(Press-News.org) New research suggests sleepiness during virtual meetings is caused by mental underload and boredom. Earlier studies suggested that fatigue from virtual meetings stems from mental overload, but new research from Aalto University shows that sleepiness during virtual meetings might actually be a result of mental underload and boredom.
‘I expected to find that people get stressed in remote meetings. But the result was the opposite – especially those who were not engaged in their work quickly became drowsy during remote meetings,’ says Assistant Professor Niina Nurmi, who led the study.
The researchers measured heart rate variability during virtual meetings and face-to-face meetings, examining different types of fatigue experiences among 44 knowledge workers across nearly 400 meetings. The team at Aalto collaborated with researchers at the Finnish Institute of Occupational Health, where stress and recovery are studied using heart rate monitors. The paper was published in the Journal of Occupational Health Psychology.
‘We combined physiological methods with ethnographic research. We shadowed each subject for two workdays, recording all events with time stamps, to find out the sources of human physiological responses,’ Nurmi says.
The study also included a questionnaire to identify people's general attitude and work engagement.
‘The format of a meeting had little effect on people who were highly engaged and enthusiastic about their work. They were able to stay active even during virtual meetings. On the other hand, workers whose work engagement was low and who were not very enthusiastic about their work found virtual meetings very tiring.’
It’s easier to maintain focus in face-to-face meetings than virtual ones, as the latter have limited cognitive cues and sensory input. ‘Especially when cameras are off, the participant is left under-stimulated and may start to compensate by multitasking,’ Nurmi explains.
Although an appropriate level of stimulation is generally beneficial for the brain, multitasking during virtual meetings is problematic. Only highly automated tasks, such as walking, can be properly carried out during a virtual meeting.
'Walking and other automated activities can boost your energy levels and help you to concentrate on the meeting. But if you're trying to focus on two things that require cognitive attention simultaneously, you can't hear if something important is happening in the meeting. Alternatively, you have to constantly switch between tasks. It’s really taxing for the brain,’ Nurmi says.
END
Virtual meetings tire people because we're doing them wrong
Drowsiness during virtual meetings results from lack of stimulation, not mental overload
2023-10-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The importance of the Earth’s atmosphere in creating the large storms that affect satellite communications
2023-10-30
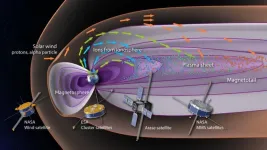
A study from an international team led by researchers from Nagoya University in Japan and the University of New Hampshire in the United States has revealed the importance of the Earth’s upper atmosphere in determining how large geomagnetic storms develop. Their findings reveal the previously underestimated importance of the Earth’s atmosphere. Understanding the factors that cause geomagnetic storms is important because they can have a direct impact on the Earth’s magnetic field such ...
Using lasers to ‘heat and beat’ 3D-printed steel could help reduce costs
2023-10-30
Researchers have developed a new method for 3D printing metal that could help reduce costs and make more efficient use of resources.
The method, developed by a research team led by the University of Cambridge, allows structural modifications to be ‘programmed’ into metal alloys during 3D printing, fine-tuning their properties without the ‘heating and beating’ process that’s been in use for thousands of years.
The new 3D printing method combines the best qualities of both worlds: the complex shapes that 3D printing makes possible, and the ability to engineer ...
Positive messages can mitigate harm from objectified fitness posts
2023-10-30
PULLMAN, Wash. – A few words of body appreciation can help counter the negative impact of viewing objectified images of female fitness influencers, according to a Washington State University study.
While fitness influencers say they want to inspire good physical health, research has found that their social media posts often inspire negative mental health, especially among younger women. The WSU experimental study, published in the journal Health Communication, revealed that the negative impact ...
Extreme heat projected to increase cardiovascular deaths
2023-10-30
For immediate release on Oct. 30, 2023 at 5 a.m. ET
Cardiovascular-related deaths due to extreme heat are expected to increase between 2036 and 2065 in the United States, according to a study supported by the National Institutes of Health. The researchers, whose work is published in Circulation, predict that adults ages 65 and older and Black adults will likely be disproportionately affected.
While extreme heat currently accounts for less than 1% of cardiovascular-related deaths, the modeling analysis predicted this will change because of a projected rise in summer ...
Heat-related cardiovascular deaths in the U.S. may more than double within decades
2023-10-30
Research Highlights:
Cardiovascular deaths from extreme heat in the United States are projected to increase by 162% by the middle of the century, based on a hypothetical scenario where currently proposed U.S. policies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions have been successfully implemented.
A more dire scenario forecasts cardiovascular deaths from extreme heat could increase by 233% in the next 13-47 years if there are only minimal efforts to reduce emissions.
The percentage increase in deaths ...
Penn research projects increase in US cardiovascular deaths due to extreme heat
2023-10-30
PHILADELPHIA— The number of heat related cardiovascular deaths in the United States will increase over the next four decades, according to a new analysis from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Extreme heat can impact heart health in many ways, including increased heart rate, changes in blood pressure, and increased inflammation. Left untreated, these issues can be deadly. The findings, published today in Circulation, also indicate that older adults and Black adults will experience greater increases in excess cardiovascular deaths due to extreme heat.
“As global temperatures rise, analyzing how demographic and environmental trends ...
Child Development Perspectives Journal Q&A: analyzing the stereotypes of adolescence
2023-10-30
In Western cultures, adolescence is often viewed as a time of rebellion and irresponsibility. A new article published in the journal Child Development Perspectives synthesized recent research on stereotypes of adolescence using an interdisciplinary approach which integrates developmental psychology, cultural psychology, and neuroscience.
The findings highlight the importance of avoiding the “one-size fits-all” assumptions about teen stereotypes across different cultures. In particular, the research ...
Trauma-informed training workshops prompt meaningful individual and organizational changes, according to outcomes surveys
2023-10-30
A McLean Hospital study of 598 people across various industries who underwent a two-day training workshop where they learned about trauma-informed care and how to deploy these skills within their organizations, found participants reported significant gains in knowledge of trauma and made improvements to organizational policies, according to a comparison of survey data collected before and after the trainings.
Among those trained, who included nurses, CEOs, academics and corrections officers, post-survey scores increased ...
Study of 1,000 selfies helps explain how we use them to communicate
2023-10-30
People have used self-portraits to communicate information about themselves for centuries — and digital cameras make it easier to share a self-portrait than ever before. But even though selfies are now almost ubiquitous, we don’t understand how people use them to communicate. So scientists from the University of Bamberg set out to investigate the semantics of selfies.
“Although the term ‘selfies’ is now celebrating its 21st birthday, and although selfies are known in art history for nearly 200 years in photography and more than 500 years in paintings, we still lack a clear classification of the different types of selfies,” ...
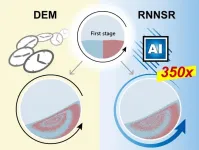
Powder engineering adds AI to the mix
2023-10-30
Imagine a world without powders. It may sound exaggerated, but our daily lives are intricately connected to powders in various ways from foods, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics to batteries, ceramics, etc. In all these industries, powder mixing is an important unit operation where different types of powders are mixed to achieve uniformity. However, it can be difficult to predict what conditions are optimal to achieve the desired uniformity as the process often relies on trial and error as well as engineers’ expertise.
Numerical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Virtual meetings tire people because we're doing them wrongDrowsiness during virtual meetings results from lack of stimulation, not mental overload