(Press-News.org) PULLMAN, Wash. – A susceptibility to gain weight may be written into molecular processes of human cells, a Washington State University study indicates.
The proof-of-concept study with a set of 22 twins found an epigenetic signature in buccal or cheek cells appearing only for the twins who were obese compared to their thinner siblings. With more research, the findings could lead to a simple cheek swab test for an obesity biomarker and enable earlier prevention methods for a condition that effects 50% of U.S. adults, the researchers said.
“Obesity appears to be more complex than simple consumption of food. Our work indicates there’s a susceptibility for this disease and molecular markers that are changing for it,” said Michael Skinner, a WSU professor of biology and corresponding author of the study published in the journal Epigenetics.
The study focused on twins to help eliminate the role of genetics and instead focus on epigenetics, molecular processes which are separate from DNA but influence how genes are expressed. The fact that the epigenetic signature was found in cheek cells rather than fat cells also suggests that the obesity signature is likely found throughout the human system.
The signature’s systemic nature also suggests that something may have occurred early in one twin’s life that triggered obesity susceptibility, Skinner added. It’s also possible that it was inherited by one twin and not the other.
For this study, Skinner worked with lead author Glen Duncan, director of the Washington State Twin Registry based at WSU, to identify 22 twin pairs, both identical and fraternal, who were discordant for obesity: one sibling had a body mass index of 30 or higher, the standard for obesity defined by the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention, while the other sibling was in the normal range of 25 and below.
The research team analyzed cells from cheek swabs provided by the twins. In the cells from the twin siblings who were obese, they found similar epigenetic changes to DNA methylation regions, areas where molecular groups made of methane attach to DNA, regulating gene expression or turning genes on or off.
The study would need to be replicated with larger groups of people to develop a biomarker test for obesity, the authors said.
The goal would be able to identify people earlier in life before they become obese so health care providers might help create interventions such as lifestyle changes, medication or both, said Duncan.
“Ultimately we would like to have some kind of preventative measure instead of our usual approach which is treatment,” he said. “It’s a simple fact that it's better to prevent a disease, then try to treat it after you have it.”
This research was funded by the John Templeton Foundation and the National Institutes of Health.
END
Epigenetic signature for obesity found in study of twins
2023-11-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
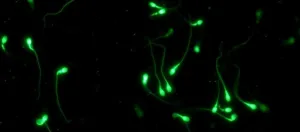
Mobile phone use may affect semen quality
2023-11-01
Does electromagnetic radiation emitted by mobile phones affect semen quality? While various environmental and lifestyle factors have been proposed to explain the decline in semen quality observed over the last fifty years, the role of mobile phones has yet to be demonstrated. A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), in collaboration with the Swiss Tropical and Public Health Institute (Swiss TPH), has published a major cross-sectional study on the subject. It shows that frequent use of mobile phones is associated with a lower sperm concentration and total sperm count. However, researchers did not ...
Study finds JAK inhibitors, common treatment for arthritis, are effective
2023-11-01
According to a new paper in Rheumatology, published by Oxford University Press, JAK inhibitors, which doctors have used to treat patients with arthritis despite concerns about the effectiveness of such drugs, actually do work quite well. In a multicenter, retrospective study Japanese researchers found that the drugs resulted in impressive remission rates in patients, most of whom choose to continue such treatment.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a common autoimmune disease characterized by chronic inflammation of joint linings and results in progressive joint destruction and other systemic ...
Do mild depressive and anxiety symptoms in fathers predict behavioral and cognitive problems in their children?
2023-11-01
While the role of mothers’ stress, anxiety and depression on children’s behavioral and cognitive development is well established, less is known about the connection between fathers’ mental health and children’s development.
Now, a team of researchers affiliated to different institutions across Quebec, Canada has examined if paternal anxious and depressive symptoms, measured during their partner’s pregnancy, and again six to eight years later, are associated with children’s cognitive function and behavior. They studied this association ...
