(Press-News.org) A research team led by Cleveland Clinic and Oregon Health and Science University (OHSU) has developed a new method for mapping how the parts of the brain "speak" to each other, critical to understanding behavior changes in patients with neurological disease.
Diseases like Alzheimer's disease change how patients communicate and act, affecting their relationships and well-being. Cleveland Clinic's Hod Dana, PhD, is collaborating with Jacob Raber, PhD, an OHSU behavioral neuroscientist, on mapping out the electrical paths that connect and coordinate the parts of the brain needed to complete different tasks.
"Effects on behavior and personality in Alzheimer's disease and related disorders are caused by changes in brain function," Dr. Dana says. "If we can understand exactly how the changes occur, we may figure out how to slow down the process or to stop it. Recording brain activity patterns that underlie behavioral changes is the first step to bridging the gap."
Decision-making, forming a memory or completing a task all involve brainwaves, signaling pathways that use cells called neurons. To study how brainwaves influence behavior and decision making, researchers observe as neurons turn "on" and "off" across the organ in different situations. Current technologies are unable to map the whole brain while still identifying the single cells. CaMPARI images can be captured during behavior, highlighting neurons that are active as red and inactive neurons as green. After the test is completed, the red and green markers remain bright for several days. This allows researchers to capture a series of images to track the brain's activity by mapping where the red appears within the brain.
The team recently published results in Nature Communications on using a calcium sensor system called CaMPARI (Calcium-modulated photoactivatable ratiometric integrator) to map brain activity in preclinical models while completing cognitive tasks. Drs. Dana and Raber plan to use CaMPARI in preclinical work to see how Alzheimer's-related genes affect the way our neurons signal through our brains in learning and memory.
Drs. Dana and Raber say they hope to take what they learn from their results to develop tests and interventions that can improve the quality of life for patients, providing better treatment options.
"We now have the capability to study the relationship between brain activation and cognitive performance at an unprecedented level," says Dr. Raber. "These are the first steps in developing strategies to reverse those changes and improve cognitive performance in those affected by neurological conditions. The future of behavioral and cognitive neuroscience looks bright."
This work was funded by NIH R21AG065914 and U01NS123658.
END
Non-invasive technology maps brain activity to investigate behavior changes in neurological disease
The new method will be used in preclinical research with the goal of improving care for patients with neurological disease
2023-11-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NIH funding helps Ghose Lab invest in innovative imaging equipment
2023-11-01
UTA will soon add a new piece of cutting-edge equipment to its already impressive and growing research armamentarium—a type of super-resolution microscope (SRM) that allows biologists to see structures within a cell in even finer detail.
The SRM will come to UTA because of additional grant funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to the lab of Piya Ghose, an assistant professor of biology at UTA. This nearly $250,000 award supplements Ghose’s existing NIH/National Institute of General Medical ...
Domestic violence involving firearms increased during COVID-19 pandemic
2023-11-01
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — Domestic violence went down or stayed the same during the first 10 months of the COVID-19 pandemic in five major U.S. cities. However, domestic violence involving firearms increased in three of those cities, according to a new UC Davis study published in the Journal of Family Violence.
“The increase in firearm domestic violence is concerning, as abuser firearm access is a risk factor for lethality,” said Elizabeth Tomsich, a research data analyst at the UC Davis Violence Prevention Research Center and ...
Microbiology: River plastics may harbour potential pathogens and antimicrobial resistance genes
2023-11-01
Microbial communities growing on plastic debris in rivers may have the capacity to harbour potentially pathogenic microbes and act as reservoirs of antimicrobial resistance genes, according to a study published in Microbiome. The findings also highlight differences in the potential pathogens and antimicrobial resistance genes that new and degraded plastics may have the capacity to harbour.
Vinko Zadjelovic, Elizabeth Wellington, Joseph Christie-Oleza and colleagues characterised the microbial communities found on the surface ...
High metabolism is an early sign of Alzheimer’s disease
2023-11-01
An early phase in the process of developing Alzheimer’s disease is a metabolic increase in a part of the brain called the hippocampus, report researchers from Karolinska Institutet in a study published in Molecular Psychiatry. The discovery opens up for new potential methods of early intervention.
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of dementia and strikes about 20,000 people in Sweden every year. Researchers now show that a metabolic increase in the mitochondria, the cellular power ...
Trust is the most important factor for British South Asians when taking part in genetic research to tailor medications
2023-11-01
Researchers from Queen Mary University of London have gathered detailed insights from the British South Asian community that could lead to more successful implementation of genetic testing to help tailor the use of routine medications. Their findings are published today (1 November 2023) in The Pharmacogenomics Journal and indicate key issues that could affect the take up of this new type of genetic testing amongst patients.
