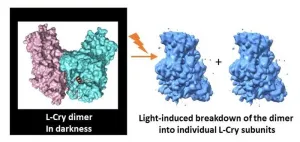
(Press-News.org) In a recent publication in Nature Communications, a joint research team of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU), the University of Cologne, and the University of Oldenburg has presented their findings on the functioning of an atypical cryptochrome protein (Cry). These proteins are found in a variety of organisms, and they are often involved in light-controlled biological processes. The marine bristle worm Platynereis dumerilii, for example, employs a special Cry protein designated L-Cry to distinguish between sunlight and moonlight as well as between different moon phases. This is essential for the worms to synchronize their reproduction to the full moon phase via an inner monthly calendar, also called circalunar clock. The researchers in Cologne used the cryo-electron microscopy platform of their university to visualize the three-dimensional structure of the L-Cry protein under different light conditions. The results of these structural analyses together with those of the biochemical investigations undertaken primarily at Mainz University revealed that, in the dark, L-Cry adopts a so-called dimer arrangement consisting of two subunits linked by a stable connection, while under intensive sunlight-like illumination it disassembles into its subunits or monomers.
It is not only the spatial arrangement of the two subunits in the dark that is unusual and corresponds to an arrangement not previously observed in other Cry proteins. The direction of light-induced changes is also unusual, since for other Cry proteins only the reverse process has been described, i.e., from monomer arrangements in the dark to dimer or higher oligomer arrangements in the light. The research team was also able to identify the main structural features in the protein that are important for this unusual behavior. Furthermore, knowledge of the three-dimensional structure enabled the researchers to introduce targeted mutations in the L-Cry protein to further characterize its functioning as a photoreceptor.
"Our findings could explain how L-Cry manages to distinguish between sunlight and moonlight: Intense sunlight always activates both subunits of the dimer simultaneously, which initiates its breakdown into individual subunits. The significantly weaker moonlight, however, statistically only activates one of two subunits," explained Professor Eva Wolf of the JGU Institute of Molecular Physiology, who led the study at Mainz University. The results of the study highlight the uniqueness of L-Cry among the highly diverse Cry proteins with their wide range of functions. They are also thought, for example, to be sensor proteins in the perception of the Earth's magnetic field in birds.
First steps of decoding the molecular processes of the circalunar clock
"Working with light-sensitive proteins is always a challenge," said Hong Ha Vu, a doctoral candidate in the JGU research group of Professor Eva Wolf and a major contributor to the study. "When preparing the L-Cry proteins for analysis, we need to carry out all experimental processes in the dark or under specifically defined red light conditions to prevent unintentional pre-activation of these very light-sensitive proteins. For the functional characterization of L-Cry, it is also necessary to use lighting conditions similar to underwater natural sunlight and moonlight illumination of the kind that the bristle worms encounter in their natural habitat. Only then we can compare the specific properties of L-Cry in its role as a sunlight and moonlight receptor with those of other cryptochromes."
And Professor Eva Wolf added: "Our investigations have provided important new insights into how this most unusual sunlight and moonlight receptor works. Furthermore, our structural and molecular mechanistic insights into L-Cry's function have opened up future avenues of research that should help us better understand the still largely unknown molecular processes involved in synchronization of the circalunar clock with the moon phases."
END
How marine bristle worms use a special protein to distinguish between sunlight and moonlight
Researchers at the universities in Mainz, Cologne, and Oldenburg gain important insights into a cryptochrome protein involved in synchronization of marine organisms' inner lunar calendar with moon phases
2023-11-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Artificial intelligence: Unexpected results
2023-11-13
Artificial intelligence (AI) is on the rise. Until now, AI applications generally have “black box” character: How AI arrives at its results remains hidden. Prof. Dr. Jürgen Bajorath, a cheminformatics scientist at the University of Bonn, and his team have developed a method that reveals how certain AI applications work in pharmaceutical research. The results are unexpected: the AI programs largely remembered known data and hardly learned specific chemical interactions when predicting drug potency. The results have now been published in Nature Machine Intelligence.
Which drug molecule is most effective? Researchers are feverishly ...
Migrant couples have better relationships when they can balance old and new cultures
2023-11-13
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Migrant couples who can effectively balance the culture of their homeland while adapting to the dominant culture of their new home are more likely to have a better relationship, according to newly published research from psychologists at Binghamton University, State University of New York.
“When immigrants venture into a new country, they embark on a journey of blending cultures while keeping their roots alive,“ said Binghamton University PhD candidate Quinn Hendershot. “There has been limited research on how their ability to adjust to a new culture while embracing the cultures of their homeland can affect the relationship.”
Hendershot ...
Worcester Polytechnic Institute researcher leads project to develop oxygen sensor for premature infants of color
2023-11-13
– The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has awarded $1.1 million to a team led by Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) researcher Ulkuhan Guler to develop a first-of-its-kind wearable sensor for premature infants that will address racial bias in healthcare by monitoring oxygen levels two different ways and correcting the measurements to account for variations in skin color.
