(Press-News.org) JMIR Infodemiology Editor-in-Chief: Tim Ken Mackey, MAS, PhD welcomes submissions to a special theme issue “Exploring the Intersection Between Health Information, Disinformation, and Generative AI Technologies.”
JMIR Infodemiology, currently indexed in PubMed Central, PubMed, Scopus, DOAJ, and CABI, is a peer-reviewed premier journal in the field of infodemiology, health information, data science, and misinformation and is inviting submissions from different disciplines of health communication, public health, informatics, data science, social and computational science, and engineering to explore the potential impact of large language models (LLMs) on health-related topics.
Specific topics of interest for this special issue include:
Infodemics, Misinformation, and Disinformation in the Context of LLMs and Emerging AI Technologies
The proliferation of health-related misinformation and disinformation presents significant challenges to public health and well-being in this era of rapid technological advancement.
Advancing Research Methods on LLMs and Emerging AI Technologies
We encourage submissions that advance interdisciplinary methodologies examining the potential impact of LLMs and emerging AI.
The Role of Public Health and Medical Professionals in Utilizing Generative AI
Public health and health care professionals play an important role in shaping the health information ecosystem. We are particularly interested in submissions that discuss the involvement of public health and medical practitioners in using LLMs to address misinformation.
Examining the use of LLMs Through the Lens of Health Equity
The rollout of new technological tools such as LLMs has the potential to make health information more accessible, but it may also result in unintended consequences, including exacerbating health disparities.
The deadline for submissions is March 31, 2024. All accepted manuscripts will be published as part of the JMIR Infodemiology special issue titled “Exploring the Intersection Between Health Information, Disinformation, and Generative AI Technologies.”
To learn more please visit: https://infodemiology.jmir.org/announcements/412
###
About JMIR Publications
JMIR Publications is a leading, born-digital, open access publisher of 35+ academic journals and other innovative scientific communication products that focus on the intersection of health and technology. Its flagship journal, the Journal of Medical Internet Research, is the leading digital health journal globally in content breadth and visibility, and it is the largest journal in the medical informatics field.
To learn more about JMIR Publications, please visit https://www.JMIRPublications.com or connect with us via Twitter, LinkedIn, YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram.
Head office: 130 Queens Quay East, Unit 1100, Toronto, ON, M5A 0P6 Canada
Media contact: communications@JMIR.org
END
Yale School of Nursing (YSN) has received a landmark gift — the largest single donation in the school’s history. The $11.1 million gift from a generous anonymous donor was announced on Sept. 21 by Azita Emami, dean of the Yale School of Nursing, at an event kicking off the school’s yearlong centennial celebration (September 2023–May 2024).
This endowed gift will support the YSN Community Scholars program, providing full-tuition scholarships to six students each year in the Master of Science in Nursing ...
A Principals’ meeting of the Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) has confirmed that HyProMag Ltd, which uses a technology developed by the University of Birmingham’s Magnetic Materials Group has been selected as one of the projects that will help to develop responsible critical mineral supply chains.
Formed in 2022 by 14 governments, the Mineral Security Partnership (MSP) aims to ensure adequate supplies of minerals such as rare earths to meet net zero-carbon goals. It aims to support public and private sector investments building diverse, secure, and responsible global critical minerals supply chains.
HyProMag was one ...
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have identified a small molecule named 5D4 that can suppress the growth of breast and ovarian cancers in animal models. 5D4 works by binding to TopBP1 protein in cancer cells, disrupting its interactions with several pathways that promote cancer growth. Combining 5D4 with another cancer inhibitor, talazoparib, enhances the effectiveness of the anti-cancer activity. The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, strongly supports continuing the investigation toward further developing this strategy for clinical use.
“Cancer development involves many steps of genetic alterations and signaling ...
When targeting problem proteins involved in causing or spreading disease, a drug will often clog up a protein’s active site so it can’t function and wreak havoc. New strategies for dealing with these proteins can send these proteins to different types of cellular protein degradation machinery such as a cell’s lysosomes, which act like a protein wood chipper.
In a new study published in Science on Oct. 20, Stanford chemists have uncovered how one of the pathways leading to this protein “wood chipper” works. In doing so, they have opened the ...
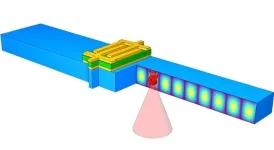
Acoustic resonators are everywhere. In fact, there is a good chance you’re holding one in your hand right now. Most smart phones today use bulk acoustic resonators as radio frequency filters to filter out noise that could degrade a signal. These filters are also used in most Wi-Fi and GPS systems.
Acoustic resonators are more stable than their electrical counterparts, but they can degrade over time. There is currently no easy way to actively monitor and analyze the degradation of the material quality of these widely used devices.
Now, researchers at the Harvard John ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. – A study spearheaded by Oregon State University has shown why certain polyunsaturated fatty acids work to combat a dangerous liver condition, opening a new avenue of drug research for a disease that currently has no FDA-approved medications.
Scientists led by Oregon State’s Natalia Shulzhenko, Andrey Morgun and Donald Jump used a technique known as multi-omic network analysis to identify the mechanism through which dietary omega 3 supplements alleviated nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, usually abbreviated to NASH.
The mechanism involves ...
A perspective recently published in Frontiers in Nutrition underscores the unique role starchy vegetables play as a vital vehicle for essential nutrients. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans currently recommend that most adults consume five to six cups (or cup equivalents) of starchy vegetables each week to help meet their total vegetable goals.1 Yet, as confusion around “good versus bad carbs” persists among consumers, there is a risk of starchy vegetable avoidance in favor of other carbohydrate foods perceived as ...
When it comes to the architecture of the human genome, it’s only a matter of time before harmful genes — genes that could compromise future generations — arise in a population. These mutations accumulate in the gene pool, primarily affected by a population’s size and practices like marrying within a small community, according to researchers.
But much of the information about the effects of a population’s mutation load is based on genetic theory, with limited direct evidence concerning the effects on evolutionary fitness, or fertility.
New research from University ...
New Haven, Conn. — When Yale neuroscientist Joy Hirsch used sophisticated imaging tools to track in real time the brain activity of two people engaged in conversation, she discovered an intricate choreography of neural activity in areas of the brain that govern social interactions. When she performed similar experiments with two people talking on Zoom, the ubiquitous video conferencing platform, she observed a much different neurological landscape.
Neural signaling during online exchanges was substantially suppressed compared to activity observed ...
In the 2009 film "Gifted Hands," based on a true story, the audience follows Black neurosurgeon Dr. Ben Carson as he successfully performs three risky surgeries, earning praise from the media and medical community. This movie was not only a hit with critics and audiences, but it also inspired Bismarck Christian Odei, MD, an assistant professor in radiation oncology at Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah, to follow his passion.
“Seeing a physician who looked like me, ...