(Press-News.org) A survey from Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago found that 40 percent of parents who worked remotely during the pandemic reported higher parenting stress compared with only 27 percent of parents who worked onsite.
Results revealed a gender difference – fathers who worked from home were twice as likely to report that parenting was stressful all or most of the time compared to fathers who worked onsite. Parenting stress for mothers who worked at home was slightly higher, but it did not reach statistical significance.
The study found no differences in mental or general health between parents who worked remotely or onsite.
“Our survey results show that teleworking during the pandemic was associated with more parenting stress, especially for fathers,” said lead author John James Parker, MD, a pediatrician at Lurie Children’s, an internist at Northwestern Medicine and Assistant Professor of Pediatrics at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. “This might be a reflection of societal expectations that men should prioritize work obligations over family needs, which creates additional stress for fathers working from home. We recommend that parents reflect on their family and work situation and try to find an arrangement that limits stress and promotes wellbeing. This can be as simple as putting a noise cancelling machine in the workspace, rearranging schedules to limit distractions and planning time for parents to step away from work to be fully engaged with their children.
The survey included 1,060 parents from all 77 neighborhoods in Chicago. The study was published in JAMA Network Open.
“Employers could provide support to fathers by offering more flexibility and recognizing that both parents need more work/life balance. Employers also could encourage parents who work from home, especially men, to take advantage of employee assistance programs if they are experiencing high levels of stress,” added Dr. Parker. “This is important, since parents’ stress is linked to negative parental health and child developmental outcomes.”
Research at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago is conducted through Stanley Manne Children’s Research Institute. The Manne Research Institute is focused on improving child health, transforming pediatric medicine and ensuring healthier futures through the relentless pursuit of knowledge. Lurie Children’s is a nonprofit organization committed to providing access to exceptional care for every child. It is ranked as one of the nation’s top children’s hospitals by U.S. News & World Report. Lurie Children’s is the pediatric training ground for Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine.
END
Higher parenting stress for dads working from home during pandemic
Fathers who worked remotely were more than twice as likely to report higher parenting stress compared to fathers who worked onsite
2023-11-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Health care expenditures for black and white adults living under similar conditions
2023-11-03
About The Study: In this study of a nationally representative sample of 7,062 non-Hispanic Black or white adults, health care spending for Black adults in the U.S. was equal to or less than that of white adults, but only in areas of racial and economic equity and equitable insurance access. The results underscore the continuing need to recognize place as a contributor to race-based differences in health care spending.
Authors: Lorraine T. Dean, Sc.D., of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.3798)
Editor’s ...
Higher parenting stress for dads working from home versus onsite during pandemic
2023-11-03
Findings revealed a gender difference
‘Might be a reflection of societal expectations that men should prioritize work obligations over family needs’
Study authors offer tips for parents, employers to mitigate stress of remote work
CHICAGO --- Forty percent of parents who worked remotely during the COVID-19 pandemic reported higher parenting stress compared with only 27 percent of parents who worked onsite, reports a new survey from scientists at Northwestern University and Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital ...
Developed the most comprehensive database for the study of protein aggregation
2023-11-03
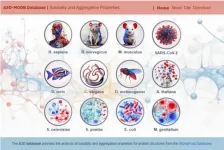
Researchers at the IBB-UAB have developed the most comprehensive database available to date to help understand the basis of protein aggregation, a phenomenon associated with ageing and several pathologies. The new resource, A3D-MOBD, brings together the proteomes of twelve of the most studied model organisms which cover distant biological clades and contains over half a million predictions of protein regions with a propensity to form aggregates.
The A3D-MOBD was developed by the Protein Folding and Computational Diseases Group at the Institut de Biotecnologia i de Biomedicina of the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (IBB-UAB), which is directed by Biochemistry and ...
The little things matter: Chemists develop new sensor for microvolume pH detection
2023-11-03
Measuring the pH of substances gives us vital clues about the world around us, such as identifying contaminated water or checking the toxicity of medical or cosmetic products.
Often, only small amounts of samples are available, but monitoring the variation in pH in these miniscule volumes matters. For example, identifying pH changes within tiny volumes of fluid from single cells can help in the detection of ovarian cancer.
However, the current methods for measuring pH are mainly for bulk solutions and are not sensitive enough or are too fragile to measure small volumes on a commercial scale.
In a recent study published in Microchimica ...
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors
2023-11-03
Teams led by Prof. DU Jiangfeng, Prof. SHI Fazhan and Prof. KONG Fei from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) used the Nitrogen-Vacancy (NV) center inside a single nanodiamond for quantum sensing to overcome the problem of random particle rotation.
The study was published on Oct. 7th in Nature Communications.
It is an important goal to detect and analyze molecules under physiological in situ conditions in the field of life sciences. Only by observing biomolecules under this condition can we reveal conformation changes when they realize physiological functions.
Thanks to its high sensitivity, good biocompatibility, and ...
Men less likely than women to share negative information, says study
2023-11-03
A new study from Carnegie Mellon University, Bayes Business School (formerly Cass), and Bocconi University has found that men are less eager and likely to share negative information than women, while there was little difference when it comes to positive news.
Published in the Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, the authors suggest that this may be due to a greater concern among men over how other people will see them, resulting in a tendency to self-promote by sharing positive information about themselves and not revealing their negative experiences to others.
Dr Erin Carbone, Visiting Assistant Professor in the Department of Social ...
Focus on AR/VR: Near-eye display based on metasurface devices
2023-11-03
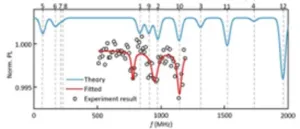
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Science; DOI 10.29026/oes.2023.230025 discusses near-eye display based on metasurface devices.
With the rise of the meta-universe, virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies have been developing rapidly in recent years. Near-eye displays are crucial technologies for VR and AR. Despite the rapid advances in near-eye display technologies, there are still challenges such as large field of view (FOV), high resolution, high image quality, natural free 3D effect, and compact form factor. Great efforts have been devoted to striking a balance between visual performance and device compactness. ...
A review of liquid crystal spatial light modulators devices and applications
2023-11-03
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Science; DOI 10.29026/oes.2023.230026 overviews liquid crystal spatial light modulators devices and applications.
Technology to control and harness light has existed for centuries, often as static solutions that must be custom-designed. It is only in the past couple of decades that the digital era of micro-electronics and computing has seen fast rewritable technology meant for displays find its way into the mainstream of optics. In this review, the authors showcase the recent advances in replacing the traditional static optical toolkit with a modern digital toolkit for “light on demand”. ...
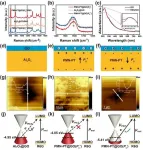
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response
2023-11-03
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances, 10.29026/oea.2023.230094 discusses Ferroelectric modulation of the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response.
Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) is a powerful fingerprint analysis and detection technique that plays an important role in the fields of food safety, environmental protection, bio-imaging and hazardous substance identification. Electromagnetic enhancement (EM) and chemical enhancement (CM) are the two recognized mechanisms of action for amplifying Raman signals. EM originates from the localized surface plasmonic resonance effect of noble metal nanostructures ...
Knot-inspired optical sensors for slip detection and friction measurement in dexterous robotic manipulation
2023-11-03
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances, 10.29026/oea.2023.230076 discusses knot-inspired optical sensors for slip detection and friction measurement in dexterous robotic manipulation.
Hands possess an awe-inspiring ability to perceive friction forces with remarkable accuracy, all thanks to the mechanical receptors nestled within skin. This natural gift allows objects to be handled deftly and tools to be wielded effortlessly, infusing daily life with a delightful flexibility. But what if this tactile prowess could be unlocked in robots?
Imagine a world where robots possess the uncanny ability to detect and understand friction and slip, just ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Start school later, sleep longer, learn better
Many nations underestimate greenhouse emissions from wastewater systems, but the lapse is fixable
The Lancet: New weight loss pill leads to greater blood sugar control and weight loss for people with diabetes than current oral GLP-1, phase 3 trial finds
Pediatric investigation study highlights two-way association between teen fitness and confidence
Researchers develop cognitive tool kit enabling early Alzheimer's detection in Mandarin Chinese
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
New record: Laser cuts bone deeper than before
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
Scientists identify key protein that stops malaria parasite growth
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
[Press-News.org] Higher parenting stress for dads working from home during pandemicFathers who worked remotely were more than twice as likely to report higher parenting stress compared to fathers who worked onsite