(Press-News.org) A University of Texas at Arlington civil engineering researcher is determining what strategies are most effective at lessening flooding in coastal communities.
Michelle Hummel, a civil engineering assistant professor, is using a $499,973 National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) grant to study the benefits and costs of flood-reduction strategies aimed at increasing coastal resilience to storms and sea-level rise.
Hummel and her colleague, Kevin Befus of the University of Arkansas, will apply advanced computer models to simulate how these strategies affect water levels both on the surface and underground and the flooding of homes, businesses and infrastructure.
“We will test a range of strategies, from gray infrastructure like seawalls or levees to green or more natural solutions like dunes,” Hummel said. “Our models will show how each strategy performs in terms of flood reduction and will also estimate economic, social and ecological benefits.”
Hummel said her project also will engage communities where the strategies would be implemented. Although the exact partner communities are yet to be decided, Hummel has previously worked with communities in California’s Santa Monica Bay and Humboldt Bay areas, thanks to NOAA funding.
“A major goal of this project is to produce locally relevant information that communities can use to pursue funding for the design and implementation of flood-mitigation projects,” Hummel said. “By working with community partners throughout the project, we can refine the types of strategies that we test and ensure that community priorities, such as equity concerns and impacts to recreation, are included in our analysis framework.”
Melanie Sattler, chair of civil engineering and holder of the Dr. Syed Qasim Professorship, said this type of project has the ability to address site-specific flooding and determine what works best at the local scale.
“This project will provide locally relevant guidance on the economic, social and ecological implications of coastal flooding,” Sattler said. “Decision-makers can use this information to select flood-reduction strategies that align with community priorities.”
Hummel has received several others grants focused on building community resilience to climate change and environmental hazards. In 2022, she earned a $2.4 million National Science Foundation (NSF) grant to help Texas coastal communities and nonprofit organizations better monitor climate and industrial changes in their neighborhoods using real-time sensor technology. In 2021, she received a $396,200 NSF grant to test how crowdsourcing can help assess and build resilience in communities susceptible to natural disasters. She also earned a $150,000 NSF grant in 2021 to help the city of Ingleside on the Bay, Texas, monitor local air and water quality.
END
A how-to for reducing flooding impacts in coastal towns
UTA civil engineer applies expertise to protecting coastal communities from rising seas
2023-11-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NJIT scientists uncover aurora-like radio emission above a sunspot
2023-11-13
In a study published in Nature Astronomy, astronomers from New Jersey Institute of Technology’s Center for Solar-Terrestrial Research (NJIT-CSTR) have detailed radio observations of an extraordinary aurora-like display — occurring 40,000 km above a relatively dark and cold patch on the Sun, known as a sunspot.
Researchers say the novel radio emission shares characteristics with the auroral radio emissions commonly seen in planetary magnetospheres such as those around Earth, Jupiter and Saturn, as well as certain low-mass stars.
The discovery offers new insights into the origin of such intense solar radio bursts and potentially opens new avenues ...
Experimental brain-like computing system more accurate with custom algorithm
2023-11-13
FINDINGS
An experimental computing system physically modeled after the biological brain “learned” to identify handwritten numbers with an overall accuracy of 93.4%. The key innovation in the experiment was a new training algorithm that gave the system continuous information about its success at the task in real time while it learned.
The algorithm outperformed a conventional machine-learning approach in which training was performed after a batch of data has been processed, producing 91.4% accuracy. The researchers also showed that memory of past inputs stored in the system itself enhanced learning. In contrast, other ...
Researchers develop gel to deliver cancer drugs for solid tumors
2023-11-13
Intratumoral therapy – in which cancer drugs are injected directly into tumors – is a promising treatment option for solid cancers but has shown limited success in clinical trials due to an inability to precisely deliver the drug and because most immunotherapies quickly dissipate from the site of injection. A team of researchers from Mass General Brigham, in collaboration with colleagues at the Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research, has developed a gel delivery system that overcomes these challenges. The gel is injectable but solidifies upon delivery; contains an imaging agent for visualization under CT scan; and can hold a high ...
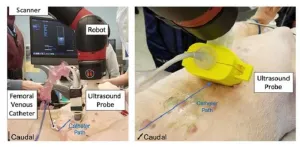
Using deep learning to process raw photoacoustic channel data and guide cardiac interventions
2023-11-13
Cardiovascular diseases rank among the top causes of death across the world, and cardiac interventions are similarly very common. For example, cardiac catheter ablation procedures, which are used to treat arrythmias, number in several tens of thousands per year in the US alone. In these procedures, surgeons insert a thin, flexible tube called a catheter into the femoral vein in the leg and navigate their way up to the heart, where the problematic tissue is destroyed using cold or focused radiation.
Even though cardiac catheter-based procedures are considered minimally invasive, the position ...
The Long Jump: Athletic, insect-scale long jumping robots reach where others can't.
2023-11-13
A team of engineers from the University of Illinois has published the first known study documenting the long-jumping motion of 3D-printed insect-scale robots.
The new study, published in the journal Smart Materials and Structures, follows a previous publication that documented the same lab’s investigation of vertical jumping in insect-scale robots. The study is led by Professor Sameh Tawfick, an associate professor and Ralph A. Andersen Faculty Scholar in the Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering. His lab, the Kinetic Materials Research Group, studies the ...
UMD engineers’ ‘cooling glass’ blasts building heat into space
2023-11-13
University of Maryland researchers aiming to combat rising global temperatures have developed a new “cooling glass” that can turn down the heat indoors without electricity by drawing on the cold depths of space.
The new technology, a microporous glass coating described in a paper published in the journal Science, can lower the temperature of the material beneath it by 3.5 degrees Celsius at noon, and has the potential to reduce a mid-rise apartment building’s yearly carbon emissions by 10%, according to the research team led by Distinguished University Professor Liangbing Hu in the Department of Materials ...
University of Oklahoma engineer elected as fellow member of Optica
2023-11-13
Optica, an international association in optics and photonics, recently announced the election of University of Oklahoma engineering professor Javier Jo, Ph.D., as a Fellow member.
Jo, a faculty member in the School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, was honored for his contributions to integrating optical imaging and artificial intelligence for biomedical applications. His research focuses on developing optical sensing and imaging technologies to understand pathophysiological mechanisms in human diseases and improve their clinical management.
“Dr. Jo’s ...
University of Toronto Engineering study finds bigger datasets might not always be better for AI models
2023-11-13
From ChatGPT to DALL-E, deep learning artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms are being applied to an ever-growing range of fields. A new study from University of Toronto Engineering researchers, published in Nature Communications, suggests that one of the fundamental assumptions of deep learning models — that they require enormous amounts of training data — may not be as solid as once thought.
Professor Jason Hattrick-Simpers and his team are focused on the design of next-generation materials, from catalysts that convert captured carbon into fuels to non-stick surfaces that keep airplane wings ice-free.
One ...
Acupuncture may offer limited relief to patients with chronic hives
2023-11-13
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. Acupuncture may offer limited relief to patients with chronic hives
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-1043
Editorial: ...
Virologic rebound observed in 20% of patients treated with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir
2023-11-13
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 13 November 2023
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
[Press-News.org] A how-to for reducing flooding impacts in coastal townsUTA civil engineer applies expertise to protecting coastal communities from rising seas