(Press-News.org)
An accountability framework, including independent monitoring of state compliance, is critical for the pandemic agreement's success, according to researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and affiliates at Spark Street Advisors. The paper and findings are published in BMJ Global Health.
“Countries signing up to a pandemic agreement is no guarantee of its effective implementation,” said Nina Schwalbe, adjunct assistant professor in the Department of Population and Family Health and principal visiting fellow at Columbia Mailman School. “Countries' lack of compliance with the International Health Regulations have contributed to several failures to contain outbreaks, including COVID-19.”
To assess how the pandemic agreement could best incorporate monitoring to promote compliance, the researchers did a comprehensive literature review of the governance of 11 existing global monitoring mechanisms and conducted over 40 interviews with stakeholders and experts. This included broad consultation with academics, advocates, activists, and officials from governments, international organizations, and foundations from around the world.
According to the researchers, an independent mechanism to monitor states’ compliance with and reporting on the pandemic agreement can promote compliance with the agreement.
Schwalbe and colleagues identified key features for successful compliance monitoring of the pandemic agreement:
Independent monitoring should be politically, financially, technically, and operationally independent of member states, the WHO, and donors to increase its reliability.
The monitor should report to a high-level political body to be effective.
Independent monitoring should review states’ self-reporting to the Conference of the Parties, the main governing body of the agreement.
It should triangulate state reports with shadow reports by civil society and UN agencies, confidential reports from the public, country visits, and inquiries to state parties.
It should share reports transparently into the public domain, highlighting best practices and promoting mutual learning.
In addition to self- and peer reviews, the pandemic agreement should have independent accountability mechanisms built into it from the start.
Currently, the Intergovernmentl Negotiating Body, tasked with negotiating a pandemic agreement, is aiming to present it for the states to adopt at the World Health Assembly in May 2024. While a precursor to this agreement provided important provisions for equity, intellectual property rights, and benefit sharing, it contained little on holding countries accountable. It suggested instead that the governing body should agree to accountability measures after the agreement is adopted. At an Intergovernmental Negotiating Body (INB) meeting held in December 2022, several WHO member states emphasized that accountability mechanisms should be negotiated into the agreement from the start.
On the basis of the findings, the researchers propose establishing an independent committee to monitor the state parties' compliance by assessing the timeliness, completeness, and accuracy of state reporting. The committee would report to a heads of state-level body, have the capacity to collect information, and share their findings publicly. The INB is meeting this week and again in December in Geneva.
Co-authors are Layth Hanbali, Elliot Hannon, and Susanna Lehtimaki, Spark Street Advisors; and Christine McNab of Toronto, Canada. Nina Schwalbe is also affiliated with United Nations University International Institute for Global Health.
About Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health
Founded in 1922, the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health pursues an agenda of research, education, and service to address the critical and complex public health issues affecting New Yorkers, the nation and the world. The Columbia Mailman School is the fourth largest recipient of NIH grants among schools of public health. Its nearly 300 multi-disciplinary faculty members work in more than 100 countries around the world, addressing such issues as preventing infectious and chronic diseases, environmental health, maternal and child health, health policy, climate change and health, and public health preparedness. It is a leader in public health education with more than 1,300 graduate students from 55 nations pursuing a variety of master’s and doctoral degree programs. The Columbia Mailman School is also home to numerous world-renowned research centers, including ICAP and the Center for Infection and Immunity. For more information, please visit www.mailman.columbia.edu.
END
Scientists using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope just made a breakthrough discovery in revealing how planets are made. By observing water vapor in protoplanetary disks, Webb confirmed a physical process involving the drifting of ice-coated solids from the outer regions of the disk into the rocky-planet zone.
Theories have long proposed that icy pebbles forming in the cold, outer regions of protoplanetary disks — the same area where comets originate in our solar system — should be the fundamental seeds of planet formation. The main requirement of these theories is that pebbles should drift inward toward the star due to friction in the gaseous disk, ...
Carlos Trejo-Pech, an associate professor in the Department of Agricultural and Resource Economics at the University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture, is a newly appointed editor of the Journal of Food Distribution Research.
