(Press-News.org) People are beginning to reconsider their reproductive decisions due to complex concerns about climate change, with many choosing to forego childbearing, or reduce the number of children they have as a result, finds a new study by UCL researchers.
The research, published in PLOS Climate, is the first systematic review to explore how and why climate change-related concerns may be impacting reproductive decision-making.
The team examined 13 studies, involving 10,788 participants, which were conducted between 2012 and 2022, primarily in Global North countries such as the USA, Canada, New Zealand, and various European countries. They found that climate change concerns were typically associated with less positive attitudes towards reproduction and a desire or intent for fewer children or none at all.
Underpinning this finding were four key factors: uncertainty about the future of an unborn child, environmentalist views centred on overpopulation and overconsumption, meeting family subsistence needs, and political sentiments.
The term eco-anxiety has rapidly entered public discourse, describing a range of negative emotional responses including fear, worry, guilt and anger as a response to climate change. In 2018, a nationally representative New York Times survey found that 33% of childfree Americans aged 20-45 cited being “worried about climate change” as a reason for not having children.
Since then, ethical concerns about the quality of life children might have in a climate-changed future have been cited as the primary rationale for individuals choosing to not have children. However, the team behind this new study wanted to understand if there was an evidence base supporting the claims that climate change concerns were causing people to change their childbearing decisions, and if so, whether any other motivating factors, aside from ethical concerns, came into play.
The new analysis found that in 12 out of 13 studies, stronger concerns about climate change were associated with a desire for fewer children, or none at all.
One of the main reasons for this was the individual’s concern for their children in a world affected by climate change. However, the review also highlighted three other factors, with a primary concern being the ecological impact of reproduction, as people feared that having children would contribute to overpopulation and overconsumption in a world with already stretched resources.
To a lesser extent, two studies in Zambia and Ethiopia also found that participants desired fewer children to meet subsistence needs during periods of declining agricultural productivity.
Finally, individuals in another study had political considerations resulting in their decision to not have children – with two participants even reporting their refusal to have children as a method of ‘striking’ until systemic change was enacted.
Interestingly, these final two themes were also raised by some participants as reasons to have a greater number of children. For example, in Zambia, participants were concerned about their ability to support their family without the household labour provided by additional children helping with domestic work, as well as water and food collection.
Lead author, Hope Dillarstone (former MSc student at the UCL Institute for Global Health, said: “Recent media attention has been paid to a growing number of individuals factoring their concerns about climate change into their childbearing plans. However, we were concerned that public discourse may have oversimplified this relationship.
“Our first-of-its-kind study shows that there is a complex and intricate relationship between climate change and reproductive choices, with differences noted both within and between countries across the world.
“Our analysis shows that not only are many people concerned about their child’s welfare growing up in a world of uncertainty, but that they are also considering the impact of having children on the environment, their family’s ability to subsist, and their politics.
“Understanding why some people choose to adjust their reproductive decisions as a result of climate change may prove instrumental for shaping public policy, showing a need for collaboration among policymakers to incorporate local-level environmental concerns within national and international climate change, mental health and sexual and reproductive health policies.”
The team are now calling for more research at the intersection of climate change, mental health, and reproductive decision-making, particularly among highly affected Global South populations where current research is lacking.
END
Ethical, environmental and political concerns about climate change affect reproductive choices
Peer reviewed | Systematic review | People
2023-11-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Photonics team develops high-performance ultrafast lasers that fit on a fingertip
2023-11-09
Lasers are essential tools for observing, detecting, and measuring things in the natural world that we can’t see with the naked eye. But the ability to perform these tasks is often restricted by the need to use expensive and large instruments.
In a newly published cover-story paper in the journal Science, researcher Qiushi Guo demonstrates a novel approach for creating high-performance ultrafast lasers on nanophotonic chips. His work centers on miniaturizing mode-lock lasers — a unique laser that emits a train of ultrashort, coherent light pulses in femtosecond intervals, which is an astonishing quadrillionth ...
Scientists flag conflicts of interest ahead of UN plastic and chemical talks
2023-11-09
An international group of 35 scientists is calling out conflicts of interest plaguing global plastic treaty negotiations and that have interfered with timely action on other health and environmental issues. They urge the implementation of strict guidelines to prevent the same problems from affecting the UN’s upcoming Science Policy Panel on chemicals. Their concerns and recommendations are outlined in a featured paper in the journal Environmental Science & Technology.
“From Big Tobacco to Big Oil, powerful industries use the same playbook to manufacture doubt and sow misinformation,” said co-author Bethanie ...
First-ever crowd-sourced small molecule discovery and a potent SARS-CoV-2 antiviral lead compound announced by COVID Moonshot Consortium
2023-11-09
The work of the COVID Moonshot Consortium is being published in the prestigious journal Science on 10 November, revealing their discovery of a potent SARS-CoV-2 antiviral lead compound. It also reflects on the success of its open science approach in launching a patent-free antiviral discovery program to rapidly develop a differentiated lead in response to a pandemic emergency. Open science discovery of potent noncovalent SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors ) DOI 10.1126/science.abo7201.
