(Press-News.org) Two papers describe the genetic basis of long-term heat tolerance in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana, with implications for crop breeding. Teruaki Taji and colleagues evaluated dozens of lines of the model mustard weed for both long term (37 °C for 36 days) and short term (42°C for 50 minutes) heat stress. The authors found considerable variation within the species, but little overlap between responses to the two different heat challenges, suggesting that long-term heat stress tolerance is controlled by different cellular mechanisms than the more commonly studied short-term heat stress. Chromosomal mapping using the F2 progeny of a cross between a long-term-heat sensitive line and a long-term-heat tolerant line identified a genetic locus responsible for long-term heat tolerance, which the authors name LHT1. This locus is identical to MAC7, in the MOS4-associated complex, a region widely conserved in eukaryotes which encodes a putative RNA helicase involved in mRNA splicing. A single amino acid deletion in a long-term-heat sensitive line caused a loss of function for LHT1, which led to widespread detrimental splicing events. In another paper, Teruaki Taji and a second team of authors also identified mutant plants that are unusually sensitive to long-term heat stress, but not short-term heat stress, which they dub sloh3 and sloh63. The team found that sloh63 was also hypersensitive to salt stress. The mutations were traced to the same MOS4-associated complex. In addition, both mutants showed abnormal mRNA splicing events and endoplasmic reticulum stress with subsequent unfolded protein response. Treatment with a splicing inhibitor led to decreased long-term heat tolerance and enhanced endoplasmic reticulum stress. According to the authors, the results suggest that maintenance of precise mRNA splicing by the MOS4-associated complex is crucial for surviving long-term heat.
END
Long-term heat tolerance in plants
2023-11-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Health plays a role in older adults’ vulnerability to scams, poll suggests
2023-11-14
Three out of every four older adults say they have experienced a fraud attempt by phone, text, email, mail or online in the last two years, a new poll shows. Three in ten say they’ve been victims of at least one scam.
The poll reveals an especially strong link between an older adult’s health and their vulnerability to scams – both being able to spot one and becoming the victim of one.
Across the board, people aged 50 to 80 who reported being in fair or poor physical or mental health, those with disabilities, and those who rate their memory as fair or poor were more likely than others their age to say they’d experienced ...
New twist on AI makes the most of sparse sensor data
2023-11-14
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., Nov. 14, 2023 — An innovative approach to artificial intelligence (AI) enables reconstructing a broad field of data, such as overall ocean temperature, from a small number of field-deployable sensors using low-powered “edge” computing, with broad applications across industry, science and medicine.
“We developed a neural network that allows us to represent a large system in a very compact way,” said Javier Santos, a Los Alamos National Laboratory researcher who applies ...
Boosting profits for technology holders and licensees through game theory
2023-11-14
Patents and licenses safeguard the intellectual property of the rights holder from being copied or sold without their permission. Companies and individuals who want to make use of the patented or licensed invention must make a formal request to do so. In industries where oligopolies operate—a small number of producers who control the supply of a good or commodity and can determine prices—the profitability of licensing a patent depends on two critical factors: the chosen method of payment for license access and the relative number of firms granted the license as opposed to those left ...
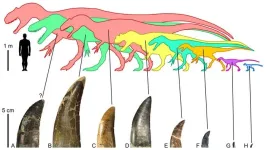
New study reveals surprising insights into feeding habits of carnivorous dinosaurs in North America
2023-11-14
New research sheds light on the dining habits of ancient carnivorous dinosaurs from Jurassic rocks of the USA. A recent scientific study published in PeerJ Life & Environment by Roberto Lei (Università degli Studi di Modena e Reggio Emilia) and colleagues explores the bite marks left on the ancient bones of the giant long-necked sauropod dinosaurs like Diplodocus and Brontosaurus by carnivorous theropod dinosaurs.
Tooth-marked bones provide invaluable insights into the feeding behaviors of long-extinct carnivorous creatures. While it is commonly thought that the giant tyrannosaurs were the primary culprits behind these tell-tale marks on dinosaur ...
Current uses of asbestos exceed exposure limits
2023-11-14
San Francisco, November 14, 2023 – A new study summarizing exposures to asbestos during the installation and removal of asbestos cement products demonstrates that these construction activities almost always exceed U.S. occupational limits. The study focused on airborne asbestos exposures from existing uses of asbestos that are still allowed in most countries.
Average task-specific asbestos exposures during the cutting of asbestos cement pipe were more than 50 times the Occupational Safety and ...
Einstein Foundation Award 2023: The Einstein Foundation Berlin awards €500,000 prize to enhance quality in research
2023-11-14
The €500,000 Einstein Foundation Award for Promoting Quality in Research honors researchers and institutions whose work helps to fundamentally advance the quality and robustness of research findings. The award is bestowed jointly with the QUEST Center for Responsible Research at the Berlin Institute of Health (BIH). “The Einstein Foundation Award is the first of its kind in the world to recognize efforts to improve research quality. Now in its third year, the award shines a spotlight on individuals and projects that exhibit outstanding dedication, but also the ...
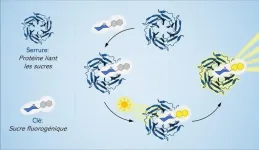
Shedding new light on sugars, the “dark matter” of cellular biology
2023-11-14
Scientists at Université de Montréal’s Department of Chemistry have developed a new fluorogenic probe that can be used to detect and study interactions between two families of biomolecules essential to life: sugars and proteins.
The findings by professor Samy Cecioni and his students, which open the door to a wide range of applications, were published in mid-October in the prestigious European journal Angewandte Chemie.
Found in all living cells
Sugar is omnipresent in our lives, present in almost all the foods we eat. But the importance of these simple carbohydrates extends far beyond tasty desserts. Sugars ...
Study sheds light on how Earth cycles fossil carbon
2023-11-14
HOUSTON – (Nov. 14, 2023) – As the primary element of life on our planet, carbon is constantly journeying from living creatures down into the Earth’s crust and back up into the atmosphere, but until recently, quantifying this journey was virtually impossible.
To help unravel the mystery of how the Earth cycles fossil carbon, Rice University’s Mark Torres and collaborators studied the chemistry of a river system extending from the Peruvian Andes to the Amazon floodplains. Together with collaborators from five other institutions, Torres helped show that high rates of carbon breakdown persist from mountaintop to floodplain, ...
High lung cancer rates in naval veterans linked to asbestos
2023-11-14
A University of Adelaide and Oxford University study has discovered asbestos exposure led to a higher incidence of asbestos-related lung cancers in British and Australian naval personnel than in other armed forces.
The data were collected from 30,085 United Kingdom and Australian personnel who served in the ’50s and ’60s, a time when asbestos-containing materials were present in British and Australian naval vessels.
Three of the four cohorts had previously been studied by the University of Adelaide and the UK Health Security Agency to identify the effects of radiation exposure from British nuclear testing; however, a raised incidence of mesothelioma, a cancer strongly linked ...
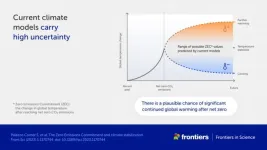
COP28: New study highlights need to address risk of continued global warming after net zero
2023-11-14
From scorching heatwaves to torrential downpours and devastating storms, the disastrous effects of global warming are sweeping across the world. Being the predicted outcome of burning fossil fuels, our best and only plan to limit warming is to reduce CO2 emissions from human activities to ‘net zero’ – where the amount of CO2 we emit into the atmosphere is equal to the amount we remove from it. To keep within the 1.5°C limit of the 2015 Paris Agreement, this needs to happen as soon as possible.
Though the ...