(Press-News.org) CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – The lungs were once at the forefront of SARS-Cov-2 research, but as reports of organ failure and other serious complications poured in, scientists set out to discover how and why the respiratory virus was causing serious damage to the body's major organs, including the lungs.
An interdisciplinary COVID-19 International Research Team (COV-IRT), which includes UNC School of Medicine’s Jonathan C. Schisler, PhD, found that SARS-CoV-2 alters mitochondria on a genetic level, leading to widespread “energy outages” throughout the body and its major organs. Their findings, published in Science Translational Medicine, explain how these effects contribute to long COVID symptoms and point to new therapeutic targets.
“We found that at peak infection time, there are distinct changes in different regions of the brain, including is a large decrease in mitochondrial genes in the cerebellum, the part of the brain that controls our muscles, balance, cognition, and emotion” said Schisler, assistant professor of pharmacology and member of the UNC McAllister Heart Institute. “The lung is the primary site of infection, but molecular signals are being transmitted affecting the entire body, with the heart, kidney, and liver being more affected than others, even long after the virus is gone.”
Every cell in our bodies is equipped with biological power stations known as mitochondria, which are especially important for maintaining the function of energy-demanding organs, such as the heart, brain, and lungs. Mitochondria require genes from their own genome (mitochondrial DNA) and nuclear DNA (nDNA) to create energy. Together, they instruct the mitochondria to convert oxygen molecules into cellular energy called adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Using nasal swabs and autopsy tissues from affected patients and animal models, researchers found that the virus blocks specific genes that use oxygen to create ATP, forcing the body to deplete finite energy reserves in the body. Without an energy source, cells throughout the body begin to starve, with the cells powering the brain and the heart suffering the most.
To keep the body functioning, cardiac and neural cells can resort to consuming their cellular parts, including their mitochondria. Eventually, the cells are deprived of their vital elements and initiate a form of programmed cell death called necroptosis. Unlike other forms of cellular death, necroptosis causes a cascade of ill effects, including a robust inflammatory response, which releases pro-inflammatory cells called cytokines throughout the body as the cells rupture. Uncontrolled necroptosis further enhances sepsis and organ failure.
Schisler says the ensuing cell death and inflammation may explain why patients with long COVID are likely to have persisting cardiovascular, cognitive, and inflammatory side effects after the initial infection has run its course.
“If we can start to appreciate and understand how each organ system adapts in the long-term to viral infection, and if we can discover the biology behind why people respond differently to SARS-CoV-2, we will be better positioned to combat chronic, long COVID symptoms that might be affecting cells in the heart, or the immune cells, or the neurons in our brain,” said Schisler.
Drawing on past research, the scientists know that a specific microRNA, a small piece of RNA that circulates throughout the body, increases in number during severe respiratory infections. This particular microRNA, which can affect mitochondrial gene expression in numerous cells and tissues, could be a new therapeutic target against SARS-CoV-2.
The new findings also highlight new ways to address the mitochondrial dysfunction that occurs during COVID infection. Diet, exercise, natural compounds, or a combination of the three, may be able to stimulate mitochondrial function, but whether or not they are effective for patients with long COVID is yet to be known. Moving forward, the research team will explore how long mitochondrial dysfunction lasts in the body, especially in cases of long-COVID, and how mitochondrial function can be restored.
About UNC School of Medicine
The UNC School of Medicine (SOM) is the state’s largest medical school, graduating more than 180 new physicians each year. It is consistently ranked among the top medical schools in the US, including 5th overall for primary care by US News & World Report, and 6th for research among public universities. More than half of the school’s 1,700 faculty members served as principal investigators on active research awards in 2021. Two UNC SOM faculty members have earned Nobel Prize awards.
# # # #
END
A groundbreaking study published in the journal Research in Aging sheds light on the financial challenges of housing-with-health-services models for low-income older adults. The report explores strategies for ensuring the sustainability of these beneficial efforts.
The study was conducted in partnership with Hebrew SeniorLife, a Harvard Medical School-affiliated nonprofit organization serving older adults in the Greater Boston area. It drew on insights from 31 key informational interviews and three focus groups ...
