(Press-News.org) SAN ANTONIO — November 3, 2023 —New images captured by NASA’s Lucy spacecraft confirmed that the small main belt asteroid Dinkinesh is a binary, two asteroids that orbit a common center of mass. The SwRI-led mission will now fly by 11 asteroids in its 12-year mission to Jupiter’s Trojan asteroids. Dinkinesh was meant to be the first asteroid that Lucy flew by but ended up being the first two.
“Dinkinesh really did live up to its name; this is marvelous,” said Lucy Principal Investigator Dr. Hal Levison, of SwRI’s Solar System Science and Exploration Division in Boulder, Colorado, referring to the meaning of Dinkinesh (“you are marvelous”) in Amharic. “When Lucy was originally selected for flight, we planned to flyby seven asteroids. With the addition of Dinkinesh, two Trojan moons, and now this satellite, we’ve turned it up to 11.”
As Lucy approached Dinkinesh, the team noticed that the asteroid’s brightness was changing in interesting ways, and the team wondered if Dinkinesh was a binary system. As the spacecraft sent back its first images, this was confirmed: Dinkinesh is a close binary. From a preliminary analysis of the first available images, the team estimates that the larger body is approximately 0.5 miles (790 m) at its widest, while the smaller is about 0.15 miles (220 m) in size.
This flyby of Dinkinesh primarily served as an in-flight test of the spacecraft, specifically focusing on testing the systems that allow Lucy to autonomously track an asteroid as it flies past at 10,000 miles per hour, referred to as the terminal tracking system.
“We have seen many asteroids up close, and one may think little is left to discover and surprise us. Well, that is clearly wrong. Dinkinesh, and its enigmatic moonlet, differ in some interesting ways from the similarly sized near-Earth asteroids that have been seen by spacecraft like OSIRIS-REx and DART,” said Deputy Principal Investigator Dr. Simone Marchi of SwRI.
While this encounter was carried out as an engineering test, the team’s scientists are excitedly poring over the data to glean insights into the nature of small asteroids.
“Sharing the anticipation of viewing the first images with the team has been incredibly thrilling, as has been the lively discussion regarding the geology of these two remarkably small yet fascinatingly intriguing targets. I am eagerly looking forward to unraveling the color variations across this binary system,” said Dr. Silvia Protopa of SwRI.
The Lucy team will continue to downlink the remainder of the encounter data from the spacecraft over the next week. They will use the data to evaluate Lucy’s behavior during the encounter and prepare for the next close-up look at an asteroid, the main belt asteroid Donaldjohanson, in 2025. Lucy will then be well prepared to observe the mission's main targets, the Jupiter Trojan asteroids, starting in 2027.
For more information, visit https://www.swri.org/planetary-science.
END
SwRI-led Lucy mission shows Dinkinesh asteroid is actually a binary
NASA’s Lucy spacecraft makes first asteroid flyby
2023-11-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
High-impact clinical trials yield results that could improve kidney care
2023-11-03
Philadelphia, PA (November 3, 2023) — The results of numerous high-impact clinical trials that could affect kidney-related medical care will be presented in-person at ASN Kidney Week 2023 November 1–November 5.
In patients with IgA nephropathy, the IgA protein accumulates and damages the filtering part of the kidney, or glomerulus. Endothelin and angiotensin II contribute to the pathogenesis of this condition through different pathways. The phase 3 PROTECT trial compared sparsentan, a dual endothelin and angiotensin II receptor blocker, with irbesartan, an angiotensin II ...
An exotic tick that can kill cattle is spreading across Ohio
2023-11-03
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A species of exotic tick arrived in Ohio in 2021 in such huge numbers that their feeding frenzy on a southeastern farm left three cattle dead of what researchers believe was severe blood loss.
The scientists from The Ohio State University have reported in the Journal of Medical Entomology on the state’s first known established population of Asian longhorned ticks, and are now conducting research focused on monitoring and managing these pests.
So far, these ticks are not deemed to be a threat to human health. They tend to favor large livestock ...
34,000 healthcare professionals surveyed indicate they have higher bias against transgender people
2023-11-03
By analyzing data from the Harvard Implicit Association Test—a widely accepted measure of a person’s attitudes toward people based on characteristics like race, gender, and sexuality—researchers find that healthcare professionals, and in particular nurses, are more biased against transgender people than are people who are not healthcare professionals. A questionnaire administered before and after the test shows that healthcare professionals are less likely to know transgender people personally and that nurses are more likely to conflate sex and gender identity. These results are reported November 3 in the journal Heliyon.
The Implicit Association Test works by asking participants ...
E-cigarette use among adults
2023-11-03
About The Study: The findings of this study of 414,000 respondents to the 2021 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System survey suggest that e-cigarette use remained common during the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly among young adults ages 18 to 24 (18% prevalence). Notably, 71.5% of individuals ages 18 to 20 who reported current e-cigarette use had never used combustible cigarettes. These results underscore the rationale for the implementation and enforcement of public health policies tailored to young adults.
Authors: Michael J. Blaha, M.D., M.P.H., of the Johns Hopkins ...
