(Press-News.org) November 2, 2023, Mountain View, CA -- The SETI Institute is delighted to announce that Dr. Pascal Lee will be honored with the 2023 Carl Sagan Prize for Science Popularization presented by Wonderfest. The prestigious Sagan Prize recognizes and encourages individuals who “have contributed wonderfully to the public understanding and appreciation of science.” Previous recipients from the SETI Institute include SETI Institute co-founder and SETI pioneer Jill Tarter, senior astronomer Seth Shostak and trustee Andrew Fraknoi.
“I am truly delighted and humbled by this award,” says Pascal Lee, “all the more because Carl Sagan was, and remains, such an inspiration and encouragement to so many to share their love of science and to advocate for informed, rational, critical thinking.”
Lee is a planetary scientist at the SETI Institute, the founder and chairman of the Mars Institute, a professor of planetary science at the Kepler Space Institute, and the director of the NASA Haughton-Mars Project at NASA Ames Research Center. His research focuses on the history of water on Mars and planning the future human exploration of the Moon and Mars. Lee has led more than 30 expeditions to the Arctic and Antarctica to study Mars by comparison with the Earth. His areas of research extend to asteroids, the moons of Mars, Saturn’s moon Titan, and SETI, the Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence.
But Lee has also been a passionate advocate for planetary and deep space exploration, and has shared with students and the public worldwide his love for space science. He has given countless public and school talks over the past decades, including his sought-after lectures “From Earth to Mars” about humanity’s future journeys to Mars, and the more speculative “N~1: Alone in The Milky Way” in which he argues that there might be very few advanced civilizations per galaxy. His first book, Mission: Mars, won the 2015 Prize for Excellence in Children’s Science Books from the American Association for the Advancement of Science. Additionally, the 2016 motion picture documentary film Passage to Mars chronicles Lee and his team’s epic, perilous and record-setting trek across the sea ice of the Northwest Passage in the Arctic to help prepare for the future human exploration of Mars.
Tucker Hiatt, Director of Wonderfest, says of Lee receiving the award: “Sagan would be proud to know that Pascal Lee, renowned for both his research and his outreach, and who served as Sagan’s last teaching assistant at Cornell University, has received Wonderfest’s Sagan Prize for 2023”.
More information about the Wonderfest Sagan Prize can be found here:
https://wonderfest.org/sagan-prize/, and about Wonderfest’s award to Dr Lee here:
https://wonderfest.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/SaganPrize2023-release-2.pdf
About the SETI Institute
Founded in 1984, the SETI Institute is a non-profit, multi-disciplinary research and education organization whose mission is to lead humanity’s quest to understand the origins and prevalence of life and intelligence in the universe and share that knowledge with the waorld. Our research encompasses the physical and biological sciences and leverages data analytics, machine learning, and advanced signal detection technologies. The SETI Institute is a distinguished research partner for industry, academia, and government agencies, including NASA and the National Science Foundation.
END
Pascal Lee awarded the 2023 Carl Sagan Prize for Science Popularization
Wonderfest recognizes Dr. Pascal Lee for excellence in science outreach
2023-11-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UMBC team makes first-ever observation of a virus attaching to another virus
2023-11-02
No one had ever seen one virus latching onto another virus, until anomalous sequencing results sent a UMBC team down a rabbit hole leading to a first-of-its-kind discovery.
It’s known that some viruses, called satellites, depend not only on their host organism to complete their life cycle, but also on another virus, known as a “helper,” explains Ivan Erill, professor of biological sciences. The satellite virus needs the helper either to build its capsid, a protective shell that encloses the virus’s genetic material, or to help it replicate ...
Research connecting gut bacteria and oxytocin provides a new mechanism for microbiome-promoted health benefits
2023-11-02
The gut microbiome, a community of trillions of microbes living in the human intestines, has an increasing reputation for affecting not only gut health but also the health of organs distant from the gut. For most microbes in the intestine, the details of how they can affect other organs remain unclear, but for gut resident bacteria L. reuteri the pieces of the puzzle are beginning to fall into place.
“L. reuteri is one of such bacteria that can affect more than one organ in the body,” said co-corresponding author Dr. Sara Di Rienzi, ...
How “blue” and “green” appeared in a language that didn’t have words for them
2023-11-02
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- The human eye can perceive about 1 million colors, but languages have far fewer words to describe those colors. So-called basic color terms, single color words used frequently by speakers of a given language, are often employed to gauge how languages differ in their handling of color. Languages spoken in industrialized nations such as the United States, for example, tend to have about a dozen basic color terms, while languages spoken by more isolated populations often have fewer.
