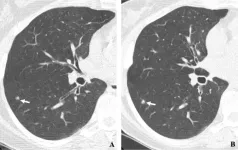
(Press-News.org) OAK BROOK, Ill. – Diagnosing early-stage lung cancer with low-dose CT screening dramatically improves the long-term survival rate of cancer patients, according to a large-scale, 20-year international study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). The results show that patients diagnosed with lung cancer by low-dose CT screening have a 20-year survival rate of 81%. If diagnosed in the earliest Stage I, long-term survival was 95%.
“It is the first time that 20-year survival rates from annual screening have been reported,” said the study’s lead author, Claudia Henschke, Ph.D., M.D., professor of radiology and director of the Early Lung and Cardiac Action Program at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York. “This 20-year survival rate of 81% is the estimated cure rate of all participants with lung cancers diagnosed by annual screening. This is a huge benefit compared to waiting for a diagnosis that, in usual care, is symptom-prompted.”
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death. According to the American Lung Association, the average lung cancer five-year survival rate is 18.6%. Only 16% of lung cancers are diagnosed at an early stage, and more than half of people with lung cancer die within one year of being diagnosed.
While treatments of more advanced-stage cancers with targeted therapy and immunotherapy have come a long way, the best tool in the fight against cancer deaths is early diagnosis through low-dose CT screening before symptoms appear.
Since 1992, Dr. Henschke and colleagues have been studying the effectiveness of low-dose CT screening for lung cancer. This led to the creation of the International Early Lung Cancer Action Program (I-ELCAP) which has enrolled more than 89,000 participants in over 80 institutions worldwide. This international program will continue its collaborations in 2024 with clinical and government organizations to roll out lung screening programs for underserved and low-income countries on two additional continents.
In 2006, the researchers identified a 10-year survival rate of 80% for the patients whose cancer was identified by CT screening. For this study, they looked at 20-year survival rates.
“We were excited to see that the estimated cure rate we reported in 2006 has persisted after 20 years of follow-up,” Dr. Henschke said.
The new study also found that among the 1,257 I-ELCAP participants diagnosed with lung cancer, 81% had Stage I disease. A Stage I lung cancer is a very small tumor that has not spread to any lymph nodes. In this study, the long-term survival rate for Stage I cancers was 87%.
The findings demonstrate the importance of low-dose CT screening for early detection of lung cancer.
The researchers also included participants who have smoked less than 10 pack-years, including those who had never smoked cigarettes but had passive exposure to cigarette smoke.
“The less than 10 pack-years of smoking includes people who have never smoked,” Dr. Henschke said. “In the United States, some 25% of lung cancers are diagnosed in people who have never smoked.”
The results from this study show that after 20 years, patients diagnosed with lung cancer at an early stage via CT screening have significantly better outcomes. By treating the cancer when it is small, patients can be effectively cured in the long term.
“Lung cancer can be cured if you enroll in an annual screening program using a well-defined protocol and comprehensive management system,” Dr. Henschke said. “It is important to return for annual screening.”
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends annual lung cancer screening with low-dose CT in adults aged 50 to 80 years who have a 20 pack-year smoking history and currently smoke or have quit within the past 15 years.
###
“A 20-year Follow-up of the International Early Lung Cancer Action Program (I-ELCAP).” Collaborating with Dr. Henschke were Rowena Yip, Ph.D., M.P.H., Dorith Shaham, M.D., Steve Markowitz, M.D., Jose Cervera Deval, M.D., Javier J. Zulueta, M.D., Luis M. Seijo, M.D., Cheryl Aylesworth, M.D., Karl Klingler, M.D., Shahriyour Andaz, M.D., Cynthia Chin, M.D., James P. Smith, M.D., Emanuela Taioli, M.D., Ph.D., Nasser Altorki, M.D., Raja M. Flores, M.D., M.P.H., and David F. Yankelevitz, M.D., for the International Early Lung Cancer Action Program Investigators.
In 2023, Radiology is celebrating its 100th anniversary with 12 centennial issues, highlighting Radiology’s legacy of publishing exceptional and practical science to improve patient care.
Radiology is edited by Linda Moy, M.D., New York University, New York, N.Y., and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (https://pubs.rsna.org/journal/radiology)
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on lung cancer screening, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
END
New York, NY (November 7, 2023) — Diagnosing early-stage lung cancer with low-dose computed tomography (CT) screening drastically improves its cure rate measured over a 20-year period, according to a large-scale international study by Mount Sinai researchers published in Radiology.
The results show that patients diagnosed with lung cancer via CT screening have a 20-year survival rate—an approximation of the cure rate—of 81 percent. Among the 1,257 participants diagnosed with lung cancer, 81 percent ...
