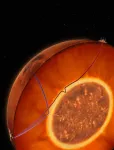
Scientists discover molten layer covering Martian core
New NASA InSight research reveals a liquid silicate ‘blanket’ wrapped around Mars’ core, leading to new clues about the planet’s evolutionary history and the loss of its potential to sustain life
2023-10-25
(Press-News.org) NASA’s InSight mission to Mars helped scientists map out Mars’ internal structure, including the size and composition of its core, and provided general hints about its tumultuous formation.
But findings from a new paper published in the journal Nature could lead to reanalysis of that data. An international team of researchers discovered the presence of a molten silicate layer overlying Mars’ metallic core—providing new insights into how Mars formed, evolved and became the barren planet it is today.
Published on October 25, 2023, the team’s paper details the use of seismic data to locate and identify a thin layer of molten silicates (rock-forming minerals that make up the crust and mantle of Mars and Earth) lying between the Martian mantle and core. With the discovery of this molten layer, the researchers determined that Mars’ core is both denser and smaller than previous estimates, a conclusion that better aligns with other geophysical data and analysis of Martian meteorites.
Vedran Lekic, a professor of geology at the University of Maryland and co-author of the paper, compared the molten layer to a ‘heating blanket’ covering the Martian core.
“The blanket not only insulates the heat coming from the core and prevents the core from cooling, but also concentrates radioactive elements whose decay generates heat” Lekic said. “And when that happens, the core is likely to be unable to produce the convective motions that would create a magnetic field—which can explain why Mars currently doesn’t have an active magnetic field around it.”
Without a functional protective magnetic field around itself, a terrestrial planet such as Mars would be extremely vulnerable to harsh solar winds and lose all the water on its surface, making it incapable of sustaining life. Lekic added that this difference between Earth and Mars could be attributed to differences in internal structure and the different planetary evolution paths the two planets took.
“The thermal blanketing of Mars’ metallic core by the liquid layer at the base of the mantle implies that external sources are necessary to generate the magnetic field recorded in the Martian crust during the first 500 to 800 million years of its evolution,” said the paper’s lead author Henri Samuel, a scientist with the French National Center for Scientific Research. “These sources could be energetic impacts or core motion generated by gravitational interactions with ancient satellites which have since then disappeared.”
The team’s conclusions support theories that Mars was at one time a molten ocean of magma that later crystallized to produce a layer of silicate melt enriched in iron and radioactive elements at the base of the Martian mantle. The heat emanating from the radioactive elements would then have dramatically altered the thermal evolution and cooling history of the red planet.
“These layers, if widespread, can have pretty big consequences for the rest of the planet,” Lekic said. “Their existence can help tell us whether magnetic fields can be generated and maintained, how planets cool over time, and also how the dynamics of their interiors change over time.”
NASA’s InSight mission officially ended in December 2022 after more than four years of collecting data on Mars, but the analysis of the observations continues. Samuel, Lekic and their co-authors are among the latest researchers to reexamine prior models of Mars using seismology to confirm the planet’s structure and turbulent history.
"This new discovery of a molten layer is just one example of how we continue to learn new things from the completed InSight mission,” Lekic said. “We hope that the information we’ve gathered on planetary evolution using seismic data is paving the way for future missions to celestial bodies like the moon and other planets like Venus.”
###
The paper, “Geophysical evidence for an enriched molten silicate layer above Mars’ core,” was published in Nature on October 25, 2023.
This research was supported by NASA (Award Nos. 80NSSC18K1628, 80NSSC19M0216 and 80NSSC18K1680), the National Center for Space Studies and the French National Research Agency (Award Nos. ANR-19-CE31-0008-08 and ANR-18-IDEX-0001), the European Research Council (Award No. 101019965) and the U.K. Space Agency (Award No. ST/W002515/1). This story does not necessarily reflect the views of these organizations.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-10-25
Scientists have long debated the Anthropocene Epoch, a proposed unit of geologic time corresponding to the most recent period in history. It’s characterized by substantial human impact on the planet.
Are we living in the Anthropocene? And if we are, then when did it start?
In a research article published this month in The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, The University of Toledo’s Dr. Trisha Spanbauer and Stanford University’s Dr. M. Allison Stegner lend credence to the argument for its existence. The pair analyzed open-source data to track vegetation ...
2023-10-25
Key takeaways
47.5% of respondents ages 13–24 feel most TV shows and movie plots don’t need sexual content; 51.5% want to see more focus on friendships and platonic relationships.
56% of those aged 10–24 prefer original content over franchises and remakes.
