(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON—Women in low- and middle-income countries, especially in the Sub-Saharan Africa region, may be 10 times more likely to have obesity or heart health issues than their male counterparts, according to a large meta-analysis published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Obesity is a chronic disease characterized by an individual having an excess of body fat or abnormal fat accumulation. People who have obesity are at an increased risk for other serious diseases and health conditions.
Obesity kills at least 2.8 million people per year, yet the public still does not recognize it as a disease, and anti-obesity medications are still under prescribed and hard to access. Obesity is preventable, but according to the World Health Organization, the disease has nearly tripled since 1975. In 2016, 52% of adults and over 340 million children and teens were considered to have overweight or obesity.
"Our findings are important as they call for urgent actions targeting obesity awareness, prevention, treatment, and control in women in low- and middle-income countries,” said study author Thaís Rocha, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Birmingham in Birmingham, U.K.
The researchers included 3,916,276 people in the meta-analysis and found obesity does not manifest evenly across women and men in low- and middle-income countries, with women being 2-3 times more likely to be affected than men. They found the greatest disparity in the risk of obesity between women and men is in the Sub-Saharan region, where women are up to 10 times more likely to have obesity than men.
Senior study author Shakila Thangaratinam, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Birmingham said, “For the first time, we are able to assess the extent of poor metabolic health faced by women compared to men in low- and middle-income countries. Funders and policymakers need to implement woman- centered measures addressing the underlying social, cultural and behavioral factors to improve their long-term metabolic health.”
The authors shared a few examples of the factors contributing to the higher rate of obesity in these women including:
Weight gain during pregnancy and menopause.
Beliefs that larger body types indicate high socioeconomic status, and fertility associated obesity in women as a sign of “wealth and health.”
Obesity risk seems to be positively and significantly associated with childhood deprivation in women but not men.
Women are also more likely to be influenced than men by other factors predisposing them to obesity, such as poor dietary habits, sedentary lifestyles and price inflation.
The other authors of this study are Eka Melson of the University of Birmingham; Javier Zamora of the University of Birmingham, Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal (IRYCIS) and the CIBERESP Instituto de Salud Carlos III in Madrid, Spain; Borja Fernandez-Felix of the CIBERESP Instituto de Salud Carlos III; and Wiebke Arlt of the Medical Research Council Laboratory of Medical Sciences and Imperial College London, U.K.
The study was funded by the Wellcome Trust and the NIHR Birmingham Biomedical Research Centre.
The manuscript, “Sex-Specific Obesity and Cardiometabolic Disease Risks in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Meta-Analysis Involving 3,916,276 Individuals," was published online.
# # #
Endocrinologists are at the core of solving the most pressing health problems of our time, from diabetes and obesity to infertility, bone health, and hormone-related cancers. The Endocrine Society is the world’s oldest and largest organization of scientists devoted to hormone research and physicians who care for people with hormone-related conditions.
The Society has more than 18,000 members, including scientists, physicians, educators, nurses and students in 122 countries. To learn more about the Society and the field of endocrinology, visit our site at www.endocrine.org. Follow us on Twitter at @TheEndoSociety and @EndoMedia.
END
Women face greater risk of obesity in low- and middle-income countries
Study finds women are 2-3 times more likely to be affected than men
2023-11-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The American Pediatric Society honors Dr. Alan Jobe with the 2024 APS John Howland award
2023-11-01
The American Pediatric Society (APS) is pleased to announce Alan Jobe, MD, PhD, as the 2024 APS John Howland Award recipient, the highest honor bestowed by the APS. The prestigious award signifies the society’s recognition of Dr. Jobe for his significant contributions to advancing child health and the profession of pediatrics. The award will be presented to Dr. Jobe during the APS Presidential Plenary at the Pediatric Academic Societies 2024 Meeting in Toronto, Ontario, May 2 – May 6.
The ...
NEA award supports study of music therapy to improve chronic pain
2023-11-01
INDIANAPOLIS -- Regenstrief Institute research scientist Matthew J. Bair, M.D., M.S., and the Indiana Institute of Medical Research (IIMR) at Richard L. Roudebush VA Medical Center have been awarded the Creative Forces®: National Endowment for the Arts Military Healing Arts Network Award for Clinical Study of Music Therapy and Chronic Pain in U.S. Veterans.
The research project titled “Stepped-Care Intervention of Music and Imagery to Assess Relief (SCIMITAR) Trial” will test whether a two-step music therapy intervention ...