Higher parenting stress for dads working from home during pandemic
2023-11-03
A survey from Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago found that 40 percent of parents who worked remotely during the pandemic reported higher parenting stress compared with only 27 percent of parents who worked onsite.
Results revealed a gender difference – fathers who worked from home were twice as likely to report that parenting was stressful all or most of the time compared to fathers who worked onsite. Parenting stress for mothers who worked at home was slightly higher, but it did not reach statistical significance.
The study found no differences ...
Health care expenditures for black and white adults living under similar conditions
2023-11-03
About The Study: In this study of a nationally representative sample of 7,062 non-Hispanic Black or white adults, health care spending for Black adults in the U.S. was equal to or less than that of white adults, but only in areas of racial and economic equity and equitable insurance access. The results underscore the continuing need to recognize place as a contributor to race-based differences in health care spending.
Authors: Lorraine T. Dean, Sc.D., of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.3798)
Editor’s ...
Higher parenting stress for dads working from home versus onsite during pandemic
2023-11-03
Findings revealed a gender difference
‘Might be a reflection of societal expectations that men should prioritize work obligations over family needs’
Study authors offer tips for parents, employers to mitigate stress of remote work
CHICAGO --- Forty percent of parents who worked remotely during the COVID-19 pandemic reported higher parenting stress compared with only 27 percent of parents who worked onsite, reports a new survey from scientists at Northwestern University and Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital ...
Developed the most comprehensive database for the study of protein aggregation
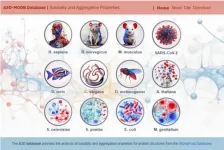
2023-11-03
Researchers at the IBB-UAB have developed the most comprehensive database available to date to help understand the basis of protein aggregation, a phenomenon associated with ageing and several pathologies. The new resource, A3D-MOBD, brings together the proteomes of twelve of the most studied model organisms which cover distant biological clades and contains over half a million predictions of protein regions with a propensity to form aggregates.
The A3D-MOBD was developed by the Protein Folding and Computational Diseases Group at the Institut de Biotecnologia i de Biomedicina of the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (IBB-UAB), which is directed by Biochemistry and ...
The little things matter: Chemists develop new sensor for microvolume pH detection
2023-11-03
Measuring the pH of substances gives us vital clues about the world around us, such as identifying contaminated water or checking the toxicity of medical or cosmetic products.
Often, only small amounts of samples are available, but monitoring the variation in pH in these miniscule volumes matters. For example, identifying pH changes within tiny volumes of fluid from single cells can help in the detection of ovarian cancer.
However, the current methods for measuring pH are mainly for bulk solutions and are not sensitive enough or are too fragile to measure small volumes on a commercial scale.
In a recent study published in Microchimica ...
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors
2023-11-03
Teams led by Prof. DU Jiangfeng, Prof. SHI Fazhan and Prof. KONG Fei from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) used the Nitrogen-Vacancy (NV) center inside a single nanodiamond for quantum sensing to overcome the problem of random particle rotation.
The study was published on Oct. 7th in Nature Communications.
It is an important goal to detect and analyze molecules under physiological in situ conditions in the field of life sciences. Only by observing biomolecules under this condition can we reveal conformation changes when they realize physiological functions.
Thanks to its high sensitivity, good biocompatibility, and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Blood test “clocks” predict when Alzheimer’s symptoms will start
Second pregnancy uniquely alters the female brain
Study shows low-field MRI is feasible for breast screening
Nanodevice produces continuous electricity from evaporation
Call me invasive: New evidence confirms the status of the giant Asian mantis in Europe
Scientists discover a key mechanism regulating how oxytocin is released in the mouse brain
Public and patient involvement in research is a balancing act of power
Scientists discover “bacterial constipation,” a new disease caused by gut-drying bacteria
DGIST identifies “magic blueprint” for converting carbon dioxide into resources through atom-level catalyst design
COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy may help prevent preeclampsia
Menopausal hormone therapy not linked to increased risk of death
Chronic shortage of family doctors in England, reveals BMJ analysis
Booster jabs reduce the risks of COVID-19 deaths, study finds
Screening increases survival rate for stage IV breast cancer by 60%
ACC announces inaugural fellow for the Thad and Gerry Waites Rural Cardiovascular Research Fellowship
University of Oklahoma researchers develop durable hybrid materials for faster radiation detection
Medicaid disenrollment spikes at age 19, study finds
Turning agricultural waste into advanced materials: Review highlights how torrefaction could power a sustainable carbon future
New study warns emerging pollutants in livestock and aquaculture waste may threaten ecosystems and public health
Integrated rice–aquatic farming systems may hold the key to smarter nitrogen use and lower agricultural emissions
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Mirror image pheromones help beetles swipe right
Prenatal lead exposure related to worse cognitive function in adults
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
Pollen counts can be predicted by machine learning models using meteorological data with more than 80% accuracy even a week ahead, for both grass and birch tree pollen, which could be key in effective
Rewriting our understanding of early hominin dispersal to Eurasia
Rising simultaneous wildfire risk compromises international firefighting efforts
[Press-News.org] SwRI-led Lucy mission shows Dinkinesh asteroid is actually a binaryNASA’s Lucy spacecraft makes first asteroid flyby