(Press-News.org) ITHACA, N.Y. – Online grocery carts tend to include less variety and fewer fruits and vegetables than those in a trip to a brick-and-mortar supermarket – but online shoppers are less susceptible to unhealthy impulse buys, according to a new Cornell University study.
In an analysis of nearly 2 million shopping trips, the researchers found that within a given household, Instacart baskets are more similar to each other from week to week than in-store carts, with more than twice as many overlapping items between successive trips to the same retailer.
Nutritionally, however, the difference in the baskets can be viewed as a wash: Instacart baskets had 13% fewer fresh vegetables but up to 7% fewer impulse purchases such as candy, baked goods and chips.
These systematic shopping pattern differences can have implications for consumers as well as retailers.
“This affects a lot of things – how brands are competing, how grocery markets are competing,” said second-author Jura Liaukonyte, a professor in the SC Johnson College of Business.
The paper published Oct. 30 in Marketing Science.
“Online shopping penetration has increased significantly, said Liaukonyte. “While it is not as high as it was during the peak of COVID, it remains considerably higher than pre-pandemic levels.”
For this work, the authors analyzed data by Numerator, a market research company that uses a mobile app receipt uploads to analyze brick-and-mortar store purchases, and proprietary methods to access Instacart purchases from the same participants. The researchers’ algorithm looked at three years’ worth of grocery purchases from 4,388 participants to get a sense of their typical in-store and online carts.
The researchers discovered a few key differences:
Online basket variety is around 10% lower compared to brick-and-mortar basket variety within the same household;
Instacart trips are 27% more similar to each other than offline trips within the same household when comparing categories; and
The number of overlapping items in Instacart baskets is more than double that of in-store carts when comparing items across successive trips to the same store.
One reason for the similarity and reduced variety in online baskets, the researchers suggest, is Instacart's “Buy it again” feature. This function simplifies the process for shoppers to initiate their new shopping baskets with items purchased during prior visits.
Overall, Liaukonyte said, the findings of the paper indicate that there might be greater consumer loyalty and inertia when shopping online.
“If we don’t pay attention,” she said, “we might fall into an echo filter bubble of repeatedly buying the same items online. This seemingly simple online convenience could make us less sensitive to price changes and limit product discovery, enhancing the pricing power of existing brands.”
First author, Sai Chand Chintala added that the heightened brand loyalty and consumer inertia could make it difficult for new brands and products to enter the market.
“Industry reports suggest that if a product isn't in a person’s cart by their first five or six online orders, it’s very unlikely that the product will ever make it in,” he said. “This highlights the importance for brands to advertise early on to ensure they are top-of-mind for consumers and make their way into their baskets.”
For additional information, see this Cornell Chronicle story.
-30-
END
Online grocery shopping promotes less variety, fewer impulse buys
2023-11-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Can AI help boost accessibility? These researchers tested it for themselves
2023-11-02
Generative artificial intelligence tools like ChatGPT, an AI-powered language tool, and Midjourney, an AI-powered image generator, can potentially assist people with various disabilities. These tools could summarize content, compose messages or describe images. Yet the degree of this potential is an open question, since, in addition to regularly spouting inaccuracies and failing at basic reasoning, these tools can perpetuate ableist biases.
This year, seven researchers at the University of Washington conducted a three-month autoethnographic study — drawing on their own experiences as people with and without disabilities — to test AI tools’ utility for accessibility. Though ...
UMass hydrogeologists develop innovative way to predict saltwater intrusion into groundwater using Plymouth, Mass. as test case
2023-11-02
November 2, 2023
UMass Hydrogeologists Develop Innovative Way to Predict Saltwater Intrusion into Groundwater Using Plymouth, Mass. as Test Case
Working closely with local conservation group, researchers develop new model to predict climate-change driven saltwater intrusion that is transferable to other vulnerable coastal communities
AMHERST, Mass. – As the world warms and ice sheets melt, the ocean continually rises. The greater Boston area can expect to see between one and six feet of sea level rise by 2100, according to recent ...