Cancer drug could hold hope for treating inflammatory diseases including gout and heart diseases
2023-11-01
A cancer drug currently in the final stages of clinical trials could offer hope for the treatment of a wide range of inflammatory diseases, including gout, heart failure, cardiomyopathy, and atrial fibrillation, say scientists at the University of Cambridge.
In a study published today in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, the researchers have identified a molecule that plays a key role in triggering inflammation in response to materials in the body seen as potentially harmful.
We are born with a defence system known as innate immunity, which acts as the first line of defence against harmful materials in the body. Some of these materials will come from outside, such as bacterial or viral ...
New cancer drug shows promise targeting genetic weakness in tumors, comments Virginia Tech expert
2023-11-01
Imagine the body’s cells are well-behaved students in the classroom. The “teachers” are tumor suppressor genes, and they make sure cells follow the rules. But when tumor suppressor genes are away, cells may go astray.
With cells, this is a serious matter. Unregulated behavior can lead to uncontrolled growth and, ultimately, the development of cancer.
In an invited review article Wednesday (Nov. 1, 2023) in Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, Kathleen Mulvaney, assistant professor with the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC, talks about the ...
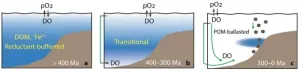
Marine oxygen landscape shaped by plate movement and biological innovation
2023-11-01
The oxygen content of seawater has a profound impact on the cycling of bioessential elements and the habitability of Earth. But how and why the marine oxygen landscape (i.e., the spatial pattern of oxygen levels) evolved since the start of the Phanerozoic 538 million years ago is not well established.
To tackle this problem, researchers led by Prof. WANG Xiangli from the Institute of Geology and Geophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IGGCAS) and Prof. LI Chao from the Chengdu University of Technology, along with collaborators from the University of Cincinnati and the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology, have reconstructed a nearly continuous record of ...
Having a bad boss makes you a worse employee
2023-11-01
uIf your boss stomps and yells, criticizes you, and then proceeds to take the credit for your work – even it is an isolated incident – it can take a profound toll on employee well-being and performance. But despite the many years of research, the precise mechanisms through which bad leadership impacts employees’ performance remain a subject of interest.
In a new study, first published online Oct. 30 in Group & Organization Management, an international group of researchers, led by Stevens Institute of Technology and University of Illinois Chicago, offer a novel explanation of the cognitive factors through which abusive ...
Non-invasive technology maps brain activity to investigate behavior changes in neurological disease
2023-11-01
A research team led by Cleveland Clinic and Oregon Health and Science University (OHSU) has developed a new method for mapping how the parts of the brain "speak" to each other, critical to understanding behavior changes in patients with neurological disease.
Diseases like Alzheimer's disease change how patients communicate and act, affecting their relationships and well-being. Cleveland Clinic's Hod Dana, PhD, is collaborating with Jacob Raber, PhD, an OHSU behavioral neuroscientist, on ...
NIH funding helps Ghose Lab invest in innovative imaging equipment
2023-11-01
UTA will soon add a new piece of cutting-edge equipment to its already impressive and growing research armamentarium—a type of super-resolution microscope (SRM) that allows biologists to see structures within a cell in even finer detail.
The SRM will come to UTA because of additional grant funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to the lab of Piya Ghose, an assistant professor of biology at UTA. This nearly $250,000 award supplements Ghose’s existing NIH/National Institute of General Medical ...
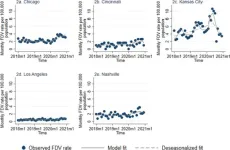
Domestic violence involving firearms increased during COVID-19 pandemic
2023-11-01
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — Domestic violence went down or stayed the same during the first 10 months of the COVID-19 pandemic in five major U.S. cities. However, domestic violence involving firearms increased in three of those cities, according to a new UC Davis study published in the Journal of Family Violence.
“The increase in firearm domestic violence is concerning, as abuser firearm access is a risk factor for lethality,” said Elizabeth Tomsich, a research data analyst at the UC Davis Violence Prevention Research Center and ...