korategere, Alecia Brown, Lena Smith, Rob Parks, Maggie Barr, Amanda Newman, Cindy Bowman, John M. Powers, Erik J. Soderblom, Katayoun Mansouri, Robert J. Edwards, Ralph S. Baric, and Barton F. Haynes.
The study received funding support from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, which is part of the National Institutes of Health (U54 CA260543, P01 AI158571).
###
END
Particle accelerators are crucial tools in a wide variety of areas in industry, research and the medical sector. The space these machines require ranges from a few square meters to large research centers. Using lasers to accelerate electrons within a photonic nanostructure constitutes a microscopic alternative with the potential of generating significantly lower costs and making devices considerably less bulky. Until now, no substantial energy gains were demonstrated. In other words, it has not been shown that electrons really have increased in speed significantly. A team of laser physicists at Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg ...
A new Corewell Health study suggests that men who have longer prostatic urethras, the part of the urethra that travels through the prostate, may be at a higher risk of experiencing moderate, often chronic urinary side effects after receiving radiation for prostate cancer.
To date, researchers have struggled to determine any risk factors that could shed light on who might experience these types of side effects ahead of time. But now, a simple MRI scan and a new metric to determine urethra length could change that.
Results, now published in the journal Academic Radiology, indicate that for every 1-centimeter increase in length of the prostatic ...
They published their work on Oct. 12 in Energy Material Advances.
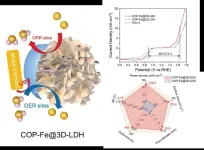
"The development of cost-effective and high-performance zinc-air battery cathode catalyst is imperative," said paper author Zhonghua Xiang, professor with the Beijing University of Chemical Technology. "Currently, zinc-air batteries still not occupy the market, because they are limited in both stability and in their energy density."
Xiang explained that zinc-air batteries can only work for very limited time at high current density, because there are lots of problems of its cathode, anode and electrolyte.
"The air ...
Annapolis, MD; October 18, 2023—Every so often, cicadas emerge above ground and blanket the earth with their exoskeletons while emitting a high-pitched chirp from sunrise to sunset. The periodical cicadas in the genus Magicicada come every 13 or 17 years, though other types of cicadas emerge much more frequently in our neighborhoods. A long-standing agricultural query related to the periodical cicadas was recently answered by an Agricultural Research Service (USDA-ARS) research team at West Virginia's Appalachian Fruit Research Station. Simply: Once periodical ...
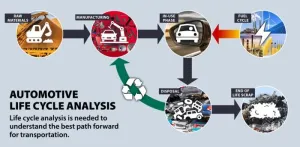
SAN ANTONIO — October 18, 2023 —Southwest Research Institute will host the Life-Cycle Analysis for Transportation Symposium on Nov. 16-17 in San Antonio. This year’s symposium will be in person for the first time.
The two-day event will highlight academic, industry and institutional research efforts to characterize the total greenhouse gas emissions produced during the entire life cycle of a vehicle, including its manufacture, service life and recycling or disposal.
“We often talk about getting to ‘zero-emissions,’ but this definition often ...
Media Contact: Kara Flynn, 202.257.8424, press@ashg.org
For Immediate Release: Wednesday, October 18, 2023, 10:00am U.S. Eastern Time
ROCKVILLE, MD — More than ever before, human genetics and genomics is an essential part of making progress in research, biotechnology, and health. As a key leader supporting research innovation, the American Society of Human Genetics (ASHG) will convene more than 8,000 researchers and clinicians at the ASHG 2023 Annual Meeting in Washington DC, Nov. 1-5 to share emerging discoveries and celebrate the Society’s 75th anniversary.
“Human genetics is transforming science and health at a rapid ...
More than 150 species of wild animals across every continent are contaminated with flame retardant chemicals, according to a new map tracking peer-reviewed research worldwide. Polluted wildlife include killer whales, red pandas, chimpanzees and other endangered species. Added to furniture, electronics, vehicles, and other everyday products to meet flammability standards, the chemicals often do not work as intended. They also migrate out of products and into wildlife—and people.
“Flame retardants don’t actually make TV enclosures and car interiors more fire-safe, but they can harm people and animals,” ...
Octopuses are fascinating animals – and serve as important model organisms in neuroscience, cognition research and developmental biology. To gain a deeper understanding of their biology and evolutionary history, validated data on the composition of their genome is needed, which has been lacking until now. Scientists from the University of Vienna together with an international research team have now been able to close this gap and, in a study, determined impressive figures: 2.8 billion base pairs - organized in ...
A collaborative research team, led by Professor Hyun-Kon Song in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST, Dr. Seo-Hyun Jung from Research Center for Advanced Specialty Chemicals at Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT), and Dr. Tae-Hee Kim from the Ulsan Advanced Energy Technology R&D Center at Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER), has achieved a groundbreaking milestone in battery technology. Their remarkable achievement in developing a non-flammable gel polymer electrolyte (GPE) is set to revolutionize the safety of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) by ...
SPOKANE, Wash. – A two-part training designed to help police officers recognize their implicit bias, revealed some behavior improvement and lowered citizen discrimination complaints in a controlled study. While a small study involving one police department, it is the first-known research to provide evidence that this type of training can produce positive behavioral effects.
Led by Washington State University researcher Lois James, the study found some improvement in the anti-bias trained officers’ behavior toward homeless people in particular, ...