(Press-News.org) A University of Texas at Dallas bioengineer has developed synthetic enzymes that can control the behavior of the signaling protein Vg1, which plays a key role in the development of muscle, bone and blood in vertebrate embryos.
The team of researchers is using a new approach, called the Synthetic Processing (SynPro) system, in zebrafish to study how Vg1 is formed. By learning the molecular rules of signal formation in a developing animal, researchers aim to engineer mechanisms — such as giving cells new instructions — that could play a role in treating or preventing disease.
Dr. P.C. Dave P. Dingal, assistant professor of bioengineering in the Erik Jonsson School of Engineering and Computer Science, and his colleagues published their research online Oct. 16 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“We’re interested in how synthetic enzymes might be used to control natural proteins, including disease-causing proteins,” Dingal said. “Our hope is to build biological circuits that, ultimately, we can introduce into cells and imbue them with new functions, like being able to detect cancer or resolve cellular disorders at the molecular level.”
Dingal said zebrafish are ideal models for observing how signaling proteins are processed and secreted because zebrafish not only have approximately 70% similarity with the human genome, but they also are small and easy to grow and image under the microscope.
The researchers studied interactions between the two proteins Vg1 and Nodal. One of the questions the research team investigated is why Vg1 remains inactive until it pairs with Nodal to form a larger protein complex called a heterodimer, which is secreted from cells and signals target embryonic cells to differentiate into specific tissues and organs.
“We discovered that there are proteins that act like chaperones that bind to Vg1 and force it to remain as an inactive monomer,” Dingal said. “In the presence of Nodal, however, the chaperones are released, and Nodal can then dimerize with Vg1.”
The researchers found that the act of pairing is not enough to activate Vg1 and Nodal. The Vg1 portion of the dimer must go through additional processing in other parts of the cell, including in the Golgi apparatus, where enzymes cut away, or cleave, unnecessary amino acids from the Vg1 section, much like a gardener prunes a rosebush.
To investigate the processing that Vg1 undergoes, Dingal and his colleagues developed a way to manipulate the protein. Using a cleaving enzyme derived from a family of viruses, the researchers developed a synthetic enzyme that could be directed to cut specific amino acids from Vg1 in the zebrafish embryo.
They discovered that Vg1-Nodal heterodimers do not need to undergo cleavage before they are released from the cell to bind with receptors on target cells. Vg1, however, must undergo cleavage — while cleavage of Nodal is not required — to activate signaling on target cells.
Dingal will continue to study the proteins in the next phase of the project to determine, for example, the molecular rules that chaperone proteins use to control the composition of signaling complexes. He recently received a $1.9 million grant (R35GM150967) from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences at the National Institutes of Health to continue his research.
Dingal, a co-corresponding author of the paper, began the study as a postdoctoral researcher at Harvard University in the lab of National Academy of Sciences member Dr. Alexander F. Schier, co-corresponding author, who is now professor of cell biology and director of the Biozentrum at the University of Basel in Switzerland. Dingal completed the work after joining UT Dallas in 2022. Co-authors of the study include Medel B. Lim Suan Jr., a UTD biomedical engineering doctoral student and Eugene McDermott Graduate Fellow, as well as former colleagues at Harvard.
The study was also funded by a grant (DP1-HD094764-02) from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the Allen Discovery Center for Cell Lineage Tracing.
END
Team creates synthetic enzymes to unravel molecular mysteries
Researchers use approach to study Vg1
2023-11-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
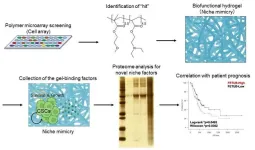
Finding your niche: A synthetic cancer stem cell microenvironment
2023-11-09
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) report the construction of a synthetic polymer biomaterial that successfully recapitulates the pancreatic adenocarcinoma microenvironment and could be used to identify novel treatment targets
Tokyo, Japan – One of the biggest challenges in biomedical research is finding a way to capture the complexity of the human body in laboratory-based techniques, to enable them to be investigated accurately. Now, researchers from Japan report an approach for precisely imitating a key feature of aggressive cancers in the laboratory.
In a study published recently in Inflammation and Regeneration, researchers from Tokyo Medical and ...
Vigorous exercise, rigorous science: What scientists learned from firefighters in training
2023-11-09
The 11 young firefighters went through a rigorous training exercise, carrying up to 40 pounds of gear over hilly terrain during a 45-minute training exercise in the California sun. Gloves, helmets, flashlights, goggles, and more weighted them down as they sprinted through the countryside wearing fire-resistant clothing to show they were ready to serve as wildland firefighters.
