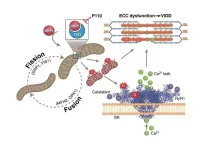
(Press-News.org) A study presents evidence that mitochondrial fragmentation is a proximal mechanism underlying ventilator-induced diaphragm dysfunction (VIDD)—and identifies a possible therapeutic to limit diaphragm atrophy during a stay in intensive care. Previous research has established that many of the cellular pathways responsible for VIDD are kicked off by oxidative stress stemming from diaphragm inactivity. Stefan Matecki and colleagues studied the molecular causes of this oxidative stress in mice. Just six hours on mechanical ventilation was enough to increase expression of dynamin-related protein 1 (DRP1), which is involved in mitochondrial membrane fission and associated with a reduction in mitochondrial size and interaction. Mechanical ventilation, by completely resting the diaphragm, results in a sudden reduction in its energy requirements. This reduction prompts the diaphragm to initiate a program of fission for breaking down its superfluous mitochondria, which previously supplied it with energy in the form of ATP. However, mitochondrial fragmentation produces reactive oxygen species in excess, which negatively impact Ca2+ homeostasis, a dysregulation at the root of VIDD. The authors show that if at the initiation of mechanical ventilation, mitochondrial fission was blocked thanks to a molecule like P110, which prevents DRP1 from interacting with the mitochondrial membrane, VIDD could be mitigated. The molecule P110, by limiting the mitochondrial fragmentation induced by mechanical ventilation, reduces the production of reactive oxygen species at the basis of calcium homeostasis impairment and VIDD. According to the authors, any pharmacological therapeutics that could limit mitochondrial fission at the initiation of mechanical ventilation, could be a promising therapeutic intervention to prevent VIDD.
END
The molecular basis of ventilator-induced diaphragm weakness
2023-11-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bisphenol A and asthma in mice
2023-11-07
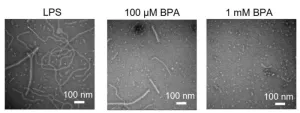
The “hygiene hypothesis” posits that allergic asthma can be triggered by a childhood environment that is too clean and sterile. One studied mechanism underlying this relationship is the influence of microbial lipopolysaccharides (LPS), which train the immune system. In the absence of LPS, Toll-like receptors in the human body will become more sensitive, which can lead to an exaggerated allergic response to triggers such as house dust mites. Mingliang Fang and colleagues explored how the environmental pollutant bisphenol ...
Mountain goats seek snow to shake off insects
2023-11-07
Losing summer snow patches may hit mountain goats hard, according to a study that suggests that goats seek out snow to avoid biting insects. Many cold-adapted species take advantage of patches of snow that linger through the summer, as corridors for travel, sources of drinking water, zones for cooling off, or places to play. As the climate changes, many species will have reduced access to snow patches. Forest Hayes and Joel Berger explored what this lack of summer snow might mean for mountain goats (Oreamnos americanus) in Glacier National Park, which has lost 85% of its glaciers since 1850. The team studied goats in the park—along with another population 1,000 ...
Mapping the landscape: Amsterdam UMC receives millions to lead European research into obesity
2023-11-07
Obesity is a growing health problem that disproportionately affects people and communities with a low socio-economic position in Europe. Thanks to a Horizon grant worth more than 10 million euros, Jeroen Lakerveld, epidemiologist at Amsterdam UMC, is now set to lead a European consortium in better identifying the causes of obesity and designing guidelines to tackle the problem.
"Social and cultural factors play a role in our lifestyle behaviours but so do our genes and the environment in which we live and work. Residents of neighbourhoods are not equally exposed to unhealthy factors: ...
Guilt not as persuasive if directly tied to personal responsibility
2023-11-07
PULLMAN, Wash. – Invoking a sense of guilt—a common tool used by advertisers, fundraisers and overbearing parents everywhere—can backfire if it explicitly holds a person responsible for another’s suffering, a meta-analysis of studies revealed.
While guilt is widely used to try and persuade people to act, research has been mixed on its effectiveness in spurring behavior change. This analysis, published in the journal Frontiers in Psychology, found that overall guilt had only a small persuasive effect, which is in line with previous research.
However, researchers uncovered that guilt worked better ...
Previous genetic association studies involving people with European ancestry may be inaccurate
2023-11-07
Researchers have found that previous studies analyzing the genomes of people with European ancestry may have reported inaccurate results by not fully accounting for population structure. By considering mixed genetic lineages, researchers at the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), part of the National Institutes of Health, demonstrated that previously inferred links between a genomic variant that helps digest lactose and traits such as a person’s height and cholesterol level may not be valid.
The study, published in Nature Communications, shows that people with European ancestry, who were previously treated as a genetically homogenous group in large-scale genetic ...
Contraceptive pills might impair fear-regulating regions in women’s brains
2023-11-07
More than 150 million women worldwide use oral contraceptives. Combined OCs (COCs), made up of synthetic hormones, are the most common type. Sex hormones are known to modulate the brain network involved in fear processes.
Now a team of researchers in Canada has investigated current and lasting effects of COC use, as well as the role of body-produced and synthetic sex hormones on fear-related brain regions, the neural circuitry via which fear is processed in the brain.
“In our study, we show that healthy women currently using COCs had a thinner ventromedial prefrontal cortex than men,” said Alexandra Brouillard, ...
Risk of dying in hospital from respiratory causes is higher in the summer than in the winter
2023-11-07
Global warming caused by climate change could exacerbate the burden of inpatient mortality from respiratory diseases during the warm season. This is the main conclusion of a study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, and published in The Lancet Regional Health - Europe. The results could help health facilities adapt to climate change.
The research team analysed the association between ambient temperature and in-hospital mortality from respiratory diseases in the provinces of Madrid and Barcelona between 2006 and 2019. ...
Poetry can help people cope with loneliness or isolation
2023-11-07
Reading, writing and sharing poetry can help people cope with loneliness or isolation and reduce feelings of anxiety and depression, a new study shows.
Research by the University of Plymouth and Nottingham Trent University, funded by the Arts and Humanities Research Council, found that many people who took to sharing, discussing and writing poetry as a means to deal with the COVID-19 pandemic experienced “demonstrable positive impact on their wellbeing”.
The findings are based on a survey of 400 people which showed that poetry helped those experiencing common mental health symptoms as well as those suffering from grief.
It was carried out with registered users of the ...
French love letters confiscated by Britain finally read after 265 years
2023-11-07
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 19:01 (US ET) ON MONDAY 6TH NOVEMBER 2023 / 00:01AM (UK TIME) ON TUESDAY 7TH NOVEMBER 2023
Over 100 letters sent to French sailors by their fiancées, wives, parents and siblings – but never delivered – have been opened and studied for the first time since they were written in 1757-8.
The messages offer extremely rare and moving insights into the loves, lives and family quarrels of everyone from elderly peasants to wealthy officer’s wives.
The messages were seized by Britain’s Royal Navy during the Seven Years’ War, taken to the Admiralty in London ...
First in human trial of new drug raises hopes for patients with relapsed blood cancer
2023-11-06
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new targeted drug, studied by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC – James), may offer a new treatment option for patients with blood cancers, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) whose disease has stopped responding to standard treatments.
In the first clinical trial of this drug in humans, nemtabrutinib ...