The next generation of cardiometabolic biomarkers should pave the way for earlier detection of risk factors for conditions such as obesity, diabetes and heart disease in children, according to a new scientific statement from the American Heart Association published in the journal Circulation.
“The rising number of children with major risk factors for cardiometabolic conditions represents a potential tsunami of preventable disease for our healthcare system,” says the statement’s lead author Michele Mietus-Snyder, M.D., ...
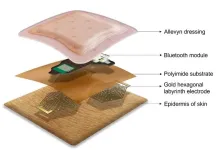
A new compact, lightweight, gel-free and waterproof electrocardiogram (ECG) sensor offers more comfort and less skin irritation, compared to similar heart monitoring devices on the market.
ECGs help manage cardiovascular disease – which affects around 4 million Australians and kills more than 100 people every day – by alerting users to seek medical care.
The team led by RMIT University in Australia has made the wearable ECG device that could be used to prevent heart attacks for people with cardiovascular disease, including in remote healthcare and ...
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- A new drug developed by professors from the School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences at Binghamton University has received Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for the treatment of patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), a common genetic disease that mostly affects young boys.
DMD is the most common genetic disease. It leads to the loss of the dystrophin protein in muscle tissues, with progressive weakness and challenges with day-to-day activities. The DMD gene is the largest gene in the human genome, ...
The antibody-drug conjugate trastuzumab deruxtecan is approved for various therapeutic indications. Since March 2023, it can also be used as monotherapy for the treatment of adults with unresectable or metastatic HER2-low breast cancer who have received prior chemotherapy at this disease stage or developed disease recurrence early after adjuvant chemotherapy. Treatment with trastuzumab deruxtecan is the first approved therapy for patients with HER2-low breast cancer. The German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) examined in an early benefit assessment whether the antibody-drug ...
Children and young people with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) use healthcare services twice as often in the two years before their diagnosis, a study by researchers at the University of Nottingham and King’s College London has found.
The research, published today in the journal Archives of Disease in Childhood shows that children with the neurodevelopmental disorder are twice as likely to see their GP, go to hospital for an admission, and even have operations, compared to children without ADHD.
The researchers say the results support the need for healthcare professionals to consider a potential diagnosis of ADHD in children who ...
In the late 1970s, the relationship between the c-Src gene and cancer was discovered. The first oncogene was identified.
Since then, c-Src has been found to be overactivated in half of colon, liver, lung, breast, prostate and pancreatic tumors, but its function is not yet fully understood.
CNIO researchers have now discovered that this oncogene is capable of 'self-activation', by means of a previously undescribed molecular mechanism. This finding has implications for the development of new drugs.
In ...
Philadelphia, October 31, 2023 – Heart attacks, or acute myocardial infarction (MI), are one of the leading causes of death worldwide. The newly released Canadian Cardiovascular Society Classification of Acute Myocardial Infarction (CCS-AMI) appearing in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology, published by Elsevier, presents a four-stage classification of heart attack based on heart muscle damage. This work by a group of noted experts has the potential to stratify risk more accurately in heart attack patients and lays the groundwork for development of new, injury-stage-specific and tissue ...
Researchers from MIT and NVIDIA have developed two techniques that accelerate the processing of sparse tensors, a type of data structure that’s used for high-performance computing tasks. The complementary techniques could result in significant improvements to the performance and energy-efficiency of systems like the massive machine-learning models that drive generative artificial intelligence.
Tensors are data structures used by machine-learning models. Both of the new methods seek to efficiently exploit what’s ...
A paper published in Trends in Cancer explains the advantages of RENACER, the world’s first repository of live brain metastases samples, created by researchers at CNIO.
Live samples allow researchers to study the way cancer cells respond to drugs. This paves the way to create avatars for each individual patient to test out possible therapies before applying them.
RENACER is made up of around twenty hospitals, who attended their first general assembly meeting today at the Fundación Ramón Areces, the foundation that is funding the ...