Despite comprising 10% of the British population, individuals of South Asian heritage have historically been under-represented in ...
Cigarette style warning labels could reduce people’s meat consumption
2023-11-01
Cigarette style graphic warning labels could reduce people’s meat consumption, according to new research published today (1 November).
The study suggests the use of warning labels on meat options could improve public health and reduce the UK’s carbon footprint.
The team from Durham University tested a range of warning labels including those which warn people of the damage to climate, health, and risk of pandemics. They found that all labels were effective at discouraging people from choosing meals with meat.
All warning labels, which showed ...
New research finds that nature-based solutions are essential for Brazil to meet its 2050 net zero pledge
2023-11-01
A new study has concluded that any credible net zero pathway for Brazil must include the implementation of nature-based solutions.
Actions such as halting deforestation and large-scale restoration of native vegetation would have immediate impact, at a fraction of the cost of carbon-negative technologies.
However, stronger policy frameworks will be needed if nature-based solutions are to achieve their full potential in Brazil.
Without the implementation of nature-based solutions, in particular ending deforestation and restoring ...
New position statement supports permanent standard time
2023-10-31
DARIEN, IL – An updated position statement from the American Academy of Sleep Medicine supports the replacement of daylight saving time with permanent standard time.
It is the position of the AASM that the United States should eliminate seasonal time changes in favor of permanent standard time, which aligns best with human circadian biology. According to the statement, evidence supports the distinct benefits of standard time for health and safety, while also underscoring the potential harms that result from seasonal time changes to and from daylight saving time.
“By causing the human body ...
Reverse engineering Jackson Pollock
2023-10-31
Can a machine be trained to paint like Jackson Pollock? More specifically, can 3D-printing harness the Pollock's distinctive techniques to quickly and accurately print complex shapes?
“I wanted to know, can one replicate Jackson Pollock, and reverse engineer what he did,” said L. Mahadevan, the Lola England de Valpine Professor of Applied Mathematics at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS), and Professor of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology, and of Physics in the Faculty of Arts and Sciences (FAS).
Mahadevan and his team combined physics and machine learning to develop a new 3D-printing ...
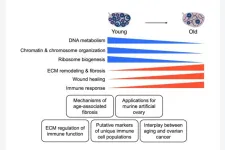
Proteomic quantification of native and ECM-enriched mouse ovaries reveals an age-dependent fibro-inflammatory signature
2023-10-31
“Overall, our study provides novel insight into how reproductive aging impacts the murine ovarian proteome and ECM.”
BUFFALO, NY- October 31, 2023 – A new priority research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 20, entitled, “Proteomic quantification of native and ECM-enriched mouse ovaries reveals an age-dependent fibro-inflammatory signature.”
The ovarian microenvironment becomes fibrotic and stiff with age, in part due to increased collagen and decreased hyaluronan. However, the extracellular matrix ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
Tibet ASγ experiment sheds new light on cosmic rays acceleration and propagation in Milky Way
AI-based liquid biopsy may detect liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and chronic disease signals
Hope for Rett syndrome: New research may unlock treatment pathway for rare disorder with no cure
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers emphasize benefits and risks of generative AI at different stages of childhood development
Why conversation is more like a dance than an exchange of words
With Evo 2, AI can model and design the genetic code for all domains of life
Discovery of why only some early tumors survive could help catch and treat cancer at very earliest stages
Study reveals how gut bacteria and diet can reprogram fat to burn more energy
Mayo Clinic researchers link Parkinson's-related protein to faster Alzheimer's progression in women
Trends in metabolic and bariatric surgery use during the GLP-1 receptor agonist era
Loneliness, anxiety symptoms, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation in the all of us dataset
A decision-support system to personalize antidepressant treatment in major depressive disorder
Thunderstorms don’t just appear out of thin air - scientists' key finding to improve forecasting
Automated CT scan analysis could fast-track clinical assessments
New UNC Charlotte study reveals how just three molecules can launch gene-silencing condensates, organizing the epigenome and controlling stem cell differentiation
Oldest known bony fish fossils uncover early vertebrate evolution
High‑performance all‑solid‑state magnesium-air rechargeable battery enabled by metal-free nanoporous graphene
[Press-News.org] Non-invasive technology maps brain activity to investigate behavior changes in neurological diseaseThe new method will be used in preclinical research with the goal of improving care for patients with neurological disease