(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON (October 27, 2023) – Boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) have a clinically proven, new treatment option with the Food and Drug Administration’s approval Thursday of vamorolone, a steroidal-type, anti-inflammatory drug developed based on research performed at Children’s National Hospital.
Created by ReveraGen BioPharma Inc., vamorolone has a molecular structure similar to traditional corticosteroids, which are currently used to treat DMD. Yet its structure was found to be chemically different enough to reduce unwanted side effects, including brittle bones and reduced stature. Nearly two decades ago, ReveraGen leaders – President and CEO Eric Hoffman, Ph.D., and Vice President for Research Kanneboyina Nagaraju, D.V.M., Ph.D. – launched research efforts into the drug when they led the Center for Genetic Medicine Research at Children’s National. They worked with then-Chief Academic Officer Mark Batshaw, M.D., on the new clinical option.
“Throughout my career, I have treated children with DMD, and I have seen over time how their shorter heights and brittle bones impact them physically and emotionally – in terms of their self-esteem and ability to participate in activities,” Dr. Batshaw said. “This drug should help these boys function more effectively and prevent certain long-term complications.”
Muscular dystrophy includes a group of degenerative genetically inherited neuro-muscular diseases that strike only boys. DMD is the most common, severe and life-threatening form of muscular dystrophy. ReveraGen studied vamorolone for patients ages two years and up in the hopes of providing a new, FDA-approved treatment option for these children. In clinical trials, daily treatment with vamorolone improved muscle strength and stature with results comparable to prednisolone, but without some of the most impactful side effects of steroids, particularly the stunted growth and weakened bones.
Kolaleh Eskandanian, Ph.D., M.B.A., P.M.P., vice president and chief innovation officer for Children’s National, said Drs. Hoffman and Nagaraju’s work on the drug paved the way for entrepreneurship at the hospital, as they were the first faculty members to launch a spin-off company. Since then, more than 130 faculty members have been named as inventors on 132 patents. Children’s National is now home to Innovation Ventures, the hospital’s intellectual property development and commercialization arm, which provides guidance and resources to academic entrepreneurs who introduce a concept for pediatric medical products.
“We cannot wait to see the tremendous effort behind vamorolone in the hands of patients and clinicians treating Duchenne muscular dystrophy,” Eskandanian said. “Today’s FDA approval for ReveraGen shows the importance of supporting clinicians and researchers who are developing solutions to advance healthcare for children.”
Hoffman said the drug has been through a series of clinical trials showing advantages over the current treatment options. In 2024, Catalyst Pharma will market vamorolone under the trade name Agamree in the United States.
“Vamorolone was developed using a different business model and drug development approach, including partnerships with the National Institutes of Health, Department of Defense, the European Commission and more than a dozen international nonprofit foundations,” Dr. Hoffman said. “The collaborative, community-engaged approach—including 32 academic clinical sites in 11 countries—and the participation of hundreds of DMD families led to this approval today.”
Contact: Katie Shrader | media@childrensnational.org | 301-244-6760
###
About Children’s National Hospital
Children’s National Hospital, based in Washington, D.C., was established in 1870 to help every child grow up stronger. Today, it is the No. 5 children’s hospital in the nation and ranked in all specialties evaluated by U.S. News & World Report. Children’s National is transforming pediatric medicine for all children. The Children’s National Research & Innovation Campus opened in 2021, a first-of-its-kind pediatric hub dedicated to developing new and better ways to care for kids. Children’s National has been designated three times in a row as a Magnet® hospital, demonstrating the highest standards of nursing and patient care delivery. This pediatric academic health system offers expert care through a convenient, community-based primary care network and specialty care locations in the D.C. metropolitan area, including Maryland and Virginia. Children’s National is home to the Children’s National Research Institute and Sheikh Zayed Institute for Pediatric Surgical Innovation. It is recognized for its expertise and innovation in pediatric care and as a strong voice for children through advocacy at the local, regional and national levels. As a nonprofit, Children's National relies on generous donors to help ensure that every child receives the care they need.
For more information, follow us on Facebook, Instagram, Twitter and LinkedIn.
END
FDA approves muscular dystrophy drug built on Children’s National research
Vamorolone offers new treatment option with fewer side effects
2023-10-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
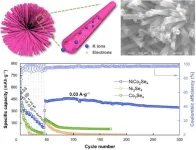
Electrodes with hollow nanotubes improve performance of potassium-ion batteries
2023-10-27
Researchers who are working to find alternatives to lithium-ion batteries have turned their attention to potassium-ion batteries. Potassium is an abundant resource and the technology functions in much the same way as lithium-ion batteries, but these batteries have not been developed at a large scale because the ionic radius causes problems in energy storage and substandard electrochemical performance.
To solve this problem, researchers are considering NiCo2Se4, a bimetallic selenide, to create sphere-shaped electrodes. The spheres are constructed with NiCo2Se4 nanotubes, which improve ...
USDA grant will help MU researchers address opioid epidemic in rural Missouri
2023-10-27
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- Childhood trauma is a key risk factor for future substance use disorder, overdose, and suicide. This is particularly problematic in rural areas where children experience higher rates of adverse childhood experiences (ACEs). ACEs are commonly defined as physical and emotional abuse and neglect, sexual abuse, parental separation or divorce, intimate partner violence, and having household members with serious mental illness, substance use disorder, or a history of incarceration.
