(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, November 9, 2023 – Research and treatment of psychiatric disorders are stymied by a lack of biomarkers – objective biological or physiological markers that can help diagnose, track, predict, and treat diseases. In a new study, researchers use a very large dataset to identify predictive brain imaging-based biomarkers of mental illness in adolescents. The work appears in Biological Psychiatry, published by Elsevier.
Traditionally, psychiatric disorders such as depression have been diagnosed based on symptoms according to subjective assessments. The identification of biomarkers to aid in diagnosis and treatment selection would greatly advance treatments.
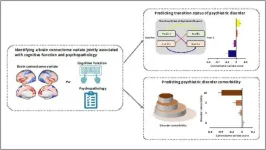
In the current study, the investigators used brain imaging data from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study of nearly 12,000 children aged 9 to 10 at the beginning of the study. Modern neuroimaging techniques, including resting-state functional connectivity (rsFC) analysis, allow researchers to investigate the organization of brain circuits through their interaction with one another over time.
Yihong Yang, PhD, senior author of the study, at the Neuroimaging Research Branch, National Institute on Drug Abuse, said, “Using a functional MRI dataset, we identified a brain connectivity variate that is positively correlated with cognitive functions and negatively correlated with psychopathological measures.”
Cognition has long been studied in the context of mental disorders, and recent research has pointed to shared neurobiology between the two, as supported in this new study.
This brain-based variate predicted how many psychiatric disorders were identified in participants at the time of the scan and over the following two years. It also predicted the transition of diagnosis across disorders over the two-year follow-up period.”
Dr. Yang added, “These findings provide evidence for a transdiagnostic brain-based measure that underlies individual differences in developing psychiatric disorders in early adolescence.”
John Krystal, MD, Editor of Biological Psychiatry, said of the work, "Mental illness in adolescence has emerged as a cardinal public health challenge in the post-COVID era. More than ever before, we would benefit from better ways to identify adolescents at risk. This study uses data from the landmark ABCD Study to illustrate how neuroimaging data could illuminate risk for mental illness across the spectrum of diagnoses.”
Dr. Yang added, “Finding biomarkers of mental illnesses, rather than relying on symptoms, may provide a more precise means of diagnosis, and thereby aligning psychiatric diagnosis with other medical diagnoses.”
END
Brain imaging identifies biomarkers of mental illness
New study in Biological Psychiatry identifies predictive signature in adolescents
2023-11-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cary Institute partners on $3M USDA-funded study on COVID-19 variants that could emerge from wildlife
2023-11-09
Many wild animals can carry COVID-19, including those that live among us, such as deer mice, red foxes, white-tailed deer, and more. These species may act as reservoirs, offering new opportunities for the virus to mutate and spill back into people. The omicron variant, for example, is thought to have emerged from mice.
With $3 million in federal grant funding, a new five-year research project will bring together virology, disease ecology, and artificial intelligence to better understand how SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19) behaves ...
The enigma of embryonic development: How certain animals trim their genomes
2023-11-09
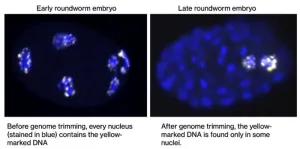
New research is underway to decipher a fascinating biological puzzle—how some animals can naturally discard more than half of their genetic information during embryonic development.
This radical natural phenomenon has captivated scientists for over 130 years, presenting a tantalizing question in the field of developmental biology and genetics.
Equipped with the latest in genetic engineering tools, the team at The University of Warwick is working to dissect the mechanisms behind this selective genomic editing. By uncovering the processes that allow some nematode worms to abandon up to ...
New URI lab developing adaptive technology, secures National Science Foundation grant
2023-11-09
New URI lab developing adaptive technology, secures National Science Foundation grant
Reza Abiri and Yalda Shahriari receive National Science Foundation award totaling $460,000 for work to improve stroke patient rehabilitation
Passing by Reza Abiri’s office at the University of Rhode Island, one might suspect him of nursing a serious coffee habit. A colorful collection of various mugs and cups dot his office, and though he is friendly enough to likely welcome any visitors stopping by to chat, the cups serve a larger purpose.
Abiri and Yalda Shahriari, professors in ...