Twice as many adolescents prefer binge releases over weekly drops.
Adolescents want to see lives like their own depicted on screen.
This year’s Teens & Screens report from UCLA’s Center for Scholars & Storytellers, or CSS, found that teens — plus the 18- to 24-year-old demographic that advertisers typically ...
2023-10-25
Existing air pollution regulations will reduce thousands of premature adult deaths in the UK, but even the most effective technically feasible actions, which will save thousands more lives, will do little to protect the country’s sensitive ecosystems, find UCL researchers.
The new research, published in GeoHealth, found that existing air pollution regulations could avoid 6,751 early deaths amongst adults in the UK by 2030 compared to if no regulations existed. That estimate nearly doubles to 13,269 avoided adult premature deaths if all possible technically feasible measures are employed to reduce air pollution immediately.
However, existing regulations don’t ...
2023-10-25
It’s the day after the Baltimore Orioles clinched the American League East Championship with their 100th win of the season, and lifelong fan Tim Evans is showing his pride on his sleeve.
“It’s so great,” Evans, 62, says with a huge smile, wearing his orange O’s jersey.
The last time the Orioles won the AL East was in 2014, the same year Evans was diagnosed with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), a progressive nervous system disease that causes muscle weakness and loss of motor and speech functions. Evans currently has severe speech and swallowing problems. He can talk slowly, but it’s hard for most people to understand him.
However, ...
2023-10-25
(LOS ANGELES) – October 25, 2023 - The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) has developed a novel organ-on-a-chip device for measuring electrical resistance across endothelial barriers. This chip had carbon-based, screen-printed electrodes incorporated into a multi-layered, microfluidic chip fabricated by a simple and cost-effective method.
Endothelial cells line blood and lymph vessels of the body and form a barrier layer which controls the flow of fluid and substances to and from the vessels and surrounding tissues. Study of the crucial roles ...
2023-10-25
(SAN ANTONIO, OCTOBER 25, 2023)—The National Science Foundation (NSF) has awarded a five-year, $3.6 million grant to two professors at The University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA) to develop a better way to communicate engineering acumen to diverse engineering classes.
Joel Alejandro Mejia and M. Sidury Christiansen are collaborating on an ethnographic project, “Rhetorical Engineering Education to Support Proactive Equity Teaching and Outcomes (RESPETO).” The project will include a handbook of recommended pedagogical approaches to address exclusionary language and linguistic practices in engineering classes.
The project was motivated by several factors. Among them, ...
2023-10-25
Researchers from TU Dortmund University and RWTH Aachen University published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines how specific types of marketing knowledge contributions have developed over the past few decades and suggests ways to move the field toward “big picture” theories that will have greater impact.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Conceptual Contributions in Marketing Scholarship: Patterns, Mechanisms, and Rebalancing Options” and is authored by Bastian Kindermann, ...
2023-10-25
Opening a clamshell of berries and seeing them coated in fuzzy mold is a downer. And it’s no small problem. Gray mold and other fungi, which cause fruit to rot, lead to significant economic losses and food waste. Now, researchers report in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry that compounds from sunflower crop waste prevented rotting in blueberries. They suggest the food industry could use these natural compounds to protect against postharvest diseases.
Sunflowers are cultivated around the world for their seeds and oil, but the flower stems — known as receptacles — are generally considered to be a waste product. Noting that this crop is particularly ...
2023-10-25
The Global Coalition for Adaptive Research (GCAR) in collaboration with the University of Pittsburgh and UPMC, on behalf of the REMAP-CAP Investigator Network, announce clinical trial results examining the use of vitamin C and simvastatin to treat severely ill patients with COVID-19.
Published today in JAMA and NEJM, and presented at the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine in Milan, the studies are part of the ongoing Randomized Embedded Multifactorial Adaptive Platform for Community Acquired Pneumonia (REMAP-CAP) trial.
Simvastatin, a widely available and inexpensive drug that is included on the WHO list of essential medicines, ...
2023-10-25
About The Study: In hospitalized patients with COVID-19, vitamin C had low probability of improving the primary composite outcome of organ support–free days and hospital survival in two harmonized randomized clinical trials.
Authors: Neill K. J. Adhikari, M.D.C.M., M.Sc., of the Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre in Toronto, and Francois Lamontagne, M.D., M.Sc., of the Universite de Sherbrooke in Sherbrooke, Canada, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists discover molten layer covering Martian core
New NASA InSight research reveals a liquid silicate ‘blanket’ wrapped around Mars’ core, leading to new clues about the planet’s evolutionary history and the loss of its potential to sustain life