(Press-News.org) About 80% of residents in the Lower Mainland, British Columbia, had been infected with SARS-CoV-2 by July 2023 and were at low risk for severe outcomes, but almost half of the oldest adults remained uninfected and were at highest risk of hospitalization and death due to COVID-19, according to a new study published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.230721.
The findings underscore the need to continue prioritizing older adults for COVID-19 vaccination.
"First-ever SARS-CoV-2 infections among older adults may still contribute substantial COVID-19 burden, reinforcing the importance of their continued prioritization for vaccination and their consideration in health care system planning," writes lead investigator Dr. Danuta Skowronski, BC Centre for Disease Control and the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, with coauthors.
Using population-based seroprevalence estimates of first-ever SARS-CoV-2 infection combined with administrative data on severe outcomes, researchers estimated the per infection risk of hospital admission and death. They found that by July 2023, more than 80% of children and adults younger than 50 had been infected and had a low risk of severe outcome, but more than 40% of adults aged 80 and older had never been infected with SARS-CoV-2 and had the highest risk of hospitalization and death.
The authors estimated that between July and December 2022 the risk of hospitalization for COVID-19 was about 1 in 30 new infections among adults 80 years and older, which was about 10 times higher than the risk among children younger than 5 years of age.
"Our estimates of the risk of hospital admission or death from a first-ever SARS-CoV-2 infection were low overall but derived in a highly vaccinated population. Risks are anticipated to be greater among unvaccinated and lower among previously infected groups of patients, with the lowest risk among those who are both vaccinated and previously infected," the authors write.
END
Risk of admission and death from COVID-19 low overall, but oldest adults remain vulnerable
2023-10-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
High engagement, high return: The secret to student success
2023-10-29
High engagement, high return. That’s the advice from education experts at the University of South Australia for teachers looking to improve student outcomes.
In a new study conducted in partnership with Flinders University and Melbourne Graduate School of Education, researchers found that less than a third of teachers are engaging students in complex learning, limiting student opportunities for building critical thinking and problem solving.
Filming and assessing* the content of classrooms ...
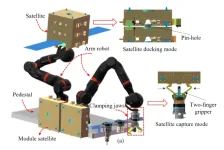
Robot space maintenance based on human arm dynamics
2023-10-28
On-orbit assembly has become a crucial aspect of space operations, where the manipulator frequently and directly interacts with objects in a complex assembly process. The traditional manipulator control has limitations in adapting to diverse assembly tasks and is vulnerable to vibration, leading to assembly failure. To address this issue, Researchers at Beijing Institute of Technology propose a human-like variable admittance control method based on the variable damping characteristics of the human arm. This method can effectively increase the safety, robustness, ...
Increasing risk of invasive species colonization on marine debris
2023-10-28
A groundbreaking scientific study conducted along the Southeast coast of India has unearthed a pressing environmental concern -the increasing risk of invasive species colonization on marine debris. The research, published recently in Marine Pollution Bulletin, delves into the critical interplay between plastic pollution and the introduction of non-indigenous organisms into Indian waters.
In recent years, the surge in anthropogenic litter in the ocean has provided an extensive array of substrates for marine ...
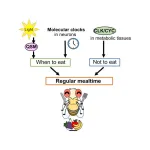
How do animals know it’s lunchtime?
2023-10-28
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have used fruit flies to study how daily eating patterns are regulated. They found that the quasimodo (qsm) gene helped sync feeding to light/dark cycles, but not in constant darkness: instead, the genes clock (clk) and cycle (cyc) keep eating/fasting cycles, while other “clocks” in nerve cells help sync it to days. Deciphering the molecular mechanism behind eating cycles helps us understand animal behavior, including our own.
Many members of the animal kingdom eat at roughly the same times each day. This is born out of the need to adapt to aspects of the environment, including ...
Interdisciplinary research team works to mitigate climate change effects in Texas Gulf Coast communities
2023-10-27
Experts in the Texas A&M University Department of Geography are teaming up with civil and chemical engineers and water resource, disaster recovery and public health researchers across the campus in a collaborative effort to better safeguard Texas Gulf Coast communities against climate-related emergencies, fueled by a three-year, $1.5 million grant from the National Academies Gulf Research Program (GRP).
The project, titled "Climate-LEAD: Climate Effects on Localized Environmental Health Disparities in Overburdened Texas Communities along Gulf Coast," is ...
An updated look at prostate cancer disparities
2023-10-27
Cedars-Sinai Cancer investigators have found that Black men respond as well as white men to systemic therapies for advanced prostate cancer when access to quality healthcare is equal, regardless of socioeconomic status. Their study, published today in the peer-reviewed Journal of Clinical Oncology, counters previous research suggesting that Black men receiving these therapies—which include hormone therapy, chemotherapy and immunotherapy—fare worse than white men do.
“We believe this is the most comprehensive look at this issue to date, and our findings suggest that, under the right conditions, Black men with metastatic ...
New battery technology could lead to safer, high-energy electric vehicles
2023-10-27
University of Maryland researchers studying how lithium batteries fail have developed a new technology that could enable next-generation electric vehicles (EVs) and other devices that are less prone to battery fires while increasing energy storage.
The innovative method, presented in a paper published Wednesday in the journal Nature, suppresses the growth of lithium dendrites—damaging branch-like structures that develop inside so-called all-solid-state lithium batteries, preventing firms from broadly commercializing the promising technology. But this new design for a battery “interlayer,” led by Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering ...
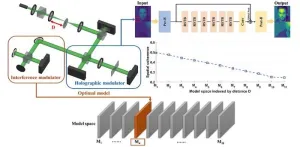
Clear holographic imaging in turbulent environments
2023-10-27
Holographic imaging has always been challenged by unpredictable distortions in dynamic environments. Traditional deep learning methods often struggle to adapt to diverse scenes due to their reliance on specific data conditions.
To tackle this problem, researchers at Zhejiang University delved into the intersection of optics and deep learning, uncovering the key role of physical priors in ensuring the alignment of data and pre-trained models. They explored the impact of spatial coherence and turbulence on holographic ...
$76,000 in grants awarded to entrepreneurs addressing health disparities in local communities
2023-10-27
DALLAS, October 27, 2023 — Approximately 50 million people in the United States are at higher risk for heart disease and/or stroke because they lack the most basic needs — healthy food, clean air and drinking water, quality education, employment, housing and access to health care. Historically, people of color -- including Black and Hispanic/Latino people, are at even higher risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) for these same reasons. Through the American Heart Association’s 2023 EmPOWERED to Serve Business Accelerator™, three local social entrepreneurs ...
Mechanics of breast cancer metastasis discovered, offering target for treatment
2023-10-27
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — The most lethal feature of any cancer is metastasis, the spread of cancer cells throughout the body. New research led by Penn State reveals for the first time the mechanics behind how breast cancer cells may invade healthy tissues. The discovery, showing that a motor protein called dynein powers the movement of cancer cells in soft tissue models, offers new clinical targets against metastasis and has the potential to fundamentally change how cancer is treated.
“This discovery marks a paradigm shift in many ways,” said Erdem Tabdanov, assistant professor of pharmacology at Penn State and a lead co-corresponding author on the study, recently published ...