(Press-News.org) A new report in Nature Geoscience has brought to light the challenge of air pollution levels in Africa and why international action is needed to combat it.
Over the last 50 years African nations have suffered from rapidly deteriorating air quality, making their cities some of the most polluted in the world. Particulate matter concentration levels are now five to ten levels greater than that recommended by the World Health Organisation, with the situation predicted to worsen as populations grow and industrialization accelerates.
However, far too little has been done to try and combat the dangerous air quality with just 0.01% of global air pollution funding currently spent in Africa.
The new perspective piece from the University of Birmingham, the University of Cambridge, Imperial College London, South Eastern Kenya University and the African Centre for Clean Air, published today (7 Nov) in Nature Geoscience, argues that tackling this issue requires collective efforts from African countries, regionally tailored solutions, and global collaboration.
Francis Pope, Professor of Atmospheric Science at the University of Birmingham and one of the co-authors, said: “The burning of biomass fuel for cooking, heating, and lighting, the crude oil exploitation and coal mining industries, and old vehicles being shipped in from Europe are all causes for the poor air quality in African nations. This dangerous air can cause complex and sometimes deadly health issues for those breathing it in. If this wasn’t enough of a reason to tackle this issue, air pollution in Africa is not just a problem for people living on the continent, but for the wider world, limiting the ability to meet global climate targets and combat the climate emergency.”
Multiple efforts have been made over the years to tackle air pollution, such as the signing of C40 Clean Air Declaration by ten major African cities. Initiatives to monitor air-pollution levels and collect much needed data have also begun to gather momentum.
But there is still much to be done. The researchers argue that regional and international efforts must be coordinated to achieve real change and leverage existing knowledge on controlling and cutting air pollution.
They call for urgent collaboration on:
Continuous air monitoring via a network of sensors in order to build a detailed picture of air pollution variations and track progress.
Investment in clean energy such as solar, hydropower and wind to meet Africa’s energy demand which is expected to double by 2040.
Improved solid waste management to prevent dumping and burning of waste and improve reuse, recycling, and recovery rates.
Investment in environmentally friendly technology to ensure African countries can grow economically whilst avoiding dirty and obsolete technology from the Global North.
Infrastructure improvements to curb emissions from the transport sector, improving public transport provision and adopting higher emission standards for fuel and imported vehicles.
Co-author of the article, Dr Gabriel Okello, from the Institute for Sustainability Leadership at the University of Cambridge and the African Centre for Clean Air, said: “Air pollution is complex and multifaceted with different sources and patterns within society. Addressing it requires more ambitious, collaborative, and participatory approaches centred on involvement of stakeholders in policy, academia, business, communities to co-design and co-produce context-specific interventions. This should be catalysed by increased investment in interventions that are addressing air pollution. Africa has the opportunity to leverage the growing political will and tap into the young population to accelerate action towards the five broad suggestions in our paper.”
Dr Andriannah Mbandi, from South Eastern Kenya University and co-author of the article, said: “The burden of air pollution unjustly rests on poorer populations, and women and children, as they most likely face higher exposure to pollutants and most probably experience more impacts. Thus, clean air actions will go some ways in redressing some of these inequalities in Africa, in addition to the benefits to health and the environment.”
Professor Pope concludes: “There is no ‘one size fits all’ solution to Africa’s air quality problems, and each region and population will have their own specific challenges to overcome. But by being proactive and doing these five actions there will be a reduction in air pollution levels, meaning healthier people and a healthier planet.”
ENDS
END
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00hrs GMT Tuesday 7 November 2023
Peer reviewed
Observational study
People
Body changes up to eight years before inflammatory bowel disease diagnosis
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and Aalborg University in Copenhagen have shown that changes can be detected in blood tests up to eight years before a diagnosis of Crohn’s disease and up to three years before a diagnosis of ulcerative colitis.
This means the beginnings of inflammatory bowel diseases start a long time before symptoms occur, and in the future may provide an opportunity for doctors to take preventative ...
Many parents experience stress, anxiety, and depressive symptoms throughout their lives, particularly during times of transition, such as pregnancy and children’s entry into school. Studies have generally found that high levels of anxiety and depression in parents are linked to poorer behavioural and cognitive outcomes in children.