The COVID Moonshot initiative ...
Cornell chemists image basic blocks of synthetic polymers
2023-11-09
ITHACA, N.Y. -- Synthetic polymers are everywhere in our society – from nylon and polyester clothing to Teflon cookware and epoxy glue. At the molecular level, these polymers’ molecules are made of long chains of monomer building blocks, the complexity of which increases functionality in many such materials.
In particular, copolymers, which consist of different types of monomers in the same chain, allow for fine-tuning of the material’s properties, said Peng Chen, the Peter J.W. Debye Professor of Chemistry in the College of Arts and Sciences (A&S). The monomer sequence plays a critical role in a material’s properties, but scientists until ...
Brain imaging identifies biomarkers of mental illness
2023-11-09
Philadelphia, November 9, 2023 – Research and treatment of psychiatric disorders are stymied by a lack of biomarkers – objective biological or physiological markers that can help diagnose, track, predict, and treat diseases. In a new study, researchers use a very large dataset to identify predictive brain imaging-based biomarkers of mental illness in adolescents. The work appears in Biological Psychiatry, published by Elsevier.
Traditionally, psychiatric disorders such as depression have been diagnosed based on symptoms according to subjective assessments. The identification of biomarkers to aid in diagnosis and treatment selection would greatly advance treatments.
In ...
Cary Institute partners on $3M USDA-funded study on COVID-19 variants that could emerge from wildlife
2023-11-09
Many wild animals can carry COVID-19, including those that live among us, such as deer mice, red foxes, white-tailed deer, and more. These species may act as reservoirs, offering new opportunities for the virus to mutate and spill back into people. The omicron variant, for example, is thought to have emerged from mice.
With $3 million in federal grant funding, a new five-year research project will bring together virology, disease ecology, and artificial intelligence to better understand how SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19) behaves ...
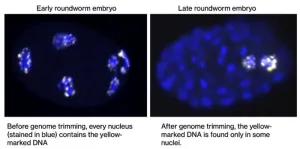
The enigma of embryonic development: How certain animals trim their genomes
2023-11-09
New research is underway to decipher a fascinating biological puzzle—how some animals can naturally discard more than half of their genetic information during embryonic development.
This radical natural phenomenon has captivated scientists for over 130 years, presenting a tantalizing question in the field of developmental biology and genetics.
Equipped with the latest in genetic engineering tools, the team at The University of Warwick is working to dissect the mechanisms behind this selective genomic editing. By uncovering the processes that allow some nematode worms to abandon up to ...
New URI lab developing adaptive technology, secures National Science Foundation grant
2023-11-09
New URI lab developing adaptive technology, secures National Science Foundation grant
Reza Abiri and Yalda Shahriari receive National Science Foundation award totaling $460,000 for work to improve stroke patient rehabilitation
Passing by Reza Abiri’s office at the University of Rhode Island, one might suspect him of nursing a serious coffee habit. A colorful collection of various mugs and cups dot his office, and though he is friendly enough to likely welcome any visitors stopping by to chat, the cups serve a larger purpose.
Abiri and Yalda Shahriari, professors in ...
MD Anderson announces Institute for Data Science in Oncology to advance mission to end cancer
2023-11-09
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today announced the launch of its Institute for Data Science in Oncology (IDSO), which integrates the most advanced computational and data science approaches with the institution’s extensive scientific and clinical expertise to significantly improve patient’s lives by transforming cancer care and research.
Bringing top data scientists from a variety of fields together with clinicians and cancer scientists, the institute builds on MD Anderson’s culture of collaboration and connectivity to tackle the field’s most pressing needs in new and innovative ways. IDSO’s efforts have been catalyzed by philanthropic ...
Researchers decipher the mechanism by which the MAF protein promotes breast cancer metastasis
2023-11-09
The MAF protein interacts with the estrogen receptor, alters its function, and promotes the spread of cancer.
The KDM1A enzyme plays a fundamental role in the epigenetic remodelling that facilitates the function of pro-metastatic genes.
The work carried out in Dr. Roger Gomis Lab at IRB Barcelona has been published in the journal Nature Cell Biology.
Barcelona, 9 November 2023 – Breast cancer is the most common form of cancer among women, with more than 2 million new cases diagnosed each year. In cases where the tumour remains localised in the breast, survival rates are remarkably high, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How periodontitis-linked bacteria accelerate osteoporosis-like bone loss through the gut
Understanding how cells take up and use isolated ‘powerhouses’ to restore energy function
Ten-point plan to deliver climate education unveiled by experts
Team led by UC San Diego researchers selected for prestigious global cancer prize
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
[Press-News.org] Ethical, environmental and political concerns about climate change affect reproductive choicesPeer reviewed | Systematic review | People