(Press-News.org) Desert birds lay larger eggs when they have more helpers to feed their chicks, new research shows.
White-browed sparrow weavers live in family groups in which only a dominant pair breeds and their grown-up offspring, particularly females, help to feed nestlings.
The study, by researchers at the University of Exeter, found that mothers increased the size of their eggs when they had more female helpers on hand.
The number of male helpers did not affect egg size, probably because male helpers feed chicks at substantially lower rates than female helpers.
“We don’t yet fully understand why helped mothers are laying heavier eggs, but our results point towards one likely explanation,” said lead author Dr Pablo Capilla-Lasheras, now at the University of Glasgow.
“Helpers may allow mothers to invest more in offspring at the egg stage by lightening maternal workloads at the chick-feeding stage.
“Our findings support this, as mothers with more female helpers did indeed enjoy significantly lighter workloads at the chick-feeding stage.”
This study is one of the first to show that mothers in cooperatively breeding birds actually change the size of their egg according to their social environment.
“Helpers feed offspring after they hatch in birds, or are born in mammals, but our findings highlight that helpers could have hitherto unexplored beneficial effects on offspring even before they are born, by triggering an increase in maternal investment before birth,” said DrAndy Young, senior author on the study at the University of Exeter.
“This discovery has potential implications for other cooperative species too, including ourselves, because this maternal strategy of increasing investment in offspring before birth when helped, whether in the egg or in the womb, could be something that occurs more widely across cooperative species.”
These findings stem from a remarkable continuous decade-long field study of 40 family groups of sparrow weavers in the Tswalu Kalahari Reserve, South Africa.
The environment is harsh, with unpredictable patterns of rainfall, and it is thought that the birds’ cooperative breeding strategy helps to reliably rear chicks despite these conditions.
Nearly 10% of the world’s birds have non-breeding “helpers” of this kind.
Sparrow weavers are among the most cooperative of birds, however, with breeding pairs being assisted by up to 10 helpers.
Remarkably, the helpers completely forego their own reproduction, remaining within their family as non-breeding adults for up to six years, helping to rear their parents’ young.
The study was funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC).
The paper, published in the journal PLOS Biology, is entitled: “Mothers in a cooperatively breeding bird increase investment per offspring at the pre-natal stage when they will have more help with post-natal care.”
END
Desert birds lay larger eggs when they have more helpers
2023-11-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ethical, environmental and political concerns about climate change affect reproductive choices
2023-11-09
People are beginning to reconsider their reproductive decisions due to complex concerns about climate change, with many choosing to forego childbearing, or reduce the number of children they have as a result, finds a new study by UCL researchers.
The research, published in PLOS Climate, is the first systematic review to explore how and why climate change-related concerns may be impacting reproductive decision-making.
The team examined 13 studies, involving 10,788 participants, which were conducted between 2012 and 2022, primarily in Global North countries ...
Photonics team develops high-performance ultrafast lasers that fit on a fingertip
2023-11-09
Lasers are essential tools for observing, detecting, and measuring things in the natural world that we can’t see with the naked eye. But the ability to perform these tasks is often restricted by the need to use expensive and large instruments.
In a newly published cover-story paper in the journal Science, researcher Qiushi Guo demonstrates a novel approach for creating high-performance ultrafast lasers on nanophotonic chips. His work centers on miniaturizing mode-lock lasers — a unique laser that emits a train of ultrashort, coherent light pulses in femtosecond intervals, which is an astonishing quadrillionth ...
Scientists flag conflicts of interest ahead of UN plastic and chemical talks
2023-11-09
An international group of 35 scientists is calling out conflicts of interest plaguing global plastic treaty negotiations and that have interfered with timely action on other health and environmental issues. They urge the implementation of strict guidelines to prevent the same problems from affecting the UN’s upcoming Science Policy Panel on chemicals. Their concerns and recommendations are outlined in a featured paper in the journal Environmental Science & Technology.
“From Big Tobacco to Big Oil, powerful industries use the same playbook to manufacture doubt and sow misinformation,” said co-author Bethanie ...
