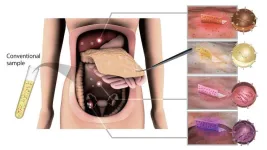
(Press-News.org) A research team in Japan, led by Nagoya University’s Akira Yokoi, has developed an innovative technique using cellulose nanofiber (CNF) sheets derived from wood cellulose to capture extracellular vesicles (EVs) from fluid samples and even organs during surgery. EVs are small structures from cancerous cells that play a crucial role in cell-to-cell communication. Extracting and analyzing EVs using this new technology has the potential to revolutionize early cancer diagnosis and open the door to personalized medicine. The researchers published their findings in Nature Communications.
Cancer is notorious for its poor prognosis and in many cases goes undetected until its advanced stages, leaving patients with limited treatment options. Detecting the cancer early using EVs and analyzing them provides vital information on disease status and its progression. This should assist physicians in monitoring and adjusting personalized cancer treatment plans. However, researchers have been limited in previous attempts to use EVs due to the lack of an effective isolation strategy.
To capture EVs, Yokoi and his colleagues used CNF sheets made from wood cellulose to extract them from fluid samples from ovarian cancer mice models. As the material has a porous nanostructure, the sheet absorbs the fluid containing the EVs into its pores and closes them upon drying. They found that the sheets captured and preserved EVs from as little as ten microliters of body fluids. In contrast, the current standard methods, such as ultra-centrifugation, are more time-consuming and require much larger samples.
“We have developed the unique cellulose nanofiber by applying paper-making and solvent displacement technology,” Yokoi said. “The cellulose nanofibers we use are a sustainable biomass material that comes mostly from wood cell walls. These sheets have attractive properties, such as being lightweight, high strength, and most importantly, easily biodegradable.”
Using the technique, the researchers successfully extracted and analyzed EVs, and the microRNAs (miRNAs) contained within them from the mice ovarian cancer models. As miRNAs differ between healthy and sick patients, they represent an ideal diagnostic marker for cancer. They also identified distinct sets of miRNAs in EVs collected from tumor surfaces, some of which decreased after tumor removal. Tracking the presence or absence of these miRNAs could be an easy way to analyze the effectiveness of treatment and then tailor treatment according to tumor heterogeneity. Heterogeneity is a common problem where even in a single tumor, cancer cells have different characteristics and properties.
The structure of the sheets is similar to that of medical gauze, so they can easily be attached and removed even when placed on organs during surgery. To test this, the group used recently removed human organs. Their successful test revealed an exciting discovery, as the EVs on the tumor surface showed unique miRNA profiles compared to the tumor tissue.
"Organ surfaces were a previously unanalyzed EV subpopulation, which can now be subjected to biological assessments,” Yokoi said. “CNF paper enables the obtaining of EVs from multiple sites in the body. Then, by checking the molecular profiles of these EVs, we can monitor disease progression and tailor the selection of the best drug, contributing to personalized medicine."
Dr. Takahiro Ochiya, Board Member of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and President of the Japanese Society for Extracellular Vesicles is enthusiastic about the potential of the sheets: “Exosome analysis using CNF sheets is an extremely novel method and is expected to have a variety of applications, including medical uses. We expect this to be a major advance that will bring the knowledge of exosomes as medical research directly to patients.”
This research has broad implications, opening up the analysis of EVs during surgery, an unexplored area until now. Looking ahead, the research team is committed to advancing the medical applications of EV sheets for various diseases, improving diagnostic accuracy, and helping usher in the era of personalized medicine.
END
Extracellular vesicles captured using sustainable wood celluose-based nanofiber sheets may identify and improve cancer treatment
2023-11-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers identify brain network that is uniquely activated through injection vs. oral drug use
2023-11-08
Results from a new clinical trial suggest that a group of brain regions known as the “salience network” is activated after a drug is taken intravenously, but not when that same drug is taken orally. When drugs enter the brain quickly, such as through injection or smoking, they are more addictive than when they enter the brain more slowly, such as when they are taken orally. However, the brain circuits underlying these differences are not well understood. This study offers new information that helps explain what may be causing this difference.
The study was published in Nature Communications and led by researchers at the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) and the National ...
Genes, cells, and embryos in development and evolution: Pere Alberch, 25 years on
2023-11-08
The last 40 years have witnessed a deep transformation in our views of animal development. From seeing development a multicellular black box where over time a mass of cells acquires shape to form organs and tissues, we now have a detailed account of this process in terms of gene expression, multicellular activity, and morphogenesis.
