Scientific strength through diverse datasets
Studying the full spectrum of human populations generates robust conclusions
2023-11-11
(Press-News.org) Research which considers the diversity of normal and diseased human populations is contributing to more resilient hypotheses regarding complex neuroscience processes, such as human brain development, autism spectrum disorders, and Alzheimer's disease. Several interwoven examples will be discussed on Sunday, November 12, 2–3 p.m. at Neuroscience 2023, the annual meeting of the Society for Neuroscience and the world’s largest source of emerging news about brain science and health.
Considering the full spectrum of human variability — including gender, sex, race, ethnicity, and neurodiversity — is benefiting neuroscience at both the basic and translational levels. Ongoing efforts are pushing to ensure these aspects of human diversity are present along the length of the research pipeline from study design to publication.
Speakers will discuss how:
The inclusion of previously underrepresented demographic groups in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study reveals novel insights into child health and brain development. (Nora Volkow, National Institute on Drug Abuse)
The development of precision medicine for Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders will require studying and reporting sex differences in symptoms, progression, biomarkers, risk factors, and treatment. (Roberta Diaz Brinton, University of Arizona)
Nature and the Nature Portfolio are improving the representation of people from diverse and underrepresented groups as both research participants and authors/peer reviewers. (Mary Elizabeth Sutherland, Nature)
Brain organoids from patient-derived stem cells reveal distinct subtypes of autism spectrum disorder characterized by differences in excitatory and inhibitory neurogenesis. (Flora Vaccarino, Yale University)
Considering sex as a biological variable addresses historical imbalances and helps enhance reproducibility, rigor, and transparency in research. (Janine Austin Clayton, National Institutes of Health)
“Inclusion of previously understudied and underrepresented populations is contributing to several research fields reassessing our current understanding of typical and atypical brain function,” says Damien Fair, a cognitive neuroscientist at the University of Minnesota and the co-director of the Masonic Institute for the Developing Brain. “Researchers are finding that inclusion of diverse populations is providing new insights and more generalizable and inclusive scientific findings that have historically been taken for granted or missed — similar to how inclusion of diverse individuals within a team can lead to 'outside-the-box' discoveries.”
The research presented in this briefing was supported by national funding agencies including the National Institutes of Health and private funding organizations. Find out more about social behavior and the brain on BrainFacts.org. The content of this press release is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
###
The Society for Neuroscience (SfN) is an organization of nearly 35,000 basic scientists and clinicians who study the brain and the nervous system.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-11-11
WASHINGTON — Researchers have a better understanding of sleep disruption — particularly in the realm of sex-specific differences and cellular dysfunction — and are developing new research to study the interplay between sleep and memory. The findings will be presented on Tuesday, November 14, 10–11 a.m. EST at Neuroscience 2023, the annual meeting of the Society for Neuroscience and the world’s largest source of emerging news about brain science and health.
Approximately one out of every three adults in the United States report not getting enough sleep. Despite years of research into sleep and memory, neuroscientists still do not ...
2023-11-11
For immediate release on Nov. 11, 2023 at 10:10 a.m. E.T.
A National Institutes of Health-supported study found that the type of transfusion approach used to support adults who developed anemia after a heart attack did not make a significant difference in their likelihood of having another heart attack or dying within 30 days. Participants in the trial were randomized to receive a red blood cell transfusion when their red blood cell counts were in a prespecified range of moderate anemia, which is considered a liberal approach, or when it was more severe, ...
2023-11-11
An international clinical trial led by physician Jeffrey L. Carson, distinguished professor of medicine at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, found that a liberal blood transfusion given to patients who have had a heart attack and have anemia may reduce the risk of a reoccurrence and improve survival rates. The results of the trial, Myocardium Infarction and Transfusion (MINT), were published today in the New England Journal of Medicine. Maria Mori Brooks, professor of epidemiology and biostatistics at the University of Pittsburgh School of Public Health, co-first authored the study.
“Transfusion threshold trials are important to help physicians inform decisions that provide ...
2023-11-11
About The Study: This secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial validated a natural language processing model developed within a single healthcare system to identify heart failure hospitalizations. Further study is needed to determine whether natural language processing will improve the efficiency of future multicenter clinical trials by identifying clinical events at scale.
Authors: Scott D. Solomon, M.D., of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
2023-11-11
Cleveland: Findings from a multi-center, international clinical trial reported by a Cleveland Clinic physician show that semaglutide reduced cardiovascular events by 20% in adults with overweight or obesity and established cardiovascular disease who do not have diabetes.
Semaglutide is primarily prescribed for adults with type 2 diabetes but is also approved for chronic weight management in adults with obesity or overweight and have at least one other health issue. In the trial, patients treated with semaglutide lost an average of 9.4% of their body weight and experienced improvements in other risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Results ...
2023-11-11
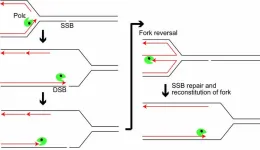
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have identified key factors in the mechanism behind DNA repair in our bodies. For the first time, they showed that the “proofreading” portion of the DNA replicating enzyme polymerase epsilon ensured safe termination of replication at damaged portions of the DNA strand, ultimately saving DNA from severe damage. This new knowledge arms scientists with ways to make anti-cancer drugs more effective, and new diagnostic methods.
Our DNA is under attack. Every day, around 55,000 single-strand breaks (SSBs) appear in the strands making up DNA helices ...
2023-11-10
MSU has a satellite uplink/LTN TV studio and Comrex line for radio interviews upon request.
There is a general understanding that pets have a positive impact on one’s well-being. A new study by Michigan State University found that although pet owners reported pets improving their lives, there was not a reliable association between pet ownership and well-being during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The study, published in the Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, assessed 767 people over three times in May 2020. The researchers took a mixed-method ...
2023-11-10
MSU has a satellite uplink/LTN TV studio and Comrex line for radio interviews upon request.
A new study, conducted in collaboration between researchers at Michigan State University and Central Michigan University, found that public spending on social safety net programs and on education spending each independently impact high school graduation rates, which are a key predictor of health and well-being later in life.
The study, published in the Journal of Adolescent Health, tested whether public financing for education and social safety net programs that aim to help ...
2023-11-10
MSU has a satellite uplink/LTN TV studio and Comrex line for radio interviews upon request.
Video and Images
Michigan State University researchers have solved the mystery of a poorly understood sperm structure called the cytoplasmic droplet, or CD. The CD is an expanded cytoplasm — watery, gel-like cell contents enclosed by cell membrane — found close to the head, at the neck of the sperm, in all mammals, including humans. This new genetic model is the first of its kind.
Despite ...
2023-11-10
With Amazon aiming to make 10,000 deliveries with drones in Europe this year and Walmart planning to expand its drone delivery services to an additional 60,000 homes this year in the states, companies are investing more research and development funding into drone delivery, But are consumers ready to accept this change as the new normal?
Northwestern University’s Mobility and Behavior Lab, led by Amanda Stathopoulos, an associate professor of civil and environmental engineering, wanted to know if consumers were ready for robots to replace delivery drivers, in the form ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientific strength through diverse datasets
Studying the full spectrum of human populations generates robust conclusions