(Press-News.org) Gene therapy currently represents the most promising approach for the treatment of hereditary diseases. Yet despite significant breakthroughs in recent years, there are still a number of hurdles that hinder the wider application of gene therapies. These include the efficient delivery of genetic material into target cells with minimal side effects using adeno-associated viral vectors (AAVs). The AAV carrier substances have an advantageous safety profile and high gene transfer efficiency, meaning they are often used in gene therapies and in gene editing with CRISPR/Cas. But, AAVs have limited DNA uptake capacity and cannot reliably transport larger genes.
In the past, various methods have been developed to circumvent these drawbacks. Such methods rely on splitting the coding DNA into two fragments that contain the ability to be rejoined in the target tissue. The disadvantage of these strategies, however, is that they are not very efficient and offer less flexibility for experimental design, as well as causing potential side effects.
Assembly at transcript level
The team of Elvir Becirovic, professor of experimental and translational opthalmology at the University of Zurich, has now developed a novel approach to circumvent these drawbacks. This new method, called REVeRT (reconstitution via mRNA trans-splicing), also uses the principle of dual AAV vectors. However, unlike previous technologies, it relies on the assembly of split gene fragments at the transcript level.
“The advantages of this method are increased efficiency and fewer side effects,” explains Becirovic. “It is also more flexible than previous methods, as the large genes can be divided into two fragments at various points.” His team has also developed the method for opthalmologic applications in cell cultures and successfully evaluated it in animal models under various conditions, for example to treat hereditary macular degeneration with gene therapy.
Possible therapies for various diseases
REVeRT is also suitable for use in gene therapies for other genetic or acquired diseases – such as various common blood disorders or diseases associated with aging. The new method can also find application in gene therapy studies using CRISPR/Cas genome editing. For such modules to be of therapeutic use, the coding DNA needs to be transferred into the target cells as efficiently as possible with the help of carriers such as AAVs. “With CRISPR/Cas further applications are possible, opening up new treatment options,” says Becirovic.
Literature:
Lisa Maria Riemayer et al. mRNA trans-splicing dual AAV vectors for (epi)genome editing and gene therapy. Nature Communications, 18 October 2023. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42386-0.
Contacts:
Prof. Elvir Becirovic
Retinal Gene Therapy Laboratory
Department of Ophthalmology
University of Zurich
Phone: +41 43 253 30 16
E-mail: elvir.becirovic@uzh.ch
END
New methods for effective transport of large genes in gene therapy
2023-10-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New tool may flag signs of pandemic-related anxiety and depression in healthcare workers
2023-10-24
An artificial intelligence tool effectively detected distress in hospital workers’ conversations with their therapists early in the pandemic, a new study shows, suggesting a potential new technology that screens for depression and anxiety.
As the coronavirus pandemic forced many hospitals to operate beyond capacity, medical workers faced overwhelming numbers of work shifts, limited rest, and increased risk of COVID-19 infection. At the same time, quarantine policies and fear of infecting family reduced their ...
Bumblebees visit flowers with more difficult-to-access nectar for immediate benefit to the colony
2023-10-24
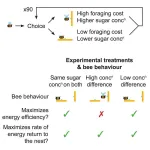
If you’ve ever watched a bumblebee move from flower to flower, you might wonder how they decide which flower to choose and how long to stay. Now, researchers reporting in the journal iScience on October 24 have new insight based on their observations of bumblebees’ interactions with slippery artificial flowers. They found that the bumblebees make choices to maximize the rate of energy return, or the amount of sugar collected each minute.
“Bumblebees can make decisions ‘on the fly’ about which nectar sources are the most energetically economical,” said Jonathan ...
Making chemistry more accessible at the University of Oxford by providing period products
2023-10-24
When it comes to the question of who gets to be a scientist, gender disparities are well-documented in many fields. Patching the infamous “leaky pipeline” can be a thorny problem, but during the 2022–2023 school year, the Department of Chemistry at the University of Oxford took a simple and practical step forward: they began offering period products in the department’s bathrooms. In an article publishing October 25 in the journal Trends in Chemistry, three students involved in the Oxford Period Project and their supervising ...
