(Press-News.org) Cleveland Clinic has been selected by Wellcome Leap to lead a quantum computing research project, while also playing a significant role in another led by Algorithmiq — both in collaboration with IBM Quantum.
The two contracts were won through Wellcome Leap’s Quantum for Bio Challenge, which will award up to $40 million to 12 researchers globally for research focused on accelerating the development of quantum computing applications for healthcare. Wellcome Leap is a U.S.- based non-profit organization founded by the Wellcome Trust to accelerate and increase the number of breakthroughs in global health.
Cleveland Clinic and IBM teams, partnering through the Cleveland Clinic-IBM Discovery Accelerator, will collaborate closely on one project, and with Algorithmiq on a second project:
Protein Conformation Prediction with Quantum Computing - In collaboration with members of the IBM Quantum team, Cleveland Clinic will work to develop quantum algorithms and workflows to explore how they could contribute to the creation of universal, scalable methods for predicting protein structures more accurately and quickly. This research could lead to new insights into how proteins function and interact with other molecules to better understand the manifestation of diseases and develop more effective, targeted therapies.
Quantum Computing for Photon-Drug Interactions in Cancer Prevention and Cancer Treatment – In collaboration with IBM Quantum and Cleveland Clinic, the Algorithmiq team will create a set of computational tools that aims to explore how quantum computing could assist in the development of photon-activated drugs for cancer. The project team will leverage Algorithmiq’s drug discovery platform, Aurora, which uses IBM’s quantum hardware, and Cleveland Clinic’s extensive experience in bringing relevant drug applications suitable for demonstrating quantum advantage.
Wellcome Leap’s Supported Challenge Program in Quantum for Bio is focused on identifying, developing, and demonstrating biology and healthcare applications that will benefit from the use of quantum computers expected to emerge in the next 3-5 years. Up to $40 million in research funding will be awarded to the selected teams and up to $10 million in challenge prizes will be available at the end of the program for successful proof-of-concept demonstrations on quantum devices with a clear path to scaling to large quantum computers.
Earlier this year, the first IBM quantum system dedicated to healthcare research was installed on Cleveland Clinic’s main campus. Deployment of the quantum system was a key milestone in the organizations’ partnership, announced in 2021, focused on advancing the pace of biomedical research through high-performance computing, artificial intelligence and quantum computing. Since then, researchers have been working together on a robust portfolio of projects with these advanced technologies to progress how they can be used to generate and quickly analyze large amounts of data for a wide-range of disease-focused research.
Cleveland Clinic has launched more than 30 projects with IBM in diverse areas of interest spanning drug discovery, predictive modeling, and digital health, aiming to shrink the time to develop new therapies for patients. The new Wellcome Leap projects, including a collaboration with startup, Algorithmiq, highlight the Cleveland Clinic-IBM Discovery Accelerator’s mission to create an innovation ecosystem in Ohio with outreach and impact around the world.
END
Cleveland Clinic selected by Wellcome Leap for Two Quantum Computing Research Projects
2023-10-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
SLAC scientists shed light on potential breakthrough biomedical molecule
2023-10-24
Scientists from the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have gained valuable insights into producing nitroxide, a molecule with potential applications in the biomedical field. While nitric oxide (NO) has long been on researchers' radar for its significant physiological effects, its lesser-known cousin, nitroxide (HNO), has remained largely unexplored.
The study, published recently in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, was born out of a joint endeavor between teams at SLAC’s Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) X-ray laser and Stanford ...
Japanese registry finds use of IVUS in coronary interventions reduces mortality and need for coronary bypass surgery
2023-10-24
SAN FRANCISCO – A novel study conducted by a Japanese multicenter registry has revealed the significant benefits of using intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) in coronary intervention procedures. The comprehensive analysis, which focused on enhancing patient outcomes, has provided valuable insights into the effectiveness of IVUS in improving the success rates of these interventions.
The study, titled "Enhancing coronary intervention outcomes with the use of intravascular ultrasound: A comprehensive analysis of long-term benefits in Japanese multicenter registry," sheds light on the positive ...