Now, a three-year, U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) grant awarded to the University of Missouri will help virtually train various members of the workforce — ...
UiB researchers solve protein mystery
2023-10-27
Proteins are key to all processes in our cells and understanding their functions and regulation is of major importance.
“For many years, we have known that nearly all human proteins are modified by a specific chemical group, but its functional impact has remained undefined”, says professor Thomas Arnesen at the Department of Biomedicine, University of Bergen.
He explains:
“One of the most common protein modifications in human cells is N-terminal acetylation, which is an addition of a small chemical group (acetyl) at the starting tip (N-terminus) of a protein. The ...
Protein root discovery seals future of climate proof plants
2023-10-27
Researchers have discovered a protein that seals plant roots to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water from the soil, the discovery could help develop climate proof crops that require less water and chemical fertilizers.
Researchers from the University of Nottingham identified new components of the lignin barrier in plant roots and the specific function of dirigent proteins (DPs), located in the root endodermis that control water and nutrient uptake. Their findings have been published today in Science Direct.
Plant roots function by absorbing ...
A relational framework for microbiome research that includes Indigenous communities
2023-10-27
Research on the trillions of microorganisms that make up a person’s microbiome can lead to medical breakthroughs to treat diseases like inflammatory bowel syndrome and diabetes. According to Alyssa Bader, a Tsimshian Assistant Professor in the Department of Anthropology at McGill University, microbiome samples from Indigenous communities have the potential to further Western medicine, but those same communities often have been excluded from the research process and may miss out on the benefits that result from their contributions to science. ...
City of Hope part of successful international Phase 3 clinical trial evaluating sotorasib medication combination for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer
2023-10-27
LOS ANGELES — An international Phase 3 clinical trial found that metastatic colorectal cancer patients with a rare genetic tumor mutation called KRAS G12C experienced superior progression-free survival rates compared to standard of care when offered a combination treatment of KRAS inhibitor sotorasib and monoclonal antibody panitumumab. City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, was a participating site and a City of Hope researcher is the lead author of the The New England Journal of Medicine study published this week.
Standard ...
Team synthesizes a new polyoxometalate-based metal-organic complex
2023-10-27
A research team has synthesized a new polyoxometalate-based metal-organic complex that they then tested as a catalyst for the oxidation reactions of various sulfides. They found that the complex possesses excellent catalytic performance, good reusability, and structural stability.
The team’s work is published in the journal Polyoxometalates on October 19, 2023.
Scientists in many fields have explored the selective oxidation of sulfides to sulfoxides. Sulfoxides are organic compounds that contain sulfur and oxygen. These sulfoxides are high value-added chemicals in pharmaceuticals, agrochemistry, ...
The sunscreen paradox: McGill University researchers warn of ‘false sense of security’
2023-10-27
Sunscreen usage is climbing, but so are melanoma and skin cancer rates: this, researchers say, is the sunscreen paradox.
“The problem is that people use sunscreen as a ‘permission slip’ to tan,” said Dr. Ivan Litvinov, an Associate Professor in the Department of Medicine and Chair of the Dermatology Division at McGill University and co-author with Dr. Sandra Peláez, Dr. Richie Jeremian and Dr. Pingxing Xie of two recent studies that explore the sunscreen paradox.
“People think they are protected from skin cancer ...
Hybrid nanomaterials promise a sustainability boost across multiple industries
2023-10-27
Polyoxometalate (POM)-based nanohybrids potentially offer a step-change in sustainability across a wide variety of industries, but research into the substances is in its infancy. A group of researchers has produced a comprehensive review of the sector’s progress and challenges yet to be overcome.
A new class of nanoscale hybrid materials has the potential to improve sustainability across energy systems, transport, biosensors, water purification and even 3D printing, but the field is still very young. A group of researchers has produced a detailed overview ...
Pinktober brings attention to the TMIST international breast cancer screening trial as a new site opens in Thailand
2023-10-27
A clinical trial led by the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN) demonstrates how diversity among study participants is vital for reducing outcomes disparities. Among the vast group of women participating in the TMIST breast cancer screening trial--nearly 93,000 so far--21% self-identify as Black or African American. This diversity offers hope that once the trial reaches its enrollment goal of nearly 129,000 women, its results can better inform and tailor future breast cancer screening for all women.
The TMIST breast cancer study is investigating whether screening for breast cancer ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
The research that got sick veterans treatment
Study finds that on-demand wage access boosts savings and financial engagement for low-wage workers
Antarctica has lost 10 times the size of Greater Los Angeles in ice over 30 years
Scared of spiders? The real horror story is a world without them
New study moves nanomedicine one step closer to better and safer drug delivery
Illinois team tests the costs, benefits of agrivoltaics across the Midwest
Highly stable self-rectifying memristor arrays: Enabling reliable neuromorphic computing via multi-state regulation
Composite superionic electrolytes for pressure-less solid-state batteries achieved by continuously perpendicularly aligned 2D pathways
Exploring why some people may prefer alcohol over other rewards
How expectations about artificial sweeteners may affect their taste
[Press-News.org] FDA approves muscular dystrophy drug built on Children’s National researchVamorolone offers new treatment option with fewer side effects