First-ever crowd-sourced small molecule discovery and a potent SARS-CoV-2 antiviral lead compound announced by COVID Moonshot Consortium
2023-11-09
The work of the COVID Moonshot Consortium is being published in the prestigious journal Science on 10 November, revealing their discovery of a potent SARS-CoV-2 antiviral lead compound. It also reflects on the success of its open science approach in launching a patent-free antiviral discovery program to rapidly develop a differentiated lead in response to a pandemic emergency. Open science discovery of potent noncovalent SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors ) DOI 10.1126/science.abo7201.
The COVID Moonshot initiative ...
Cornell chemists image basic blocks of synthetic polymers
2023-11-09
ITHACA, N.Y. -- Synthetic polymers are everywhere in our society – from nylon and polyester clothing to Teflon cookware and epoxy glue. At the molecular level, these polymers’ molecules are made of long chains of monomer building blocks, the complexity of which increases functionality in many such materials.
In particular, copolymers, which consist of different types of monomers in the same chain, allow for fine-tuning of the material’s properties, said Peng Chen, the Peter J.W. Debye Professor of Chemistry in the College of Arts and Sciences (A&S). The monomer sequence plays a critical role in a material’s properties, but scientists until ...
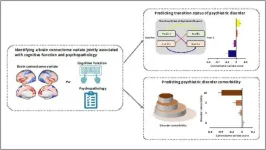
Brain imaging identifies biomarkers of mental illness
2023-11-09
Philadelphia, November 9, 2023 – Research and treatment of psychiatric disorders are stymied by a lack of biomarkers – objective biological or physiological markers that can help diagnose, track, predict, and treat diseases. In a new study, researchers use a very large dataset to identify predictive brain imaging-based biomarkers of mental illness in adolescents. The work appears in Biological Psychiatry, published by Elsevier.
Traditionally, psychiatric disorders such as depression have been diagnosed based on symptoms according to subjective assessments. The identification of biomarkers to aid in diagnosis and treatment selection would greatly advance treatments.
In ...
Cary Institute partners on $3M USDA-funded study on COVID-19 variants that could emerge from wildlife
2023-11-09
Many wild animals can carry COVID-19, including those that live among us, such as deer mice, red foxes, white-tailed deer, and more. These species may act as reservoirs, offering new opportunities for the virus to mutate and spill back into people. The omicron variant, for example, is thought to have emerged from mice.
With $3 million in federal grant funding, a new five-year research project will bring together virology, disease ecology, and artificial intelligence to better understand how SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19) behaves ...
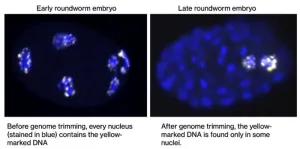
The enigma of embryonic development: How certain animals trim their genomes
2023-11-09
New research is underway to decipher a fascinating biological puzzle—how some animals can naturally discard more than half of their genetic information during embryonic development.
This radical natural phenomenon has captivated scientists for over 130 years, presenting a tantalizing question in the field of developmental biology and genetics.
Equipped with the latest in genetic engineering tools, the team at The University of Warwick is working to dissect the mechanisms behind this selective genomic editing. By uncovering the processes that allow some nematode worms to abandon up to ...
New URI lab developing adaptive technology, secures National Science Foundation grant
2023-11-09
New URI lab developing adaptive technology, secures National Science Foundation grant
Reza Abiri and Yalda Shahriari receive National Science Foundation award totaling $460,000 for work to improve stroke patient rehabilitation
Passing by Reza Abiri’s office at the University of Rhode Island, one might suspect him of nursing a serious coffee habit. A colorful collection of various mugs and cups dot his office, and though he is friendly enough to likely welcome any visitors stopping by to chat, the cups serve a larger purpose.
Abiri and Yalda Shahriari, professors in ...
MD Anderson announces Institute for Data Science in Oncology to advance mission to end cancer
2023-11-09
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today announced the launch of its Institute for Data Science in Oncology (IDSO), which integrates the most advanced computational and data science approaches with the institution’s extensive scientific and clinical expertise to significantly improve patient’s lives by transforming cancer care and research.
Bringing top data scientists from a variety of fields together with clinicians and cancer scientists, the institute builds on MD Anderson’s culture of collaboration and connectivity to tackle the field’s most pressing needs in new and innovative ways. IDSO’s efforts have been catalyzed by philanthropic ...