NIH Kids First program releases nine new data sets for childhood cancer and congenital disorder research
2023-10-24
Philadelphia, PA., October 24, 2023
WHO: The Gabriella Miller Kids First Pediatric Research Program (Kids First), an initiative of the National Institutes of Health (NIH)
WHAT: Kids First announces the release of nine robust new pediatric research datasets spanning childhood cancers, congenital disorders, and cross-condition data. New publicly available datasets include:
PEDIATRIC CROSS-CONDITION
Kids First and INCLUDE: Down Syndrome, Heart Defects, and Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Principal ...
Case report shows promising results using transcranial magnetic stimulation for post-stroke ataxia
2023-10-24
In a new case report, researchers at UCLA Health describe promising results using repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in the management of post-stroke cerebellar ataxia, a debilitating condition marked by impaired coordination and balance.
Cerebellar ataxia describes a group of neurological disorders that affect coordination, balance, and control of muscle movements. It results from damage or dysfunction of the cerebellum, a part of the brain responsible for coordinating voluntary movements. Ataxia can manifest as unsteady walking, difficulties with fine motor skills, and problems with speech, ...
$9 million award from the Department of Defense will fund groundbreaking FutureG research
2023-10-24
Lingjia Liu, professor of electrical and computer engineering who is also an inaugural faculty member at the Virginia Tech Innovation Campus, has been awarded the Mobile Distributed Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output (Mobile dMIMO) project by the U.S. Department of Defense’s (DoD’s) Office of the Under Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering (OUSD(R&E)) as part of its flagship FutureG program. The Mobile dMIMO project consists of three phases, with $9 million total planned funding — $1.5 million is for Phase 1 of the project. The Mobile dMIMO project represents one ...
Smartphone attachment could increase racial fairness in neurological screening
2023-10-24
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed a smartphone attachment that could enable people to screen for a variety of neurological conditions, such as Alzheimer’s disease and traumatic brain injury, at low cost—and do so accurately regardless of their skin tone.
The technology, published in Scientific Reports, has the potential to improve the equity and accessibility of neurological screening procedures while making them widely available on all smartphone models.
The attachment fits over a smartphone’s camera and improves its ...
New methods for effective transport of large genes in gene therapy
2023-10-24
Gene therapy currently represents the most promising approach for the treatment of hereditary diseases. Yet despite significant breakthroughs in recent years, there are still a number of hurdles that hinder the wider application of gene therapies. These include the efficient delivery of genetic material into target cells with minimal side effects using adeno-associated viral vectors (AAVs). The AAV carrier substances have an advantageous safety profile and high gene transfer efficiency, meaning they are often used in gene therapies and in gene editing with CRISPR/Cas. But, AAVs have limited DNA uptake capacity ...
New tool may flag signs of pandemic-related anxiety and depression in healthcare workers
2023-10-24
An artificial intelligence tool effectively detected distress in hospital workers’ conversations with their therapists early in the pandemic, a new study shows, suggesting a potential new technology that screens for depression and anxiety.
As the coronavirus pandemic forced many hospitals to operate beyond capacity, medical workers faced overwhelming numbers of work shifts, limited rest, and increased risk of COVID-19 infection. At the same time, quarantine policies and fear of infecting family reduced their ...
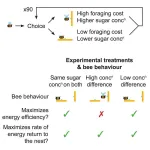
Bumblebees visit flowers with more difficult-to-access nectar for immediate benefit to the colony
2023-10-24
If you’ve ever watched a bumblebee move from flower to flower, you might wonder how they decide which flower to choose and how long to stay. Now, researchers reporting in the journal iScience on October 24 have new insight based on their observations of bumblebees’ interactions with slippery artificial flowers. They found that the bumblebees make choices to maximize the rate of energy return, or the amount of sugar collected each minute.
“Bumblebees can make decisions ‘on the fly’ about which nectar sources are the most energetically economical,” said Jonathan ...
Making chemistry more accessible at the University of Oxford by providing period products
2023-10-24
When it comes to the question of who gets to be a scientist, gender disparities are well-documented in many fields. Patching the infamous “leaky pipeline” can be a thorny problem, but during the 2022–2023 school year, the Department of Chemistry at the University of Oxford took a simple and practical step forward: they began offering period products in the department’s bathrooms. In an article publishing October 25 in the journal Trends in Chemistry, three students involved in the Oxford Period Project and their supervising ...