Immune checkpoint inhibition, when administered together with single fraction stereotactic radiosurgery, does not appear to increase risk of radiation necrosis in patients with brain metastases
Multi-institutional study found that V12 Gy given to radiosurgical volume of larger than 10 cm3 , was a significant predictor of radiation necrosis in patients with brain metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer
2023-11-01
(Press-News.org) MIAMI, FL – November 1, 2023 -- Miami Cancer Institute, part of Baptist Health South Florida, announced the publication of a multi-institutional retrospective cohort study about the impact of immune checkpoint inhibition (ICI) and single-fraction stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) on radiation necrosis (RN) in patients with brain metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer. The study, titled “Immune Checkpoint Inhibition and Single Fraction Stereotactic Radiosurgery in Brain Metastases from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: An International Multicenter Study of 395 Patients” published in the Journal of Neuro-Oncology.
“One of the key findings of the study is that immune checkpoint inhibition, when administered together with stereotactic radiosurgery, does not increase the risk of radiation necrosis,” said Manmeet S. Ahluwalia, M.D., MBA, FASCO, chief of medical oncology, chief scientific officer, deputy director, and Fernandez Family Foundation Endowed Chair in Cancer Research at Miami Cancer Institute, and senior author of the study. “We did, however, find a relationship between the volume of the brain area that is targeted during radiation and radiation necrosis.”
The study included 395 patients with 2,540 brain metastases who were treated with SRS and ICI across four countries with a median follow-up of 14.2 months. The median age of the study participants was 67 years. The median margin SRS dose was 19 Gy, but 36.5% of patients had a V12 Gy of larger or equal to 10 cm3. On multivariable analysis, V12 Gy of larger or equal to 10 cm3 was a significant predictor of developing any grade RN and symptomatic RN (SRN). At one year, the cumulative incidence of any grade RN and SRN for all patients was 4.8% and 3.8%, respectively. For concurrent and non-concurrent groups, the cumulative incidence of any grade RN was 3.8% versus 5.3%, respectively; and for SRN was 3.8% vs. 3.6%, respectively.
“The risk of any grade radiation necrosis and symptomatic radiation necrosis following single fraction stereotactic radiosurgery and immune checkpoint inhibition for non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases increases as V12 Gy exceeds 10 cm3,” added Ahluwalia. “Concurrent immune checkpoint inhibition and stereotactic radiosurgery do not appear to increase this risk. Instead, radiosurgical planning techniques should aim to minimize V12 Gy. In addition, the study suggests that treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors can continue when radiation necrosis occurs.”
The study was organized by the International Radiosurgery Research Foundation.
About Miami Cancer Institute
Miami Cancer Institute brings to South Florida access to personalized clinical treatments and comprehensive support services delivered with unparalleled compassion. No other cancer program in the region has the combination of cancer-fighting expertise and advanced technology—including the first proton therapy center in South Florida, Latin America and the Caribbean, and one of the only radiation oncology programs in the world with each of the newest radiation therapies in one place—to diagnose and deliver precise cancer treatments that achieve the best outcomes and improve the lives of cancer patients. The Institute offers an impressive roster of established community oncologists and renowned experts, clinical researchers and genomic scientists recruited from the nation’s top cancer centers. Selected as Florida’s only member of the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer (MSK) Alliance, Miami Cancer Institute is part of a meaningful clinical collaboration that affords patients in South Florida access to innovative treatments and ensures that the standards of care developed by their multidisciplinary disease management teams match those at MSK. For more information, please visit https://cancer.baptisthealth.net/miami-cancer-institute.
Miami Cancer Institute is part of Baptist Health Cancer Care, the largest cancer program in South Florida, with locations from the Florida Keys to the Palm Beaches.
###
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-11-01
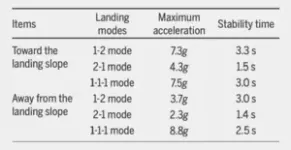
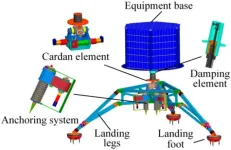
Landing stably is the precondition for exploring the small celestial body in situ. The surface of small body is weak gravity and irregular, and the surface environment is unknown and uncertain. The landing mechanism tends to rebound and turn over, and the landing stability time is long. However, there is difference on the Moon and the Mars surface while most of the landing performance researches are focused on the lunar landing so far. Therefore, it is of great important to study the landing ...
2023-11-01
ATLANTA, November 1, 2023 — Today, the American Cancer Society (ACS) released an update of its lung cancer screening guideline to help reduce the number of people dying from the disease due to smoking history. The new guideline recommends yearly screening for lung cancer for people aged 50 to 80 years old who smoke or formerly smoked and have a 20-year or greater pack-year history. The recommended annual screening test for lung cancer is a low-dose computed tomography scan (also called a low-dose CT scan, or LDCT). The guideline, last updated ...