Looking sharp! Shark skin is unique and may have medical use, too
2023-11-02
By David L. Chandler
WOODS HOLE, Mass. -- Sharks differ from other fish in many ways, including an apparently remarkable ability to heal from wounds, according to reports of sharks recovering from injuries sustained in the wild. While this healing ability has not yet been documented in controlled laboratory conditions, some of the chemical compounds found in shark skin may have significant biomedical potential.
To investigate this possibility, two dermatology researchers from the Karolinska Institute in Sweden carried out research on a small shark, the spiny dogfish (Squalus acanthias) and other cartilaginous fish species at the ...
A known environmental hazard can change the epigenetics of cells
2023-11-02
Epigenetics, the chemical mechanisms that controls the activity of genes, allows our cells, tissues and organs to adapt to the changing circumstances of the environment around us. This advantage can become a drawback, though, as this epigenetic regulation can be more easily altered by toxins than the more stable genetic sequence of the DNA.
An article recently published at Science with the collaboration of the groups of Dr. Manel Esteller, Director of the Josep Carreras Leukaemia Research Institute ...
Golden Retriever Lifetime Study data uncovers potential connection between sterilization, hemangiosarcoma
2023-11-02
DENVER/Nov. 2 – A scientific analysis published in Veterinary and Comparative Oncology using Golden Retriever Lifetime Study data notes a potential correlation between canine sterilization and hemangiosarcoma development. This startling finding has been previously suggested by experts but still is poorly understood.
The authors note that the likelihood of diagnosing hemangiosarcoma appears consistently low across all sexes and neutering statuses until about eight years of age. Beyond this point, intact and neutered male ...
Herbivory limits vegetation restoration success at sites worldwide, new meta-analysis shows
2023-11-02
Excluding herbivores – or reintroducing their predators – may aid restoration efforts in many locations, suggests a new meta-analysis of more than 600 global studies. According to the analysis, herbivores at restoration sites reduced vegetation abundance by 89%, on average, a larger effect than they had at relatively undisturbed sites. Herbivores also suppressed plant diversity at these locations. Vegetation is a primary foundation of most ecosystems. However, in many, it has been dramatically degraded, contributing to the loss of biodiversity and ...
Southern hemisphere dominates decline in global water availability
2023-11-02
Driven in part by large-scale atmospheric climate modes, the Southern Hemisphere accounts for more than 95% of the recent decline in global water availability, according to a new study. Global land water availability has varied due to climate change and increased human water use. Although this crucial resource underpins livelihoods, socioeconomic development, and ecosystems worldwide, it remains unclear how water availability has changed in recent decades and what is driving these changes at a global scale. Yongqiang Zhang and colleagues combine various data, including streamflow observations of large river basins of ...
Researchers caution that biodiversity benefit-sharing needs a radically new approach
2023-11-02
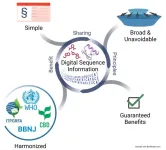
At the 2022 COP-15 meeting, signatories of the Convention on Biological Diversity reached a new agreement called the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework, which contained provisions to establish a separate, multilateral benefit-sharing mechanism for the use of “digital sequence information” (DSI), that is, the biological data associated with, or derived from, genetic resources such as nucleotide sequences and epigenetic, protein, and metabolite data.
In a new Policy Forum analysis published ...
Research outlines how sex differences have evolved
2023-11-02
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 18:00hrs GMT Thursday 2 November 2023
Peer reviewed
Observational study
People and animals
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and Heidelberg University in Germany have shown that sex differences in animals vary dramatically across species, organs and developmental stages, and evolve quickly at the gene level but slowly at the cell type level.
Mammals have different traits depending on sex, like antlers in male deer. These are known as ‘sexually dimorphic’ traits, and include differences which aren’t visible, ...
UCLA researchers develop solid-state thermal transistor for better heat management
2023-11-02
A team of researchers from UCLA has unveiled a first-of-its-kind stable and fully solid-state thermal transistor that uses an electric field to control a semiconductor device’s heat movement.
The group’s study, which will be published in the Nov. 3 issue of Science, details how the device works and its potential applications. With top speed and performance, the transistor could open new frontiers in heat management of computer chips through an atomic-level design and molecular engineering. The advance could also further the understanding of how heat is regulated in the human body.
“The precision control of how heat flows through materials has been a long-held ...