Traditional chinese medicine compound (tongxinluo) and clinical outcomes of patients with acute myocardial infarction
2023-10-24
About The Study: In this randomized clinical trial of 3,777 patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI; a type of heart attack), the Chinese patent medicine Tongxinluo, as an adjunctive therapy in addition to STEMI guideline-directed treatments, significantly improved both 30-day and 1-year clinical outcomes. Further research is needed to determine the mechanism of action of Tongxinluo in STEMI.
Authors: Yuejin Yang, M.D., Ph.D., and Runlin Gao, M.D., of the Chinese Academy of Medical ...
Getting maximum calories in shortest time is the priority for bumblebees
2023-10-24
Research has found that bumblebees make foraging choices to collect the most sugar from flowers in the shortest time – even if that means using more energy in the process – to provide an immediate energy boost for the colony.
A new study investigating nectar drinking in one of the most common bumblebees in the UK, Bombus terrestris, has found that when foraging they maximise the amount of nectar sugar they take back to the colony each minute.
To make their choices, the bumblebees trade off the time they spend collecting nectar with the energy content of that nectar. This means ...
Incidence and transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in child care centers after COVID-19 vaccines
2023-10-24
About The Study: In this examination of SARS-CoV-2 incidence and transmission in child care centers (CCCs) and students’ households, transmission within CCCs and from children infected at CCCs into households was low in this study that included 83 children in 11 CCCs. These findings suggest that current testing and exclusion recommendations for SARS-CoV-2 in CCCs should be aligned with those for other respiratory viruses with similar morbidity and greater transmission to households.
Authors: Timothy R. Shope, ...
Neurodevelopmental outcomes among offspring exposed to corticosteroid and B2-adrenergic agonists in utero
2023-10-24
About The Study: The results of this study of 91,460 mother-offspring pairs found no association between in utero corticosteroid and β2-adrenergic agonist exposure and offspring neurodevelopmental outcomes, regardless of the timing of exposure. Despite the limitations and low power of the study, the findings suggest that corticosteroids and β2-adrenergic agonists are safe for pregnant individuals with asthma and the neurodevelopment of their offspring.
Authors: Abir Nagata, Ph.D., of Osaka University in Osaka, Japan, and Toshio Masumoto, Ph.D., of Tottori University ...
Child care centers unlikely source for COVID-19 transmission, study finds
2023-10-24
Children in child care centers are not spreading COVID-19 at significant rates to caregivers or other children at the center, nor to their households, according to a study led by University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and UPMC Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh pediatrician-scientists and published today in JAMA Network Open.
The findings suggest that recommendations to test symptomatic children for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, and keep positive children home from child care for prolonged periods can be revised to align with those for other serious ...
Pew funds 6 teams to advance cutting-edge biomedical research
2023-10-24
PHILADELPHIA—The Pew Charitable Trusts announced today the six pairs of researchers who will make up its 2023 class of Innovation Fund investigators.
These 12 acclaimed scientists—all alumni or advisors of Pew’s biomedical programs in the United States and Latin America—will partner on interdisciplinary research projects exploring key questions in human biology and disease. Combining the researchers’ expertise in topics ranging from neuroscience and immunology to cancer biology, these collaborations will help boost scientific discovery and improve human health.
“An interdisciplinary approach to research is critical to uncovering scientific breakthroughs ...
Givers to crowdfunding campaigns enjoy vicarious success
2023-10-24
Why would someone decide to give their money to help a stranger bring a creative project to life?
Recent research has found that backers of crowdfunding projects participate, in part, because of a sense of indirect success and the feeling that they are contributing to something bigger.
Crowdfunding — raising money for a new venture by collecting small amounts from many people — is most often done online, and messaging on the most popular sites reinforces the perception of a more democratic market.
But the reality is a bit ...