2023-11-01
Kuala Lumpur, 1 November 2023
An Independent Expert Group (IEG) convened by the United Nations University’s International Institute for Global Health (UNU IIGH) has released a strong statement criticizing the wide and uncritical use of global university rankings.
The IEG highlights the vital importance of universities in delivering not just education, training, and research, but also in shaping public policy, promoting informed public discourse, and helping advance democracy and human rights.
However, although marketed as a tool for improving university performance and providing information to prospective students, the statement describes how global university ...
2023-11-01
WASHINGTON—Women in low- and middle-income countries, especially in the Sub-Saharan Africa region, may be 10 times more likely to have obesity or heart health issues than their male counterparts, according to a large meta-analysis published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Obesity is a chronic disease characterized by an individual having an excess of body fat or abnormal fat accumulation. People who have obesity are at an increased risk for other serious ...
2023-11-01
The American Pediatric Society (APS) is pleased to announce Alan Jobe, MD, PhD, as the 2024 APS John Howland Award recipient, the highest honor bestowed by the APS. The prestigious award signifies the society’s recognition of Dr. Jobe for his significant contributions to advancing child health and the profession of pediatrics. The award will be presented to Dr. Jobe during the APS Presidential Plenary at the Pediatric Academic Societies 2024 Meeting in Toronto, Ontario, May 2 – May 6.
The ...
2023-11-01
INDIANAPOLIS -- Regenstrief Institute research scientist Matthew J. Bair, M.D., M.S., and the Indiana Institute of Medical Research (IIMR) at Richard L. Roudebush VA Medical Center have been awarded the Creative Forces®: National Endowment for the Arts Military Healing Arts Network Award for Clinical Study of Music Therapy and Chronic Pain in U.S. Veterans.
The research project titled “Stepped-Care Intervention of Music and Imagery to Assess Relief (SCIMITAR) Trial” will test whether a two-step music therapy intervention ...
2023-11-01
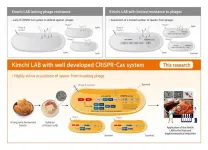
Researchers at the World Institute of Kimchi have isolated lactic acid bacteria (LAB) strains with high levels of resistance to phages from kimchi fermented at low temperatures for a long period of time. They have also identified the defense mechanism of the LAB strains against phages, viruses that infect and replicate within bacteria.
Kimchi, a traditional Korean food, is a lactic acid-fermented vegetable product. Unlike fermented dairy products, which are produced under a sterilized-closed fermentation system, kimchi is produced through spontaneous fermentation initiated by various microorganisms present in the raw materials under a non-sterilized-open fermentation system. Thus, ...
2023-11-01
For some, the eyes are a window into the soul. But for Jayashree Kalpathy-Cramer, PhD, professor of ophthalmology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, they're a window into human health.
The researcher was granted $300,000 by The Michael J. Fox Foundation this fall to analyze clinical data curated at the Sue Anschutz-Rodgers Eye Center using artificial intelligence (AI) in an effort to identify biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease, a progressive disorder that affects the nervous system and causes uncontrollable movements, such as shaking, throughout the body.
“This approach could be impactful ...
2023-11-01
Fidel Santamaria, a professor in the UTSA College of Sciences’ neuroscience, developmental and regenerative biology department, received a $2 million grant through the National Science Foundation’s Emerging Frontiers in Research and Innovation (EFRI) program to develop new artificial intelligence (AI) applications in the most energy-efficient manner yet.
For machine-learning tools to analyze new data, they must first sort data into various categories. For example, if a tool is sorting photos by color, then it needs to recognize which photos are red, yellow or blue to accurately classify them. While this is an easy chore for a human, the task presents a ...
2023-11-01
Researchers from Boston University published a Journal of Marketing study showing that tapping into consumers’ sense of ownership prompts them to place a higher value on products from a circular economy.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Affording Disposal Control: The Effect of Circular Take-Back Programs on Psychological Ownership and Valuation” and is authored by Anna Tari and Remi Trudel.
Governments worldwide view a circular economy as part of the solution to the climate crisis. In the U.S., several states such as California, Connecticut, Maine, Oregon, and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Immune checkpoint inhibition, when administered together with single fraction stereotactic radiosurgery, does not appear to increase risk of radiation necrosis in patients with brain metastases
Multi-institutional study found that V12 Gy given to radiosurgical volume of larger than 10 cm3 , was a significant predictor of radiation necrosis in patients with brain metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer