Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) is a powerful fingerprint analysis and detection technique that plays an important role in the fields of food safety, environmental protection, bio-imaging and hazardous substance identification. Electromagnetic enhancement (EM) and chemical enhancement (CM) are the two recognized mechanisms of action for amplifying Raman signals. EM originates from the localized surface plasmonic resonance effect of noble metal nanostructures such as gold, silver, and copper, while CM originates from the charge transfer between the substrate and the probe molecules. In principle, the charge transfer efficiency depends on the coupling of the incident laser energy to the energy levels of the substrate-molecule system. Compared to EM-based SERS substrates, CM-based SERS substrates are usually made of two-dimensional materials including semiconductor oxides, metal carbides, and graphene and its evolutions, which have weaker signal enhancement capabilities. However, the advantages of CM-based SERS substrate, such as high specificity, homogeneity and biocompatibility, have attracted the attention of researchers. It has been shown that the charge transfer efficiency between the substrate and the probe molecule can be optimized and the tunability of the substrate can be improved by means of phase change engineering and elemental doping. However, the existing techniques are difficult and irreversible to modulate, which somewhat limits the application of CM-based SERS substrates. Therefore, how to realize the flexible and reversible regulation of the energy level coupling of the substrate-molecule system remains to be further explored.
The authors of this article introduce a new strategy to flexibly and reversibly modulate the chemical enhancement of SERS based on the ferroelectric effect, realizing the ultra-sensitive universal detection of molecules with different band structures at different excitation wavelengths. In ferroelectric materials, the net charge induced by polar stacking is passivated by surface reconstruction, mobile charges and adsorbed materials, which makes it possible to modulate the electronic structure of the two-dimensional materials on their surfaces.
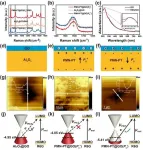
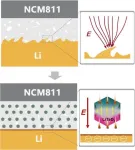
Large-scale modulation of the Fermi level of surface-adsorbed graphene oxide was first achieved by controlling the polarization direction of ferroelectric lead magnesium niobate-lead titanate (PMN-PT). Using Kelvin probe force microscopy, the precise positions of the Fermi levels of graphene oxide can be obtained. When the polarization direction of PMN-PT is downward, the Fermi level of graphene oxide is modulated to approach the HOMO of Rhodamine 6G (R6G), which effectively improves the coupling efficiency of the system's energy level to the incident laser energy (532 nm) and optimizes the photo-induced charge transfer (PICT) resonance, thus further enhancing the SERS signal (Fig. 1). The shift of the G-band Raman peak indicates a change in charge density of graphene oxide, while the shift in the UV absorption peak proves the charge transfer interaction. In addition, changing the temperature can further regulate the polarization strength of PMN-PT, achieving a flexible and reversible modulation of the Fermi level of graphene oxide, with a 102-fold enhancement of the detection sensitivity.
Based on this, to verify the universality of the ferroelectric effect for the modulation of chemical enhancement during SERS detection, the researchers also investigated three probe molecules possessing different band structures, namely crystalline violet (CV), methylene blue (MB) and p-nitrothiophenol (PNTP). It was found that the SERS signals of the three molecules could also be optimized by adjusting the polarization direction or polarization strength of PMN-PT. Unlike CV and MB, for PNTP, the energy level of the system can be better coupled with the incident laser energy (532 nm) when the polarization direction of PMN-PT is upward, which leads to the effective optimization of its SERS signal. In conclusion, the Fermi level of graphene oxide can be flexibly and reversibly tuned under different ferroelectric polarization directions and polarization strengths, and the highly sensitive SERS detection of molecules with different band structures has been achieved based on the same SERS substrate, which effectively solves the universality problem of CM-based SERS substrates.
This method provides a new idea for the preparation and application of surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates based on chemical enhancement mechanisms, which is expected to be extended to other low-dimensional materials.
# # # # # #
The Laboratory of Optoelectronic Functional Materials and Devices is a key laboratory in Shandong Province in the 13th Five-Year Plan, which is based on the School of Physics and Electronics of Shandong Normal University. With Prof. Baoyuan Man as the discipline leader, the research team aims at the frontier of the materials field, conducts scientific research and practical application of new materials and new device technologies; solves key scientific problems in the research fields of environmental monitoring, biomolecule detection, high-efficiency laser output and flexible stretchable devices. The research team has published more than 300 papers in international high level journals including Nature Communication,ACS Photonics,Nano Energy,Nano Research,Opto-Electronic Advance,Phys. Rev. B, etc., and has been awarded 25 national invention patents. The team members have been awarded the first prize of Natural Science Award of Shandong Province and have undertaken a number of national topics such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China, as well as provincial and ministerial scientific research projects.
# # # # # #
Opto-Electronic Advances (OEA) is a high-impact, open access, peer reviewed monthly SCI journal with an impact factor of 14.1 (Journal Citation Reports for IF2022). OEA is indexed in SCI, EI, DOAJ, Scopus, CA and ICI databases.
The journal is published by The Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, aiming at providing a platform for researchers, academicians, professionals, practitioners, and students to impart and share knowledge in the form of high quality empirical and theoretical research papers covering the topics of optics, photonics and optoelectronics.
# # # # # #
More information: http://www.oejournal.org/oea
Editorial Board: http://www.oejournal.org/oea/editorialboard/list
All issues available in the online archive (http://www.oejournal.org/oea/archive).
Submissions to OEA may be made using ScholarOne (https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/oea).
ISSN: 2096-4579
CN: 51-1781/TN
Contact Us: oea@ioe.ac.cn
Twitter: @OptoElectronAdv (https://twitter.com/OptoElectronAdv?lang=en)
WeChat: OE_Journal
# # # # # #
Shao MR, Ji C, Tan JB, Du BQ, Zhao XF et al. Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response. Opto-Electron Adv 6, 230094 (2023). doi: 10.29026/oea.2023.230094
# # # # # #
END