New designs for solid-state electrolytes may soon revolutionize the battery industry
Scientists achieve monumental improvements in lithium-metal-chloride solid-state electrolytes
2023-11-02
(Press-News.org)
Researchers led by Professor KANG Kisuk of the Center for Nanoparticle Research within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), have announced a major breakthrough in the field of next-generation solid-state batteries. It is believed that their new findings will enable the creation of batteries based on a novel chloride-based solid electrolyte that exhibits exceptional ionic conductivity.
A pressing concern with current commercial batteries their reliance on liquid electrolytes, which leads to flammability and explosion risks. Therefore, the development of non-combustible solid electrolytes is of paramount importance for advancing solid-state battery technology. As the world gears up to regulate internal combustion engine vehicles and expand the use of electric vehicles in the ongoing global shift toward sustainable transportation, research into the core components of secondary batteries, particularly solid-state batteries, has gained significant momentum.
To make solid-state batteries practical for everyday use, it is crucial to develop materials with high ionic conductivity, robust chemical and electrochemical stability, and mechanical flexibility. While previous research successfully led to sulfide and oxide-based solid electrolytes with high ionic conductivity, none of these materials fully met all these essential requirements.
In the past, scientists have also explored chloride-based solid electrolytes, known for their superior ionic conductivity, mechanical flexibility, and stability at high voltages. These properties led some to speculate that chloride-based batteries are the most likely candidates for solid-state batteries. However, these hopes quickly died out, as the chloride batteries were considered impractical due to their heavy reliance on expensive rare earth metals, including yttrium, scandium, and lanthanide elements, as secondary components.
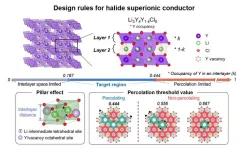
To address these concerns, the IBS research team looked at the distribution of metal ions in chloride electrolytes. They believed the reason trigonal chloride electrolytes can achieve low ionic conductivity is based on the variation of metal ion arrangements within the structure.
They first tested this theory on lithium yttrium chloride, a common lithium metal chloride compound. When the metal ions were positioned near the pathway of lithium ions, electrostatic forces caused obstruction in their movement. Conversely, if the metal ion occupancy was too low, the path for lithium ions became too narrow, impeding their mobility.
Building on these insights, the research team introduced strategies to design electrolytes in a way that mitigates these conflicting factors, ultimately leading to the successful development of a solid electrolyte with high ionic conductivity. The group went further to successfully demonstrate this strategy by creating a lithium-metal-chloride solid-state battery based on zirconium, which is far cheaper than the variants that employ rare earth metals. This was the first instance where the significance of the metal ions arrangement on a material’s ionic conductivity was demonstrated.
This research brings to light the often-overlooked role of metal ion distribution in the ionic conductivity of chloride-based solid electrolytes. It is expected that the IBS Center’s research will pave the way for the development of various chloride-based solid electrolytes and further drive the commercialization of solid-state batteries, promising improved affordability and safety in energy storage.
Corresponding author KANG Kisuk states, “This newly discovered chloride-based solid electrolyte is poised to transcend the limitations of conventional sulfide and oxide-based solid electrolytes, bringing us one step closer to the widespread adoption of solid-state batteries.”
This research was published on November 3, 2023, in Science, which is one of the world's most prestigious scientific journals.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-11-02
New observations down to light-year scale of the gas flows around a supermassive black hole have successfully detected dense gas inflows and shown that only a small portion (about 3 percent) of the gas flowing towards the black hole is eaten by the black hole. The remainder is ejected and recycled back into the host galaxy.
Not all of the matter which falls towards a black hole is absorbed, some of it is ejected as outflows. But the ratio of the matter that the black hole “eats,” and the amount “dropped” ...
2023-11-02
A surprising mechanism that makes some cancers treatment-resistant has been discovered by Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian investigators. The mechanism, which involves the shuttling of messenger RNAs (mRNAs) from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, ultimately facilitates DNA repair in cancer cells. These cancer cells can thereby thwart treatments aimed at damaging their DNA.