When the training was over, they immediately went to the medical tent—not to rest and recover but to give samples of their blood, ...
Study reveals the structure of brain waves associated with memory consolidation
2023-11-09
The reactivation of patterns of neuronal activity based on experience is crucial for learning and memory, but these patterns and the associated brain waves vary widely and are difficult to classify. Such events, dubbed ripples, are characteristic of the hippocampus, a brain region responsible for memory. Until now, the most common way to study ripples was using frequency analysis, but a project led by the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) has proposed a new classification strategy.
Using data science tools, a research group from the Instituto Cajal (IC-CSIC) headed by Liset M. de la Prida has managed to figure out the temporal structure of hippocampal ripples. The scientists ...
Reducing vitamin B5 slows breast cancer growth in mice
2023-11-09
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00hrs GMT Thursday 9 November 2023
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
People and animals
Reducing vitamin B5 slows breast cancer growth in mice
A group of researchers led by the Francis Crick Institute, working with the National Physical Laboratory (NPL) and Imperial College London, have discovered that breast cancer cells expressing a cancer-driving gene heavily rely on vitamin B5 to grow and survive. The researchers are part of Cancer Grand Challenges team Rosetta, funded by Cancer Research UK.
In their research published today in Nature Metabolism, the team studied the metabolic effects of one of the major cancer-driving ...
Smell and taste function 3 years after mild COVID-19
2023-11-09
About The Study: There was a favorable evolution in smell and taste function throughout the observation period of this study, with taste dysfunction showing lower frequency and faster recovery compared with smell dysfunction in this analysis that included 88 cases and 88 controls. Recovery from smell dysfunction continued over the 3-year study period. At the 3-year study endpoint, smell dysfunction was comparable between both groups. Patients with post–COVID-19 condition exhibiting chemosensory alterations should be reassured that a recovery of smell function appears to continue over three years ...
Assessment of changes in cancer treatment during the first year of the pandemic
2023-11-09
About The Study: In this study including 3.5 million patients diagnosed with cancer, a significant deficit was noted in the number of cancer treatments provided in the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic in the U.S. Data indicated that this deficit in the number of cancer treatments provided was associated with decreases in the number of cancer diagnoses, not changes in treatment strategies.
Authors: Leticia M. Nogueira, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the American Cancer Society in Kennesaw, Georgia, is the corresponding author.
To access ...
Social-behavioral findings can be highly replicable, six-year study by four labs suggests
2023-11-09
Roughly two decades ago, a community-wide reckoning emerged concerning the credibility of published literature in the social-behavioral sciences, especially psychology. Several large scale studies attempted to reproduce previously published findings to no avail or to a much lesser magnitude, sending the credibility of the findings — and future studies in social-behavioral sciences — into question.
A handful of top experts in the field, however, set out to ...
187 new genetic variants linked to prostate cancer found in largest, most diverse study of its kind
2023-11-09
A globe-spanning scientific team has compiled the most comprehensive list of genetic variants associated with prostate cancer risk — 451 in all — through a whole-genome analysis that ranks as the largest and most diverse investigation into prostate cancer genetics yet. The research, led by the USC Center for Genetic Epidemiology, the Keck School of Medicine of USC and USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, and in the United Kingdom by The Institute of Cancer Research, London, included major increases in representation ...
The autism-linked gene SYNGAP1 could impact early stages of human brain development, USC study reveals
2023-11-09
The gene SYNGAP1, the variants of which are top risk factors for Autism Apectrum Disorder (ASD), has previously unappreciated effects on the developing brain, according to a new study published in Nature Neuroscience. The study shows how disease-causing variants of SYNGAP1, thought primarily to affect synapses between mature neurons, could disrupt early development in a key region of the brain known as the cortex.
“Our findings reframe our understanding ...
Almost half of people who use drugs in rural areas were recently incarcerated
2023-11-09
New research finds that almost half of people who use illicit drugs in rural areas have been recently incarcerated.
Results from a survey of almost 3,000 people in eight rural areas nationwide who report using illicit drugs published today in the journal JAMA Network Open. The study found that 42% had been incarcerated, either in prison or local jails, in the preceding six months.
The study was conducted by researchers at Oregon Health & Science University and institutions across 10 states.
The findings suggest a prime ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] Team creates synthetic enzymes to unravel molecular mysteriesResearchers use approach to study Vg1