“It is a great honor and big responsibility to serve as a journal editor of a publication outlet in the agricultural economics and agribusiness discipline,” said Trejo-Pech. “We, the editors, are committed to disseminating the results of high-quality research.”
The journal was established in 1969 under the auspices of the Food Distribution Research Society, the only body of scholars and practitioners in the United States dedicated ...
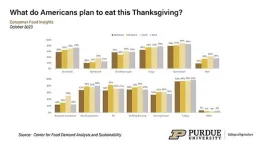
October Consumer Food Insights Report highlights Thanksgiving meal plans
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Nearly eight in 10 Americans will celebrate the upcoming Thanksgiving holiday with a special meal, according to the October 2023 Consumer Food Insights Report.
The survey-based report out of Purdue University’s Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainabilityassesses food spending, consumer satisfaction and values, support of agricultural and food policies, and trust in information sources. Purdue ...
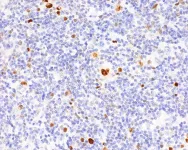
Hodgkin’s lymphoma is one of the most common types of lymphoma in young adults. It is characterized by the presence of enlarged B lymphocytes, which are unusual in that they bear on their surface the identifying markers of many other immune cells – such as those found on phagocytes, dendritic cells, or T cells. Now, a team led by Stephan Mathas from the Experimental and Clinical Research Center (ECRC) has explained how these changes take place in the cells and what impact they have. The ECRC is a joint institution of the Max Delbrück Center and Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin.
“Many different ...
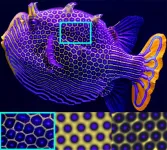
Nature has no shortage of patterns, from spots on leopards to stripes on zebras and hexagons on boxfish. But a full explanation for how these patterns form has remained elusive.
Now engineers at the University of Colorado Boulder have shown that the same physical process that helps remove dirt from laundry could play a role in how tropical fish get their colorful stripes and spots. Their findings were published Nov. 8 in the journal Science Advances.
“Many biological questions are fundamentally ...
A new analysis of 14,669 threatened species of plants and animals found in Europe reveals that about one fifth face the risk of extinction, and that agricultural land-use change poses a significant threat to these species. Axel Hochkirch of the Musée National d’Histoire Naturelle, Luxembourg, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on November 8, 2023.
The variety of species of living things—biodiversity—is declining around the world, as more and more species face the risk of extinction. Many efforts, including some by governments and nonprofit organizations, aim to reduce the loss ...
A new analysis of lice genetic diversity suggests that lice came to the Americas twice – once during the first wave of human migration across the Bering Strait, and again during European colonization. Marina Ascunce, currently at the USDA-ARS, and colleagues, report these findings in a new study published November 8 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
The human louse is a wingless, blood-sucking parasite that lives its entire life on its host. It is one of the oldest known parasites to live on humans, and the two species have coevolved ...
A digital detox may not improve wellbeing: social media users who reduced their use for a week saw decreases in positive emotions as well as in negative ones
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293467
Article Title: Restricting social networking site use for one week produces varied effects on mood but does not increase explicit or implicit desires to use SNSs: Findings from an ecological momentary assessment study
Author Countries: UK
Funding: This work was supported by the Economic and Social Research ...
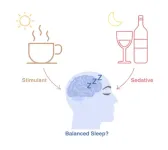
Financial traders may seek better sleep by self-medicating with caffeine and alcohol to balance the effects of the stimulant and the sedative, per micro-longitudinal study
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0291675
Article Title: Sleep, alcohol, and caffeine in financial traders
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Neuroscientists have discovered a fascinating connection between the retention of early life memories and brain developmental trajectories associated with autism [Wednesday 8th November 2023].
Most of us remember little of our experiences from before two years of age. This form of memory loss, termed “infantile amnesia” refers to the seemingly complete loss of episodic and autobiographical memories formed during early life. The research team at Trinity College Dublin investigated how infantile amnesia is affected by forms of autism.
The maternal immune response, sparked into life in response to infection during pregnancy, ...