However, the way that a language ...
Plant populations in Cologne are adapted to their urban environments
2023-11-02
A research team from the Universities of Cologne and Potsdam and the Max Planck Institute for Plant Breeding Research has found that the regional lines of the thale cress (Arabidopsis thaliana), a small ruderal plant which populates the streets of Cologne, vary greatly in typical life cycle characteristics, such as the regulation of flowering and germination. This allows them to adapt their reproduction to local environmental conditions such as temperature and human disturbances. The researchers from Collaborative Research Center / Transregio 341 “Plant Ecological Genetics” found that environmental ...
Making gluten-free, sorghum-based beers easier to brew and enjoy
2023-11-02
Though beer is a popular drink worldwide, it’s usually made from barley, which leaves those with a gluten allergy or intolerance unable to enjoy the frothy beverage. Sorghum, a naturally gluten-free grain, could be an alternative, but complex preparation steps have hampered its widespread adoption by brewers. Now, researchers reporting the molecular basis behind sorghum brewing in ACS’ Journal of Proteome Research have uncovered an enzyme that could improve the future of sorghum-based beers.
Traditionally, beer brewers start with barley grains, which they malt, mash, ...
Jurassic worlds might be easier to spot than modern Earth
2023-11-02
ITHACA, N.Y. –Things may not have ended well for dinosaurs on Earth, but Cornell University astronomers say the “light fingerprint” of the conditions that enabled them to emerge here provide a crucial missing piece in our search for signs of life on planets orbiting alien stars.
Their analysis of the most recent 540 million years of Earth’s evolution, known as the Phanerozoic Eon, finds that telescopes could better detect potential chemical signatures of life in the atmosphere of an Earth-like exoplanet more closely resembling the age the dinosaurs inhabited than the ...
Archaeology: Larger-scale warfare may have occurred in Europe 1,000 years earlier
2023-11-02
A re-analysis of more than 300 sets of 5,000-year-old skeletal remains excavated from a site in Spain suggests that many of the individuals may have been casualties of the earliest period of warfare in Europe, occurring over 1,000 years before the previous earliest known larger-scale conflict in the region. The study, published in Scientific Reports, indicates that both the number of injured individuals and the disproportionately high percentage of males affected suggest that the injuries resulted from a period of conflict, potentially lasting at least months.
Conflict during the European Neolithic period (approximately 9,000 ...
Study warns API restrictions by social media platforms threaten research
2023-11-02
University researchers from the UK, Germany and South Africa warn of a threat to scientific knowledge and the future of research in a paper published in Nature Human Behaviour, outlining the implications of changes to social media Application Programming Interfaces (APIs).
Over the course of 2023, numerous social media platforms including X, TikTok, and Reddit made substantial changes to their APIs – drastically reducing access or increasing charges for access, which the researchers say will in many cases make research harder.
APIs have been routinely tapped by researchers ...
Researchers engineer colloidal quasicrystals using DNA-modified building blocks
2023-11-02
Evanston, IL. --- A team of researchers from the Mirkin Group at Northwestern University’s International Institute for Nanotechnology in collaboration with the University of Michigan and the Center for Cooperative Research in Biomaterials- CIC biomaGUNE, unveils a novel methodology to engineer colloidal quasicrystals using DNA-modified building blocks. Their study will be published in the journal Nature Materials under the title "Colloidal Quasicrystals Engineered with DNA."
Characterized ...
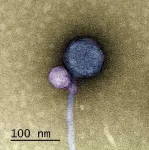
Nanoparticle quasicrystal constructed with DNA
2023-11-02
Images
Nanoengineers have created a quasicrystal—a scientifically intriguing and technologically promising material structure—from nanoparticles using DNA, the molecule that encodes life.
The team, led by researchers at Northwestern University, the University of Michigan and the Center for Cooperative Research in Biomaterials in San Sebastian, Spain, reports the results in Nature Materials.
Unlike ordinary crystals, which are defined by a repeating structure, the patterns in quasicrystals don't repeat. Quasicrystals built from atoms can have exceptional properties—for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Pascal Lee awarded the 2023 Carl Sagan Prize for Science PopularizationWonderfest recognizes Dr. Pascal Lee for excellence in science outreach