(Press-News.org) Scientists have long known that chloroplasts help plants turn the sun’s energy into food, but a new study, led by plant biologists at the University of California, Davis, shows that they are also essential for plant immunity to viral and bacterial pathogens.
Chloroplasts are generally spherical, but a small percentage of them change their shape and send out tube-like projections called “stromules.” First observed over a century ago, the biological function of stromules has remained enigmatic.
Previous studies have shown that chloroplasts produce more stromules when a plant detects an infection. Stromules aid in clustering chloroplasts around the nucleus and function as conduits to transport pro-defense signals from chloroplasts to the nucleus. Despite these findings, researchers have not been able to determine the role of stromules in immunity, as no genes involved with the formation of stromules have been identified.
In the new study, Savithramma Dinesh-Kumar, professor and chair in the Department of Plant Biology, graduate student Nathan Meier and colleagues have identified a key protein involved in stromule biogenesis during immunity. Their findings were published Oct. 25 in Science Advances.
A hidden player in immune defense
In order to test the stromules’ role in immunity, researchers need to switch them off and then observe how stromule-less plant cells fare when faced with a pathogen. However, without knowing which genes are involved with the creation of stromules, researchers have had no way to know which genes to switch off.
To overcome this roadblock, Dinesh-Kumar and his colleagues turned to kinesins, proteins that function as tiny motors that allow molecules and organelles to move around a cell. This intracellular movement usually involves the cell’s cytoskeleton, which is made up of two different types of fiber: large microtubules and smaller actin filaments.
The researchers wanted to investigate a type of kinesin that is unique to plants and capable of binding both microtubules and actin filaments. The researchers found that overexpression of one of these kinesins, KIS1, induced stromule formation in the absence of pathogen infection. When the researchers manipulated tobacco and Arabidopsis plants so that they could not produce the KIS1 kinesin, they found that neither plant was able to form stromules, and their chloroplasts did not migrate toward the nucleus. This left the plants unable to defend themselves from introduced pathogens.
Secrets of chloroplast movement
To disentangle the roles of microtubules and actin, the researchers engineered one set of KIS1 variants that could only bind to microtubules, and another that could only bind to actin. Expression of these variants in tobacco showed that KIS1 needs to bind to microtubules in order for chloroplasts to form stromules, but in order for chloroplasts to move toward the nucleus, it must also bind to actin.
The team also wanted to know how stromules fit into the bigger picture of plant immunity. By using genetic manipulation to switch different immune signals off, they found that stromule formation is triggered by molecular signaling and that an intact immune signaling system is needed in order for stromules to form.
“If we remove any of the known immune signaling genes, the chloroplasts lose the ability to make stromules, which suggests that these structures are an integral part of the immune signaling pathways that activate defense,” said Dinesh-Kumar.
New light on plant immunity
This study is the first evidence of a plant kinesin directly involved in plant immunity. It’s also the first time that scientists have identified a gene—KIS1—involved in chloroplast stromule biogenesis, which opens the door to understanding the role of chloroplast stromules and why chloroplasts cluster around the nucleus during plant immune defense.
“If we can better understand at the cellular level how organelles like chloroplasts help cells to defend themselves, we could help to engineer resistance to the pathogen.” Dinesh-Kumar said.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture. Additional authors include Kody Seward and Jeffrey Caplan of the Delaware Biotechnology Institute and the University of Delaware.
END
Chloroplasts do more than photosynthesis: They’re also a key player in plant immunity
New research sheds light on chloroplast structures 100 years after discovery
2023-10-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mystery of the Martian core solved
2023-10-25
For four years, NASA’s InSight lander recorded tremors on Mars with its seismometer. Researchers at ETH Zurich collected and analysed the data transmitted to Earth to determine the planet’s internal structure. “Although the mission ended in December 2022, we’ve now discovered something very interesting,” says Amir Khan, a Senior Scientist in the Department of Earth Sciences at ETH Zurich.
An analysis of recorded marsquakes, combined with computer simulations, paint ...
Book examines history of standardized tests in American schools, why they persist
2023-10-25
LAWRENCE — For the past 50 years, standardized tests have been the norm in American schools, a method proponents say determines which schools are not performing and helps hold educators accountable. Yet for the past 20 years, it has become clear that testing has failed to improve education or hold many accountable, according to a University of Kansas researcher whose new book details its history.
“An Age of Accountability: How Standardized Testing Came to Dominate American Schools and Compromise Education” by John Rury, professor emeritus of educational leadership & policy studies at KU, tells the story of how testing became ...