The four-year project will create a convenient, affordable, noninvasive sensor about the size of a bandage that will enable infants at risk of lung disease to leave hospitals sooner and be accurately monitored at home, said Guler, an associate professor in the Department ...
Fluorine catch-and-attach process could boost drug efficiency
2023-11-13
HOUSTON – (Nov.13, 2023) – When it comes to chemical reactions, fluorine has a reputation as a ‘magic bullet atom’ for its ability to increase a drug’s absorption and prolong its lifetime. However, traditional methods of adding it to compounds entail expensive materials and can be difficult to pull off.
Rice University scientists developed a reliable and cost-effective process of adding fluorine to molecules for increased pharmaceutical drug efficiency using an iron and ...
New assay could revolutionize detection and treatment of acute myeloid leukemia
2023-11-13
Philadelphia, November 13, 2023 – A novel assay that detects a unique molecular marker in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) may revolutionize the way this disease is detected and treated according to a new report in The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics published by Elsevier. This assay may improve detection of AML driven by KMT2A gene fusions and may affect treatment decision-making, assessing response to therapy, and long-term surveillance.
AML is a rare, aggressive blood cancer diagnosed in around 120,000 individuals worldwide each year. Detecting residual disease during treatment is essential for determining prognosis and ...
Curiosity and pure maths
2023-11-13
The German Research Foundation (DFG) will be funding a new Research Training Group (RTG) at the University of Göttingen from next year. The RTG "Curiosity" is based at the Faculty of Biology and Psychology. Funding is expected to total around 7.8 million euros over the following five years. In addition, the DFG has extended the funding for the RTG "Fourier Analysis and Spectral Theory" at the Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science by five years. The award for this RTG totals around 4.5 million euros over the extended funding period.
Curiosity is broadly defined ...
Limited positive childhood experiences linked to higher binge-eating risk in college
2023-11-13
New findings from the University of Houston Department of Health and Human Performance reveal a significant association between a lower number of positive childhood experiences and a higher prevalence of binge-eating disorder characteristics, as well as lower scores for intuitive eating.
Binge eating, which includes consuming a substantial amount of food within a brief timeframe and experiencing a loss of control, is linked to adverse weight-related health effects and challenges in mental well-being. Intuitive eating, ...
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Nanotechnology expert Nikhil Koratkar named American Physical Society Fellow
2023-11-13
Nikhil Koratkar, Ph.D., John A. Clark and Edward T. Crossan Professor of Engineering at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, has been named a fellow of the American Physical Society (APS). Koratkar was recognized for his pioneering contributions to the field of nanoscale science and technology and the use of nanoscale materials in composites and energy storage devices. Each year, no more than 0.05% of the society membership is recognized by their peers for election to the status of fellow of the American Physical Society.
The APS Fellowship Program recognizes members ...
Children’s National Hospital selected as member of ARPA-H Investor Catalyst Hub spoke network
2023-11-13
WASHINGTON, D.C. (Nov. 13, 2023) – Children’s National Hospital was selected as a spoke for the Investor Catalyst Hub, a regional hub of ARPANET-H, a nationwide health innovation network launched by the Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H).
The Investor Catalyst Hub seeks to accelerate the commercialization of groundbreaking and accessible biomedical solutions. It uses an innovative hub-and-spoke model designed to reach a wide range of nonprofit organizations and Minority-Serving Institutions, with the aim of delivering scalable healthcare outcomes for all Americans.
“The needs of ...
Antiviral treatment is largely underused in children with influenza, study findings show
2023-11-13
Despite national medical guidelines supporting the use of antiviral medications in young children diagnosed with influenza, a new study reports an underuse of the treatment.
“Trends in Outpatient Influenza Antiviral Use Among Children and Adolescents in the United States” was published in Pediatrics, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Academy of Pediatrics.
“Antiviral treatment, when used early, improves health outcomes with influenza,” said lead author and principal investigator James Antoon, MD, PhD, MPH, assistant professor of Pediatrics and Hospital ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Hairdressers could be a secret weapon in tackling climate change, new research finds
Genetic risk for mental illness is far less disorder-specific than clinicians have assumed, massive Swedish study reveals
A therapeutic target that would curb the spread of coronaviruses has been identified
Modern twist on wildfire management methods found also to have a bonus feature that protects water supplies
AI enables defect-aware prediction of metal 3D-printed part quality
Miniscule fossil discovery reveals fresh clues into the evolution of the earliest-known relative of all primates
World Water Day 2026: Applied Microbiology International to hold Gender Equality and Water webinar
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
[Press-News.org] How marine bristle worms use a special protein to distinguish between sunlight and moonlightResearchers at the universities in Mainz, Cologne, and Oldenburg gain important insights into a cryptochrome protein involved in synchronization of marine organisms' inner lunar calendar with moon phases