In a project encompassing both fundamental research and clinical studies they demonstrated that a combination of approved chemotherapies, ...
2023-11-02
One in seven people in the US reported having had long Covid by the end of 2022, suggests a large-scale investigation of long Covid and symptom prevalence by academics at UCL and Dartmouth.
Having had long Covid is associated with anxiety and low mood, as well as an increased likelihood of continued physical mobility problems and challenges with memory, concentration or understanding, according to the findings published in PLOS ONE.
The risk of anxiety and low mood appeared to be lower for those who have been vaccinated, ...
2023-11-02
New York, NY (November 2nd, 2023) — The Mount Sinai Health System has received a $7 million grant from the Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation for a three-year project that aims to fast-track novel translational concepts to improve outcomes for people with high risk myeloma, the second most common blood cancer in the United States.
This grant award will facilitate a multidisciplinary research project that will analyze a large, diverse cohort of patient samples from all over the United States at the genomic and immune level and apply novel functional genomics technology to understand the critical events that drive ...
2023-11-02
November 2, 2023, Mountain View, CA -- The SETI Institute is delighted to announce that Dr. Pascal Lee will be honored with the 2023 Carl Sagan Prize for Science Popularization presented by Wonderfest. The prestigious Sagan Prize recognizes and encourages individuals who “have contributed wonderfully to the public understanding and appreciation of science.” Previous recipients from the SETI Institute include SETI Institute co-founder and SETI pioneer Jill Tarter, senior astronomer Seth Shostak and trustee Andrew Fraknoi.
“I am truly delighted and humbled by this award,” says Pascal Lee, “all the more because Carl Sagan was, and remains, ...
2023-11-02
No one had ever seen one virus latching onto another virus, until anomalous sequencing results sent a UMBC team down a rabbit hole leading to a first-of-its-kind discovery.
It’s known that some viruses, called satellites, depend not only on their host organism to complete their life cycle, but also on another virus, known as a “helper,” explains Ivan Erill, professor of biological sciences. The satellite virus needs the helper either to build its capsid, a protective shell that encloses the virus’s genetic material, or to help it replicate ...
2023-11-02
The gut microbiome, a community of trillions of microbes living in the human intestines, has an increasing reputation for affecting not only gut health but also the health of organs distant from the gut. For most microbes in the intestine, the details of how they can affect other organs remain unclear, but for gut resident bacteria L. reuteri the pieces of the puzzle are beginning to fall into place.
“L. reuteri is one of such bacteria that can affect more than one organ in the body,” said co-corresponding author Dr. Sara Di Rienzi, ...
2023-11-02
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- The human eye can perceive about 1 million colors, but languages have far fewer words to describe those colors. So-called basic color terms, single color words used frequently by speakers of a given language, are often employed to gauge how languages differ in their handling of color. Languages spoken in industrialized nations such as the United States, for example, tend to have about a dozen basic color terms, while languages spoken by more isolated populations often have fewer.
However, the way that a language ...
2023-11-02
A research team from the Universities of Cologne and Potsdam and the Max Planck Institute for Plant Breeding Research has found that the regional lines of the thale cress (Arabidopsis thaliana), a small ruderal plant which populates the streets of Cologne, vary greatly in typical life cycle characteristics, such as the regulation of flowering and germination. This allows them to adapt their reproduction to local environmental conditions such as temperature and human disturbances. The researchers from Collaborative Research Center / Transregio 341 “Plant Ecological Genetics” found that environmental ...
2023-11-02
Though beer is a popular drink worldwide, it’s usually made from barley, which leaves those with a gluten allergy or intolerance unable to enjoy the frothy beverage. Sorghum, a naturally gluten-free grain, could be an alternative, but complex preparation steps have hampered its widespread adoption by brewers. Now, researchers reporting the molecular basis behind sorghum brewing in ACS’ Journal of Proteome Research have uncovered an enzyme that could improve the future of sorghum-based beers.
Traditionally, beer brewers start with barley grains, which they malt, mash, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New designs for solid-state electrolytes may soon revolutionize the battery industry
Scientists achieve monumental improvements in lithium-metal-chloride solid-state electrolytes