MD Anderson announces Institute for Data Science in Oncology to advance mission to end cancer
2023-11-09
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today announced the launch of its Institute for Data Science in Oncology (IDSO), which integrates the most advanced computational and data science approaches with the institution’s extensive scientific and clinical expertise to significantly improve patient’s lives by transforming cancer care and research.
Bringing top data scientists from a variety of fields together with clinicians and cancer scientists, the institute builds on MD Anderson’s culture of collaboration and connectivity to tackle the field’s most pressing needs in new and innovative ways. IDSO’s efforts have been catalyzed by philanthropic ...
Researchers decipher the mechanism by which the MAF protein promotes breast cancer metastasis
2023-11-09
The MAF protein interacts with the estrogen receptor, alters its function, and promotes the spread of cancer.
The KDM1A enzyme plays a fundamental role in the epigenetic remodelling that facilitates the function of pro-metastatic genes.
The work carried out in Dr. Roger Gomis Lab at IRB Barcelona has been published in the journal Nature Cell Biology.
Barcelona, 9 November 2023 – Breast cancer is the most common form of cancer among women, with more than 2 million new cases diagnosed each year. In cases where the tumour remains localised in the breast, survival rates are remarkably high, ...
New research: Fivefold increase in the melting of Greenland's glaciers over the last 20 years
2023-11-09
New research: Fivefold increase in the melting of Greenland's glaciers over the last 20 years
In the largest survey of its kind ever conducted, using both satellite imagery and old aerial photos from the Danish National Archives, researchers from the University of Copenhagen firmly establish that Greenland’s glaciers are melting at an unprecedented pace. Melting has increased fivefold in the past 20 years. The study eliminates any lingering doubts about the impact of climate change on Greenland's more than 20,000 glaciers.
Based on the most comprehensive monitoring ...
Drug screen points toward novel diabetes treatments
2023-11-09
A drug currently in clinical trials as a cancer therapy can also stimulate pancreatic beta cells to secrete insulin, revealing a previously unknown mechanism for insulin regulation in type 2 diabetes, according to a new study by Weill Cornell Medicine investigators. The preclinical discovery, reported Nov. 9 in Nature Chemical Biology, provides a new chemical tool for probing the biology of diabetes, and could point the way toward better treatments for the disease.
“We have known about insulin for a century, but when it comes to the major mechanisms controlling insulin secretion, there ...
Team creates synthetic enzymes to unravel molecular mysteries
2023-11-09
A University of Texas at Dallas bioengineer has developed synthetic enzymes that can control the behavior of the signaling protein Vg1, which plays a key role in the development of muscle, bone and blood in vertebrate embryos.
The team of researchers is using a new approach, called the Synthetic Processing (SynPro) system, in zebrafish to study how Vg1 is formed. By learning the molecular rules of signal formation in a developing animal, researchers aim to engineer mechanisms — such as giving cells new instructions — that could play a role in treating or preventing disease.
Dr. P.C. Dave P. Dingal, assistant professor of bioengineering in the Erik Jonsson ...
Finding your niche: A synthetic cancer stem cell microenvironment
2023-11-09
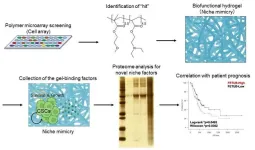
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) report the construction of a synthetic polymer biomaterial that successfully recapitulates the pancreatic adenocarcinoma microenvironment and could be used to identify novel treatment targets
Tokyo, Japan – One of the biggest challenges in biomedical research is finding a way to capture the complexity of the human body in laboratory-based techniques, to enable them to be investigated accurately. Now, researchers from Japan report an approach for precisely imitating a key feature of aggressive cancers in the laboratory.
In a study published recently in Inflammation and Regeneration, researchers from Tokyo Medical and ...
Vigorous exercise, rigorous science: What scientists learned from firefighters in training
2023-11-09
The 11 young firefighters went through a rigorous training exercise, carrying up to 40 pounds of gear over hilly terrain during a 45-minute training exercise in the California sun. Gloves, helmets, flashlights, goggles, and more weighted them down as they sprinted through the countryside wearing fire-resistant clothing to show they were ready to serve as wildland firefighters.
When the training was over, they immediately went to the medical tent—not to rest and recover but to give samples of their blood, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Brain imaging identifies biomarkers of mental illnessNew study in Biological Psychiatry identifies predictive signature in adolescents