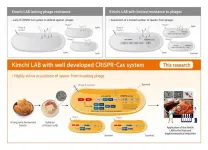
Research team at World Institute of Kimchi discovers lactic acid bacteria strains with high virus resistance from kimchi
2023-11-01
Researchers at the World Institute of Kimchi have isolated lactic acid bacteria (LAB) strains with high levels of resistance to phages from kimchi fermented at low temperatures for a long period of time. They have also identified the defense mechanism of the LAB strains against phages, viruses that infect and replicate within bacteria.
Kimchi, a traditional Korean food, is a lactic acid-fermented vegetable product. Unlike fermented dairy products, which are produced under a sterilized-closed fermentation system, kimchi is produced through spontaneous fermentation initiated by various microorganisms present in the raw materials under a non-sterilized-open fermentation system. Thus, ...
CU Ophthalmology researcher funded to study Parkinson's disease biomarkers
2023-11-01
For some, the eyes are a window into the soul. But for Jayashree Kalpathy-Cramer, PhD, professor of ophthalmology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, they're a window into human health.
The researcher was granted $300,000 by The Michael J. Fox Foundation this fall to analyze clinical data curated at the Sue Anschutz-Rodgers Eye Center using artificial intelligence (AI) in an effort to identify biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease, a progressive disorder that affects the nervous system and causes uncontrollable movements, such as shaking, throughout the body.
“This approach could be impactful ...
UTSA researchers develop energy-efficient AI with $2 million NSF grant
2023-11-01
Fidel Santamaria, a professor in the UTSA College of Sciences’ neuroscience, developmental and regenerative biology department, received a $2 million grant through the National Science Foundation’s Emerging Frontiers in Research and Innovation (EFRI) program to develop new artificial intelligence (AI) applications in the most energy-efficient manner yet.
For machine-learning tools to analyze new data, they must first sort data into various categories. For example, if a tool is sorting photos by color, then it needs to recognize which photos are red, yellow or blue to accurately classify them. While this is an easy chore for a human, the task presents a ...
The secret to enhancing consumer valuation and addressing the climate crisis at once: introduce circular take-back programs
2023-11-01
Researchers from Boston University published a Journal of Marketing study showing that tapping into consumers’ sense of ownership prompts them to place a higher value on products from a circular economy.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Affording Disposal Control: The Effect of Circular Take-Back Programs on Psychological Ownership and Valuation” and is authored by Anna Tari and Remi Trudel.
Governments worldwide view a circular economy as part of the solution to the climate crisis. In the U.S., several states such as California, Connecticut, Maine, Oregon, and ...
Plastic-eating bacteria turn waste into useful starting materials for other products
2023-11-01
Mountains of used plastic bottles get thrown away every day, but microbes could potentially tackle this problem. Now, researchers in ACS Central Science report that they’ve developed a plastic-eating E. coli that can efficiently turn polyethylene terephthalate (PET) waste into adipic acid, which is used to make nylon materials, drugs and fragrances.
Previously, a team of researchers including Stephen Wallace engineered a strain of E. coli to transform the main component in old PET bottles, terephthalic acid, into something tastier and ...
Younger Middle Eastern patients with new acute coronary syndrome more likely to smoke, have high cholesterol
2023-11-01
Young patients from the Middle East and Gulf region presenting with acute coronary syndrome have a greater prevalence of risk factors, including smoking and high cholesterol compared to older patients also presenting with first acute coronary syndrome. The study, presented at the American College of Cardiology Middle East & Eastern Mediterranean 2023 conference, found these patients still had similar outcomes compared to older patients.
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) describes a variety of cardiovascular conditions related to sudden reduction in blood flow to the heart, including heart attack and unstable angina ...
Reducing breast cancer disparities in Delaware: 'Getting the village back together'
2023-11-01
There’s a tried and proven pathway to reducing racial disparities in cancer in Delaware. It worked with colon cancer 10 years ago and should now be applied to the incidence of breast cancer in the state. That's the recommendation of clinicians, program leaders and researchers from the ChristianaCare Helen F. Graham Cancer Center & Research Institute in a new commentary published in Population Health Management on Nov. 1, 2023.
The commentary — "Reducing Racial Disparities in Breast Cancer: Getting the ...
New research links high salt consumption to risk of Type 2 diabetes
2023-11-01
Those at risk for Type 2 diabetes may already know to avoid sugar, but new research suggests they may want to skip the salt as well.
A new study from Tulane University published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings found that frequently adding salt to foods was associated with an increased risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
The study surveyed more than 400,000 adults registered in the UK Biobank about their salt intake. Over a median of 11.8 years of follow-up, more than 13,000 cases of Type 2 diabetes developed among participants. Compared ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Women face greater risk of obesity in low- and middle-income countriesStudy finds women are 2-3 times more likely to be affected than men