A team of researchers led by Tina Montreuil, Associate Professor in McGill’s Department of Educational and Counselling Psychology and Scientist in the Child Health and Human ...
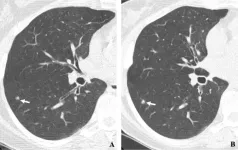
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Diagnosing early-stage lung cancer with low-dose CT screening dramatically improves the long-term survival rate of cancer patients, according to a large-scale, 20-year international study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). The results show that patients diagnosed with lung cancer by low-dose CT screening have a 20-year survival rate of 81%. If diagnosed in the earliest Stage I, long-term survival was 95%.
“It is the first time that 20-year survival rates ...
New York, NY (November 7, 2023) — Diagnosing early-stage lung cancer with low-dose computed tomography (CT) screening drastically improves its cure rate measured over a 20-year period, according to a large-scale international study by Mount Sinai researchers published in Radiology.
The results show that patients diagnosed with lung cancer via CT screening have a 20-year survival rate—an approximation of the cure rate—of 81 percent. Among the 1,257 participants diagnosed with lung cancer, 81 percent ...
BACKGROUND
One of the hallmarks of cancer cell development is its dependence on sugar, especially glucose, to grow and divide. Scientists have long been studying how to restrict or block this process that promotes tumor growth, called glycolysis, from happening as a possible effective strategy against cancer.
Previously, researchers from the UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center identified a specific protein sodium glucose transporter 2, or SGLT2, as a mechanism that lung cancer cells can utilize to obtain glucose. Drugs that inhibit SGLT2 are already FDA approved for other conditions and the UCLA team found these drugs could also delay the development ...
St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital today announced Giles Robinson, M.D., has assumed the role of director for the Department of Oncology’s Division of Neuro-Oncology. He has also become co-leader of the Neurobiology and Brain Tumor Program within the St. Jude Comprehensive Cancer Center. These combined units comprise one of the largest clinical brain tumor programs in North America.
“Dr. Robinson has been an exemplary member of St. Jude since joining as a hematology/oncology fellow in 2007,” said Julie R. Park, M.D., Department of Oncology ...
HOUSTON and DUBLIN ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and Jazz Pharmaceuticals plc today announced a five-year strategic research collaboration agreement to evaluate zanidatamab, Jazz’s investigational HER2-targeted bispecific antibody, in multiple HER2-expressing cancers.
The collaboration will combine MD Anderson’s translational medicine and clinical research expertise with Jazz’s expanding oncology drug development capabilities to investigate the potential of zanidatamab as monotherapy and in combination with other treatments for patients with different tumor types and stages. This includes its possible applicability ...
They reveal the origin of wine, the age of bones and fossils, and they serve as diagnostic tools in medicine. Isotopes and isotopologues – molecules that differ only in the composition of their isotopes – also play an increasingly important role in astronomy. For example, the ratio of carbon-12 (12C) to carbon-13 (13C) isotopes in the atmosphere of an exoplanet allows scientists to infer the distance at which the exoplanet orbits its central star.
Until now, 12C and 13C bound in carbon monoxide were the only isotopologues that could be measured in the atmosphere of an exoplanet. Now a team of researchers has succeeded in detecting ammonia isotopologues ...
Online shopping for cigarettes and vaping products increased significantly in the weeks following the implementation of SB-793, a 2022 California law prohibiting the sale of flavored tobacco products. Researchers at the Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human Longevity Science at University of California San Diego identified potential loopholes in tobacco control policies due to the absence of explicit regulations on e-commerce sales in retailer licensing programs.
Reporting in the journal Tobacco Control on Nov. 7, 2023, researchers assessed the ...
Karl Klose, director of The South Texas Center for Emerging Infectious Diseases (STCEID) and the Robert J. Kleberg, Jr. and Helen C. Kleberg College of Sciences Endowed Professor, coauthored a research article with Cameron Lloyd ’23, a UTSA doctoral student who graduated in August with a Ph.D. in molecular microbiology and immunology under the guidance of Klose.
The research paper investigates a novel strategy for inhibiting the spread and infection of Vibrio cholerae, the bacteria responsible for the disease, cholera.
The research article is entitled, “A peptide-binding ...