This new point of view has raised questions about the relationships between genes, cells, and organisms. These questions are impacting our thinking about evolution, ...
Rapid high-dose buprenorphine treatment strategy reduces opioid withdrawal in individuals using fentanyl
2023-11-08
Buprenorphine is a medication approved for pain and opioid dependence. New findings published in The American Journal on Addictions indicate that a transmucosal dose (which dissolves in the mouth) of buprenorphine followed by an injection of extended-release buprenorphine (BUP‐XR) may be an effective treatment for individuals with opioid use disorder who use fentanyl.
The results come from a recent secondary analysis of an open-label study in which 24 participants received a single 4 mg dose of transmucosal buprenorphine followed by an injection ...
Do allergic conditions increase the risk of developing Long-COVID after SARS-CoV-2 infection?
2023-11-08
In an analysis of published prospective studies of people of all ages with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection who were followed for at least 12 months, pre-existing allergic conditions were linked to higher risks of experiencing long-term symptoms associated with COVID-19, or Long-COVID.
The analysis, which is published in Clinical & Experimental Allergy, identified 13 relevant studies (with a total of 9,967 participants) published between January 1, 2020 and January 19, 2023.
Although the data as a whole from the studies suggested that individuals with asthma or rhinitis might be at increased risk of Long-COVID after SARS-CoV-2 ...
Does being a caregiver affect older women’s longevity?
2023-11-08
In an analysis published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society that included older US women, caregiving was associated with a lower risk of death over an average follow-up of 17.5 years.
In the analysis of 158,987 women aged 50–79 years when enrolled in the Women’s Health Initiative (a long-term national health study), 31.8% of women died during follow-up, and women who reported being a caregiver over 2 assessments 10 years apart had a 9% lower risk of dying from any cause compared with non-caregivers. Caregiving was also associated with lower risks of death from cardiovascular disease ...
Does having law enforcement officers at school benefit or harm students?
2023-11-08
A systematic review that analyzed the results of published studies concluded that school-based law enforcement (SBLE)—having sworn law enforcement officers stationed in schools on at least a part-time basis—is likely ineffective for keeping schools safe, and it may even have detrimental consequences.
The research, which is published in Campbell Systematic Reviews, included 32 studies that examined the relationship between SBLE presence and school-related outcomes including crime and behavior problems, perceptions of school, and student learning. The studies compared outcomes in schools with SBLE to those without SBLE, ...
Are some children genetically predisposed to poor sleep?
2023-11-08
Previous research has identified genetic variants associated with insomnia and sleep duration in adults. Now a study published in the Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry has found that these variants also likely affect sleep quality and quantity in children.
In the study of 2,458 children of European ancestry, children who were genetically predisposed to insomnia (based on a polygenic risk score developed for adults) had more insomnia-like sleep problems such as frequent awakenings or difficulty initiating sleep, as reported ...
Does cannabis use affect empathy?
2023-11-08
In a study published in the Journal of Neuroscience Research, psychological assessments indicated that people who regularly use cannabis, or marijuana, tend to have a greater understanding of the emotions of others. Brain imaging tests also revealed that cannabis users’ anterior cingulate—a region generally affected by cannabis use and related to empathy—had stronger connectivity with brain regions related to sensing the emotional states of others within one’s own body.
The study included ...
Framework provides guidance for ethical wildlife management
2023-11-08
Wildlife management decisions and practices face increasing ethical scrutiny. In research published in the Journal of Wildlife Management, investigators have developed a framework for incorporating ethical considerations into decisions in a systematic way.
The framework includes 3 domains: moral theory, which focuses on consequences and outcomes; principle- and rule-based approaches that deal with what is considered right or wrong; and virtue ethical therapy, which considers factors such as character, virtue, and aesthetics.
Wildlife ...
Could willow bark provide our next life-saving antiviral medicine?
2023-11-08
From a seasonal cold to a stomach bug, nobody likes catching a virus — and epidemics can be devastating. We need safe, sustainable antiviral options to treat the outbreaks of the future. Scientists in Finland have now shown that an extract of willow bark — a plant which has already provided several medicines, including the precursor to modern aspirin — has a broad-spectrum antiviral effect in cell sample experiments.
The extract worked both on enveloped coronaviruses, which cause colds as well as Covid-19, and non-enveloped enteroviruses, which cause infections such as flu and meningitis. There are no clinically approved drugs which work against enteroviruses directly, ...