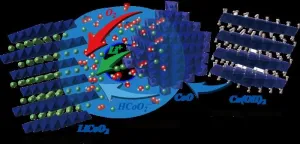
(Press-News.org) Layered lithium cobalt oxide, a key component of lithium-ion batteries, has been synthesized at temperatures as low as 300°C and durations as short as 30 minutes.
Lithium ion batteries (LIB) are the most commonly used type of battery in consumer electronics and electric vehicles. Lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) is the compound used for the cathode in LIB for handheld electronics. Traditionally, the synthesis of this compound requires temperatures over 800°C and takes 10 to 20 hours to complete.
A team of researchers at Hokkaido University and Kobe University, led by Professor Masaki Matsui at Hokkaido University’s Faculty of Science, have developed a new method to synthesize lithium cobalt oxide at temperatures as low as 300°C and durations as short as 30 minutes. Their findings were published in the journal Inorganic Chemistry.
“Lithium cobalt oxide can typically be synthesized in two forms,” Matsui explains. “One form is layered rocksalt structure, called the high-temperature phase, and the other form is spinel-framework structure, called the low-temperature phase. The layered LiCoO2 is used in Li-ion batteries.”
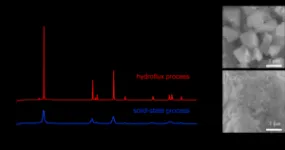
Using cobalt hydroxide and lithium hydroxide as starting materials, with sodium or potassium hydroxide as an additive, the team conducted a series of high-precision experiments under varying conditions to synthesize layered LiCoO2 crystals. The process was called the “hydroflux process”. They were also able to determine the reaction pathway that led to the formation of the layered crystals.
“By understanding the reaction pathway, we were able to identify the factors that promoted the crystal growth of layered LiCoO2,” Matsui said. “Specifically, the presence of water molecules in the starting materials significantly improved crystallinity of the end product.”
The team also measured the electrochemical properties of the layered LiCoO2, showing that they were only marginally inferior to that of commercially available LiCoO2 synthesized by the traditional high temperature method.
“This work is the first experimental demonstration of the thermochemical stability of layered LiCoO2 at low temperatures under ambient pressure,” concludes Matsui. “Our development of this hydroflux process will enable energy saving measures in various ceramic production processes. Our immediate next steps will be the improvement of the hydroflux process based on our understanding of the reaction pathway.”
END
Cathode active materials for lithium-ion batteries could be produced at low temperatures
2023-10-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How to slow the spread of deadly ‘superbugs’
2023-10-24
Harnessing new advances in genomic surveillance technology could help detect the rise of deadly ‘superbugs’ and slow their evolution and spread, improving global health outcomes, a new Australian study suggests.
Antimicrobial resistance occurs when bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites change over time and no longer respond to the medicines and chemicals we use to kill them. These ‘superbugs’ make infections harder to treat and increase the risk of disease spread, severe illness and death.
Without significant intervention, global annual deaths involving antimicrobial resistance are estimated ...
Burning sugarcane possible cause of mystery kidney disease in agricultural workers
2023-10-24
AURORA, Colorado (October 23, 2023) - The burning of sugarcane and rice husks may be releasing a toxicant causing a mysterious kidney disease in agricultural workers, according to a paper out today in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases.
An ongoing epidemic of chronic kidney disease has been observed among manual laborers in hot agricultural communities throughout the world, including along the Pacific coast of Central America, India and Sri Lanka. While heat stress and climate change have contributed to this epidemic, researchers have identified tiny silica particles released from sugarcane ash that can be inhaled or ingested through contaminated drinking water that cause ...
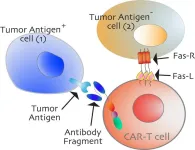
Researchers identify ‘switch’ to activate cancer cell death
2023-10-24
A research team from the UC Davis Comprehensive Cancer Center has identified a crucial epitope (a protein section that can activate the larger protein) on the CD95 receptor that can cause cells to die. This new ability to trigger programmed cell death could open the door for improved cancer treatments. The findings were published Oct. 14 in the Nature journal Cell Death & Differentiation.
CD95 receptors, also known as Fas, are called death receptors. These protein receptors reside on cell membranes. When activated, ...
Role of innate immunity in SARS-CoV-2 infection
2023-10-24
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.005
During severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, activated macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils, and natural killer cells are the first defense against infection. These immune effectors trap and ingest the virus, kill infected epithelial cells, or produce anti-viral cytokines. Evidence suggests that aging, obesity, and mental illness can lead to weakened innate immunity and, thus, are all associated with elevated infection and severe disease progression of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). ...
Viral rebound and safety of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for lung-transplant recipients infected with SARS-CoV-2
2023-10-24
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004
Data on the viral rebound and safety of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in lung transplant (LTx) recipients are limited. The study prospectively followed four LTx recipients. Clinical characteristics, viral RNA dynamic in throat swabs, and tacrolimus blood concentration were monitored regularly. All four LTx recipients, aged 35–74 years, were not vaccinated against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). They got coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) after ...
Residents unprepared for wildland fires, face barriers in implementing prevention measures: York U study
2023-10-23
TORONTO, October 23, 2023 –This year, Canada saw the worst wildfire season in its history, with fires destroying homes, displacing thousands of residents, and burning the largest area since contemporary records began in 1983. Much of this damage to communities could be reduced with better wildfire preparedness – but wildland urban interface (WUI) communities often face significant barriers in implementing these improvements, according to a study by York University’s Disaster and Emergency Management researchers.
According to the study, Determinants of residential wildfire mitigation uptake: A ...
Diffraction-limited visible imaging for large aperture telescopes: development and application of piezoelectric deformable secondary mirror
2023-10-23
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances, 10.29026/oea.2023.230039 discusses diffraction-limited visible imaging for large aperture telescopes.
The deformable mirror used in adaptive optics can change its surface to instantly correct the static wavefront aberration of the optical system and atmospheric turbulence wavefront disturbance. This allows the optical system to automatically adapt to changes in the environment and maintain optimal performance. High-resolution astronomical observation, laser atmospheric transmission, and biomedical imaging all make extensive use ...
Texas A&M joins multimillion-dollar moon orbit tracking project
2023-10-23
Texas A&M University is joining a multi-university team on a major research project to track objects orbiting the moon. The Air Force Research Laboratory is awarding up to $5 million over five years for the Space University Research Initiative (SURI).
“The SURI is an outstanding initiative to train our next-generation workforce. We look forward to carrying out creative research aimed at addressing astronautical challenges in cislunar space,” said Dr. Manoranjan Majji, an associate professor and Josey Family Foundation Faculty Fellow in the Department of Aerospace Engineering at ...
Nurse practitioners and physicians are similarly likely to inappropriately prescribe medications to older patients
2023-10-23
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 23 October 2023
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization ...
UArizona researchers probe how a piece of the moon became a near-Earth asteroid
2023-10-23
In 2021, a team of University of Arizona astronomers suggested that a recently discovered near-Earth asteroid, Kamo`oalewa, could be a chunk of the moon. Two years after the striking discovery, another UArizona research group has found that a rare pathway could have enabled this to happen.
So far, only distant asteroids from beyond the orbit of Mars have been considered a source of near-Earth asteroids, said Renu Malhotra, Regents Professor of Planetary Sciences and a senior author on the paper.
"We are now establishing that the moon is a more likely source ...