Apoptotic cells may drive cell death in hair follicles during regression cycle
2023-10-23
(Press-News.org)
“Revealing the stem cell niche self-renewal dynamics is important not only for understanding tissue homeostasis but also for understanding the initiation of cancer [7].”
BUFFALO, NY- October 23, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on October 19, 2023, entitled, “Apoptotic cells may drive cell death in hair follicles during their regression cycle.”
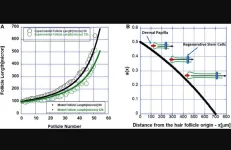
Intravital microscopy in live mice has shown that the elimination of epithelial cells during hair follicle regression involves supra-basal cell differentiation and basal cell apoptosis through synergistic action of TGF-β (transforming growth factor) and mesenchymal-epithelial interactions. In this process the basal epithelial cells are not internally committed to death and the mesenchymal dermal papilla (DP) plays an essential role in death induction. Given that DP cells are not necessary for completion of the cycle, only for its initiation, it is still an open question as to the mechanism that leads to the propagation of apoptosis towards the regenerative stem cell population.
In their new study, researchers Bradley D. Keister, Kailin R. Mesa and Krastan B. Blagoev from the National Science Foundation, The Jane Coffin Childs Memorial Fund for Medical Research, Yale School of Medicine, Johns Hopkins University, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, and Sorbonne Université performed a quantitative analysis of the length of hair follicles to investigate their regression cycle.
“In this paper we introduced a mathematical model of the hair follicle regression cycle that postulates that the regression is initiated by the dermal papilla, but that this signal affects only the cells adjacent to it.”
The data are consistent with a propagation mechanism driven by apoptotic cells inducing apoptosis in their neighboring cells. The observation that the apoptosis slows down as the apoptotic front approaches the stem cells at the end of the follicle is consistent with a gradient of a pro-survival signal sent by these stem cells. An experiment that can falsify this mechanism is proposed.
“In conclusion, hair follicle regression may be governed by cell-cell induced programmed cell death, which slows down as the stem cell compartment is approached and does not affect the stem cell compartment from which the growth phase is initiated. The class of models introduced here can be used to describe the renewal kinetics of other stem cell niches like the intestinal stem cell niche [18].”
Read the full study: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28529
Correspondence to: Krastan B. Blagoev
Email: kblagoev@nsf.gov
Keywords: hair follicle, stem cells, regression cycle, mathematical model, analysis
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
X, formerly known as Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
LabTube
Soundcloud
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://oncotarget.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Foncotarget.28529
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact: media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-10-23
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A $3.6 million award from the National Institutes of Health will allow neurosurgical, neurology and neuroscience researchers at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine to test a novel diagnosis and treatment combination for painful diabetic neuropathy. The approach combines spinal cord stimulation with measurement of small fiber nerve activity using a patent-pending device called Detecting Early Neuropathy (DEN).
Diabetes is a growing health concern worldwide, ...
2023-10-23
Washington, DC—Diamonds contain evidence of the mantle rocks that helped buoy and grow the ancient supercontinent Gondwana from below, according to new research from a team of scientists led by Suzette Timmerman—formerly of the University of Alberta and now at the University of Bern—and including Carnegie’s Steven Shirey, Michael Walter, and Andrew Steele. Their findings, published in Nature, demonstrate that superdeep diamonds can provide a window through space and time into the supercontinent growth and formation ...
2023-10-23
The American Cancer Society has awarded the University of Cincinnati Cancer Center an Institutional Research Grant.
Cancer Center member David Plas, PhD, is primary investigator for the grant, with members Maria Czyzyk-Krzeska, MD, PhD, and Kathryn Wikenheiser-Brokamp, MD, PhD, serving as co-principal investigators.
The American Cancer Society awards Institutional Research Grants to academic and nonprofit organizations that have a track record of outstanding cancer research and a pool of experienced researchers who can mentor junior faculty. The purpose is to support early-stage ...
2023-10-23
Washington, DC— As climate change warms the Earth, higher-latitude regions will be at greater risk for toxins produced by algal blooms, according to new research led by Carnegie’s Anna Michalak, Julian Merder, and Gang Zhao. Their findings, published in Nature Water, identify water temperatures of 20 to 25 degrees Celsius (68 to 77 degrees Fahrenheit) as being at the greatest risk for developing dangerous levels of a common algae-produced toxin called microcystin.
Harmful algal blooms result when bodies of water get overloaded with nitrogen and phosphorus ...
2023-10-23
The Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine (ABM) has released new literature-based recommendations related to breastfeeding in the setting of substance use and substance use disorder (SUD) treatments. The new clinical protocol is published in the peer-reviewed journal Breastfeeding Medicine. Click here to read the article now.
Miriam Harris, MD and Elisha Wachman, MD, from Boston Medical Center, and coauthors, provide breastfeeding recommendations in the setting of non-prescribed opioid, stimulant, sedative-hypnotic, alcohol, nicotine, and cannabis use, and SUD treatments. They also offer guidance on the use of toxicology testing in breastfeeding ...
2023-10-23
A new study leverages the NASA Exoplanet Archive and planetary system simulations to make narrowband SETI searches more efficient.
October 23, 2023, Mountain View, CA -- In a new study published in the Astronomical Journal, researchers used the known population of exoplanets and extrapolated to the much larger, unknown population of exoplanets to set better thresholds for planetary effects on signals from ETIs (extraterrestrial intelligences). The prior recommendation for the threshold “drift rate” contribution, caused by a planet’s motion around its host star, was 200 nHz. In this work, lead ...
2023-10-23
Lisbon, Portugal – 23 October, 2023
The International Society of Microbiota (ISM) is proud to present the 14th International Conference on Skin Ageing & Challenges 2023. This monumental event will unfold at the Altis Grand Hotel in Lisbon, Portugal, and virtually, on November 9-10, 2023.
Skin ageing, a multifaceted issue combining both basic research, mechanistic, clinical aspects and health concerns, is gaining significant attention in the scientific community.
This year’s conference promises to be a beacon of innovation, ...
2023-10-23
Certain gut-dwelling fungi flourish in severe cases of COVID-19, amplifying the excessive inflammation that drives this disease while also causing long-lasting changes in the immune system, according to a new study led by investigators at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian. This discovery identifies a group of patients who may benefit from specialized, but yet-to-be determined treatments.
Utilizing patient samples and preclinical models, the research team determined that the growth of fungi in the intestinal ...
2023-10-23
Before modern humans settled definitively in Europe, other human populations left Africa for Europe beginning approximately 60,000 years ago, albeit without settling for the long term. This was due to a major climatic crisis 40,000 years ago, combined with a super-eruption originating from the Phlegraean Fields volcanic area near current-day Naples, subsequently precipitating a decline in ancient European populations. To determine who the first modern humans to settle definitively in Europe were, a team led by CNRS scientists1 analysed the genome of two skull ...
2023-10-23
Alem & Narayanan Advancing Infectious Disease Capabilities Through Biomedical Research Laboratory Core Support
Farhang Alem, Interim Director of the Biomedical Research Laboratory, Institute for Biohealth Innovation, and Aarthi Narayanan, Professor, Biology, received funding for the project: "Advancing Infectious Disease Capabilities through BRL Core Support."
As part of this project, Alem and Narayanan will: 1) implement a comprehensive BSL-3 facilities preventative maintenance and upgrade plan to ensure continuity of operations, compliance with federal regulations, and a safe and secure facility; 2) enhance safety ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Apoptotic cells may drive cell death in hair follicles during regression cycle