(Press-News.org)
A team of University of Waterloo researchers has created smart, advanced materials that will be the building blocks for a future generation of soft medical microrobots.
These tiny robots have the potential to conduct medical procedures, such as biopsy, and cell and tissue transport, in a minimally invasive fashion. They can move through confined and flooded environments, like the human body, and deliver delicate and light cargo, such as cells or tissues, to a target position.
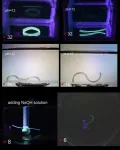
The tiny soft robots are a maximum of one centimetre long and are bio-compatible and non-toxic. The robots are made of advanced hydrogel composites that include sustainable cellulose nanoparticles derived from plants.
This research, led by Hamed Shahsavan, a professor in the Department of Chemical Engineering, portrays a holistic approach to the design, synthesis, fabrication, and manipulation of microrobots. The hydrogel used in this work changes its shape when exposed to external chemical stimulation. The ability to orient cellulose nanoparticles at will enables researchers to program such shape-change, which is crucial for the fabrication of functional soft robots.
"In my research group, we are bridging the old and new," said Shahsavan, director of the Smart Materials for Advanced Robotic Technologies (SMART-Lab). "We introduce emerging microrobots by leveraging traditional soft matter like hydrogels, liquid crystals, and colloids."
The other unique component of this advanced smart material is that it is self-healing, which allows for programming a wide range in the shape of the robots. Researchers can cut the material and paste it back together without using glue or other adhesives to form different shapes for different procedures.
The material can be further modified with a magnetism that facilitates the movement of soft robots through the human body. As proof of concept of how the robot would maneuver through the body, the tiny robot was moved through a maze by researchers controlling its movement using a magnetic field.
"Chemical engineers play a critical role in pushing the frontiers of medical microrobotics research," Shahsavan said. "Interestingly, tackling the many grand challenges in microrobotics requires the skillset and knowledge chemical engineers possess, including heat and mass transfer, fluid mechanics, reaction engineering, polymers, soft matter science, and biochemical systems. So, we are uniquely positioned to introduce innovative avenues in this emerging field".
The next step in this research is to scale the robot down to submillimeter scales.
Shahsavan's research group collaborated with Waterloo’s Tizazu Mekonnen, a professor from the Department of Chemical Engineering, Professor Shirley Tang, Associate Dean of Science (Research), and Amirreza Aghakhani, a professor from the University of Stuttgart in Germany. They published their results last month in Nature Communications.
END
The INTERLACE phase III trial, funded by Cancer Research UK and UCL Cancer Trials Centre, assessed whether a short course of induction chemotherapy (IC) prior to chemoradiation (CRT) could reduce the rate of relapse and death among patients with locally advanced cervical cancer. As part of an analysis of clinical data, the preliminary results will be presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) congress on Sunday 22 October 2023.
The peak incidence of cervical cancer is in women in their early thirties, with around 3,200 new cases each year in the UK. CRT has been the standard treatment for cervical cancer since 1999, but despite improvements ...
New York, NY (October 22, 2023) — A clinical trial co-led by Mount Sinai researchers is the first to show that using chemotherapy with immunotherapy resulted in improved survival in patients with an advanced type of bladder cancer. The results were simultaneously reported in The New England Journal of Medicine and at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology.
The randomized phase 3 trial, named ”CheckMate 901,” showed significantly improved outcomes in patients who received the immunotherapy nivolumab with a combination of the chemotherapies gemcitabine and cisplatin, ...
Cabozantinib, which targets tumor cell growth and tumor blood vessel growth, sharply improved progression-free survival over placebo in patients with extra-pancreatic and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors
Boston - A drug that simultaneously strikes cancer cells' growth circuits and pipeline to the bloodstream produced encouraging results in a clinical trial involving patients with advanced neuroendocrine tumors, according to a study led by Dana-Farber Cancer Institute investigators.
Jennifer Chan, MD, MPH, director of the Program ...
The Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology today announced detailed results will be presented at ESMO 2023 from CABINET (A021602), a phase III pivotal trial evaluating cabozantinib compared with placebo in two cohorts of patients with previously treated neuroendocrine tumors: one cohort of patients with advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNET) and a second cohort of patients with advanced extra-pancreatic NET (epNET). The study met the primary objective for each cohort, demonstrating that cabozantinib provided dramatic improvements in median progression-free survival (PFS) for the patients in the pNET and epNET cohorts. ...
MADRID ― Compared with pre-surgical (neoadjuvant) chemotherapy alone, adding perioperative immunotherapy – given before and after surgery – significantly improved event-free survival (EFS) in patients with resectable early-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Results from the Phase III CheckMate 77T study were presented today at the 2023 European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress by researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
At a median follow-up of 25.4 months, the median EFS with chemotherapy alone was 18.4 months, while the median had not yet been reached for patients receiving perioperative nivolumab, meaning EFS was prolonged ...
Boston – Belzutifan significantly reduced the risk of progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), the most common type of kidney cancer, in patients previously treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors and anti-angiogenic therapies compared with everolimus in a phase 3 clinical trial. The trial, led by Toni K. Choueiri, MD, Director of the Lank Center for Genitourinary Cancer at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, showed the risk of progression was reduced by 25-26%.
The results were presented at the annual European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress on October ...
The following Lancet papers will be presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress 2023 (#ESMO 2023). The conference will take place between Friday 20th – Tuesday 24th October 2023.
Contact details for corresponding authors are provided should you wish to arrange an interview with the authors. Funding information is listed on the first page of each Article.
**Embargo: 13.00 [BST] / 14.00 [CEST] Friday 20th October 2023**
The Lancet: Pembrolizumab plus trastuzumab and chemotherapy for HER2-positive gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma: interim analyses from the phase ...
A secondary analysis from the SWOG S0931 EVEREST trial has found that in the subgroup of patients with clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) who were at very-high risk of recurrence, those who were treated with everolimus after surgery had a statistically significant improvement in recurrence-free survival compared to patients getting placebo after surgery.
The results will be presented at the European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress 2023 in Madrid, Spain, on Oct. 23, 2023 (poster 1887P) by Primo N. Lara, Jr., MD, lead author on the abstract. ...
Media contacts: Lisa Black, lblack@aap.org; or Adam Alexander, aalexander@aap.org
The parent’s universal cry in response to loud music-- “Turn that thing down!” -- is well-founded, as evidence shows that children and teens risk hearing loss by cranking up their personal listening devices. What families may not realize is that children are exposed to potentially harmful noise from infancy and that the effects are cumulative over a lifetime.
The American Academy of Pediatrics discusses the common sources and effects of noise, from infant sleep ...
Four senior bioengineering students at The University of Texas at Arlington have won the Biomedical Engineering Society (BMES) Coulter College for Healthcare Innovation competition for their work on an early detection device for atrial fibrillation.
Brady Killham, Juan Ramirez, Jeannette Santos and Michael Ikefuna, all seniors in UTA’s Bioengineering Department, earned the Best Overall award for their plan to develop FibGuard, a wearable, non-invasive atrial fibrillation early detection device.
UTA competed against teams from Vanderbilt, Purdue, Virginia Tech, Wake Forest, Texas A&M, the University of Oklahoma and Rensselaer Polytechnic ...