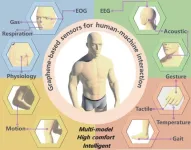
Interaction between machines and humans is paramount to the development of the new technologies of the metaverse, which are designed to augment the human experience through cloud computing and extended reality (XR). Graphene, a two-dimensional carbon material, has emerged as an ideal candidate for wearable sensor technology, paving the way for a new era of seamless human-machine interaction (HMI).
A team of material scientists led by Tian-Ling Ren from Tsinghua University in Beijing, China recently outlined the state of graphene-based HMI sensor technology to advance research in the field. Advanced sensor technologies that are flexible, lightweight and can be worn continuously are ideal for HMI and have potential applications in both the immersive virtual world of the metaverse and wearable healthcare technologies. Current research is aimed at creating sensors capable of interfacing nearly every part of the body that can be measured, including the brain, eyes and mouth. These measurements can then be used to characterize bodily information by an interfacing machine.
The team published their review in Carbon Future on August 13, 2023.
“In this review, we present an overview of some of our research team’s efforts to create graphene-based sensors for human-machine interfaces. These sensors, designed for use on various parts of the human body, are introduced with a focus on their target signals, design, manufacturing process and performance features. Additionally, we delve into potential future developments for graphene-based sensors, including multi-modality, improved comfort, and intelligence,” said Tian-Ling Ren, senior author of the review paper, professor in the School of Integrated Circuit and deputy dean of the School of Information Science and Technology at Tsinghua University. Dr. Ren is also the Yangtze River Scholar Professor of Chinese Ministry of Education and vice director of the Center for Environmental and Health Sensing Technology at Tsinghua University.
Graphene is made up of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged as a hexagonal lattice. The unique properties of graphene, including impressive conductivity, low chemical reactivity, flexibility and light weight, make the material an ideal candidate for human-machine interface sensor development.
The research team outlines the progress made in graphene-based sensors designed to measure a variety of different signals from the body. “Many parts of the human body, from head to toe, have the potential to be developed into human-machine interfaces. Brain, eyes, ears, nose, mouth, throat, fingertips, skin, joints, and feet can all be used as HMI interfaces based on electroencephalogram (EEG), electromyography (EMG), electrooculogram (EOG), eye movement, light, breathing, voice, touch, temperature, movement, gait and other physiological information,” Tian-Ling Ren said.
Humans can also benefit from output generated by machines, and development of multi-modal sensors that can alternate between signal measurement, such as sound perception, and signal output, such as sound generation, will be particularly useful for HMIs. Ren’s team demonstrated graphene sound production in a previous study. Tian-Ling Ren said, “With the help of machine learning, this interface can achieve speech recognition, emotion analysis, content processing, and more, making it ideal for intelligent robotic communication.”
One of the challenges of graphene-based sensor development is achieving a measurement range large enough to detect very dynamic senses, such as the sense of touch. To address this issue, graphene pressure sensors with a wide sensitivity range have been developed using loosely stacked laser-scribed graphene (LSG) films that increase in density with increasing pressure. The increased film density, in turn, causes a change in measured resistance with a range large enough to achieve high sensitivity.
The research team expects the review to spur development of new graphene-based sensors designed to facilitate more natural HMIs and improve real-time data collection and response in healthcare. “Graphene-based sensors for HMI are expected to become more diverse and practical in the coming years. In the same part of the body, the human and machine can interact with different signals… in many different ways,” said Tian-Ling Ren.
Other contributors include Tianrui Cui, Ding Li, Thomas Hirtz, Jiandong Xu, Yancong Qiao, Haokai Xu, He Tian and Yi Yang from the School of Integrated Circuit and the Beijing National Research Center for Information Science and Technology (BNRist) at Tsinghua University in Beijing, China; and Houfang Liu from the BNRist at Tsinghua University.
This work was supported by by the National Key R&D Program of China (2021YFC3002200 and 2022YFB3204100), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U20A20168, 51861145202, 61874065, and 62022047).
##
About Carbon Future
Carbon Future is an open access, peer-reviewed and international interdisciplinary journal that reports carbon-related materials and processes, including catalysis, energy conversion and storage, as well as low carbon emission process and engineering. Carbon Future will publish Research Articles, Reviews, Minireviews, Highlights, Perspectives, and News and Views from all aspects concerned with carbon. Carbon Future will publish articles that focus on, but not limited to, the following areas: carbon-related or -derived materials, carbon-related catalysis and fundamentals, low carbon-related energy conversion and storage, low carbon emission chemical processes.
About SciOpen
SciOpen is a professional open access resource for discovery of scientific and technical content published by the Tsinghua University Press and its publishing partners, providing the scholarly publishing community with innovative technology and market-leading capabilities. SciOpen provides end-to-end services across manuscript submission, peer review, content hosting, analytics, and identity management and expert advice to ensure each journal’s development by offering a range of options across all functions as Journal Layout, Production Services, Editorial Services, Marketing and Promotions, Online Functionality, etc. By digitalizing the publishing process, SciOpen widens the reach, deepens the impact, and accelerates the exchange of ideas.
END