BACKGROUND
One of the hallmarks of cancer cell development is its dependence on sugar, especially glucose, to grow and divide. Scientists have long been studying how to restrict or block this process that promotes tumor growth, called glycolysis, from happening as a possible effective strategy against cancer.
Previously, researchers from the UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center identified a specific protein sodium glucose transporter 2, or SGLT2, as a mechanism that lung cancer cells can utilize to obtain glucose. Drugs that inhibit SGLT2 are already FDA approved for other conditions and the UCLA team found these drugs could also delay the development ...
St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital today announced Giles Robinson, M.D., has assumed the role of director for the Department of Oncology’s Division of Neuro-Oncology. He has also become co-leader of the Neurobiology and Brain Tumor Program within the St. Jude Comprehensive Cancer Center. These combined units comprise one of the largest clinical brain tumor programs in North America.
“Dr. Robinson has been an exemplary member of St. Jude since joining as a hematology/oncology fellow in 2007,” said Julie R. Park, M.D., Department of Oncology ...
HOUSTON and DUBLIN ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and Jazz Pharmaceuticals plc today announced a five-year strategic research collaboration agreement to evaluate zanidatamab, Jazz’s investigational HER2-targeted bispecific antibody, in multiple HER2-expressing cancers.
The collaboration will combine MD Anderson’s translational medicine and clinical research expertise with Jazz’s expanding oncology drug development capabilities to investigate the potential of zanidatamab as monotherapy and in combination with other treatments for patients with different tumor types and stages. This includes its possible applicability ...
They reveal the origin of wine, the age of bones and fossils, and they serve as diagnostic tools in medicine. Isotopes and isotopologues – molecules that differ only in the composition of their isotopes – also play an increasingly important role in astronomy. For example, the ratio of carbon-12 (12C) to carbon-13 (13C) isotopes in the atmosphere of an exoplanet allows scientists to infer the distance at which the exoplanet orbits its central star.
Until now, 12C and 13C bound in carbon monoxide were the only isotopologues that could be measured in the atmosphere of an exoplanet. Now a team of researchers has succeeded in detecting ammonia isotopologues ...
Online shopping for cigarettes and vaping products increased significantly in the weeks following the implementation of SB-793, a 2022 California law prohibiting the sale of flavored tobacco products. Researchers at the Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human Longevity Science at University of California San Diego identified potential loopholes in tobacco control policies due to the absence of explicit regulations on e-commerce sales in retailer licensing programs.
Reporting in the journal Tobacco Control on Nov. 7, 2023, researchers assessed the ...
Karl Klose, director of The South Texas Center for Emerging Infectious Diseases (STCEID) and the Robert J. Kleberg, Jr. and Helen C. Kleberg College of Sciences Endowed Professor, coauthored a research article with Cameron Lloyd ’23, a UTSA doctoral student who graduated in August with a Ph.D. in molecular microbiology and immunology under the guidance of Klose.
The research paper investigates a novel strategy for inhibiting the spread and infection of Vibrio cholerae, the bacteria responsible for the disease, cholera.
The research article is entitled, “A peptide-binding ...
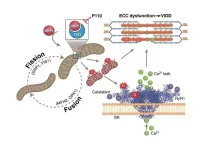
A study presents evidence that mitochondrial fragmentation is a proximal mechanism underlying ventilator-induced diaphragm dysfunction (VIDD)—and identifies a possible therapeutic to limit diaphragm atrophy during a stay in intensive care. Previous research has established that many of the cellular pathways responsible for VIDD are kicked off by oxidative stress stemming from diaphragm inactivity. Stefan Matecki and colleagues studied the molecular causes of this oxidative stress in mice. Just six hours on mechanical ventilation was enough to increase expression of dynamin-related protein 1 (DRP1), which is involved in mitochondrial ...
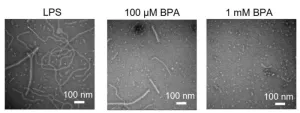
The “hygiene hypothesis” posits that allergic asthma can be triggered by a childhood environment that is too clean and sterile. One studied mechanism underlying this relationship is the influence of microbial lipopolysaccharides (LPS), which train the immune system. In the absence of LPS, Toll-like receptors in the human body will become more sensitive, which can lead to an exaggerated allergic response to triggers such as house dust mites. Mingliang Fang and colleagues explored how the environmental pollutant bisphenol ...
Losing summer snow patches may hit mountain goats hard, according to a study that suggests that goats seek out snow to avoid biting insects. Many cold-adapted species take advantage of patches of snow that linger through the summer, as corridors for travel, sources of drinking water, zones for cooling off, or places to play. As the climate changes, many species will have reduced access to snow patches. Forest Hayes and Joel Berger explored what this lack of summer snow might mean for mountain goats (Oreamnos americanus) in Glacier National Park, which has lost 85% of its glaciers since 1850. The team studied goats in the park—along with another population 1,000 ...