On the trail of the silver king: Researchers at UMass Amherst reveal unprecedented look at tarpon migration
2023-10-25
October 25, 2023
On the Trail of the Silver King: Researchers at UMass Amherst Reveal Unprecedented Look at Tarpon Migration
Culmination of more than five-years’ research, $1.1 million in grants and collaborations with anglers, industry and Bonefish & Tarpon Trust promises to reshape conservation efforts
AMHERST, Mass. – New research led by the University of Massachusetts and published recently in Marine Biology unveils a first-of-its-kind dataset, gathered over five years, that gives the finest-grained ...
Stanford collaboration offers new method to analyze implications of large-scale flood adaptation
2023-10-25
During the summer of 2022, the Indus River in Pakistan overflowed its banks and swept through the homes of between 30-40 million people. Eight million were permanently displaced, and at least 1,700 people died. Damages to crops, infrastructure, industry, and livelihoods were estimated at $30 billion. In response to this, Stanford researchers from the Natural Capital Project (NatCap) and the Carnegie Institution for Science collaborated on a new way to quickly calculate the approximate depths of ...
Amid cocaine addiction, the brain struggles to evaluate which behaviors will be rewarding
2023-10-25
Rutgers researchers have used neuroimaging to demonstrate that cocaine addiction alters the brain’s system for evaluating how rewarding various outcomes associated with our decisions will feel. This dampens an error signal that guides learning and adaptive behavior.
The observed changes likely propagate a mysterious aspect of some addictive behavior—the tendency to keep doing harmful things that sometimes have no immediate benefit. Those changes also make it harder for long-term users of cocaine to correctly estimate how much benefit they’ll derive from other available actions.
Experts have long hypothesized that cocaine and other addictive ...
Study shows thyroid cancer is more common among transgender female veterans
2023-10-25
A new study by UC Davis Health endocrinology researchers has shown a high prevalence of thyroid cancer among transgender female veterans. It’s the first evidence of such a disparity in the transgender female population in the United States.
The researchers presented their findings this month at the American Thyroid Association Annual Meeting.
The study was prompted by what the doctors noticed while caring for patients.
“As a group of physicians, we observed anecdotally through clinical observation that among 50 transgender women in our clinic, two were diagnosed with thyroid ...
Study suggests marijuana use damages brain immune cells vital to adolescent development
2023-10-25
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
In a mouse study designed to explore the impact of marijuana’s major psychoactive compound, THC, on teenage brains, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they found changes to the structure of microglia, which are specialized brain immune cells, that may worsen a genetic predisposition to schizophrenia. The findings, published Oct. 25 in Nature Communications, add to growing evidence of risk to brain development in adolescents who smoke or eat marijuana products.
“Recreational ...
NASA's Webb makes first detection of heavy element from star merger
2023-10-25
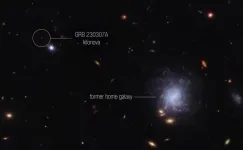
A team of scientists has used multiple space and ground-based telescopes, including NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, and NASA’s Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory, to observe an exceptionally bright gamma-ray burst, GRB 230307A, and identify the neutron star merger that generated an explosion that created the burst. Webb also helped scientists detect the chemical element tellurium in the explosion’s aftermath.
Other elements near tellurium on the periodic table – like iodine, which is needed ...
A bold plan to 3D print artificial coral reef
2023-10-25
Inspired by the remarkable durability of ancient Roman construction materials in seawater, a University of Texas at Arlington civil engineering researcher is attempting to duplicate Roman concrete by developing 3D-printed materials to restore damaged or dying coral reefs.
Warda Ashraf, associate professor in the Department of Civil Engineering, will lead a multidisciplinary team, funded by a $2 million National Science Foundation (NSF) grant, that aims to build 3D-printed artificial reefs. The team’s project is titled “Carbon Sequestration and Coastal Resilience Through 3D Printed Reefs” ...
ESnet turns on 400G circuits to four DOE national labs, supercharging multi-site scientific research
2023-10-25
– By Bonnie Powell
Today’s world-changing scientific research is being conducted by collaborators at far-flung national laboratories who require high-speed, low-latency access to high performance computing facilities and specialized instruments. The Energy Sciences Network (ESnet) is proud to announce that it has supercharged the current and future bandwidth for four of the Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) national laboratories and user facilities, unleashing 400 Gigabit per second (400G) capability for Argonne National Laboratory, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
[Press-News.org] Chloroplasts do more than photosynthesis: They’re also a key player in plant immunityNew research sheds light on chloroplast structures 100 years after discovery